Where is the site of gas exchange in the lungs?
The alveoli
What are the primary inspiratory muscles?
What are the primary expiratory muscles
Diaphragm and external intercostals are the primary inspiratory muscles.
The abdominal muscles and the internal intercostals are the primary expiratory muscles.
The complex of hemoglobin and bound oxygen is called ________; a hemoglobin molecule without any oxygen is called ________.
The complex of hemoglobin and bound oxygen is called oxyhemoglobin; a hemoglobin molecule without any oxygen is called deoxyhemoglobin.
What four factors affect the affinity of hemoglobin for oxygen?
1. Temperature; increased temperature - increased affinity
2. pH - Bohr effect
3. PCO2 - carbamino effect
2,3-BPG
Nonregulated reabsorption occurs in the proximal tubule of the kidney whereas regulated reabsorption occurs in the distal tubule and collecting duct
True or false. If false, correct the statement.
During metabolic acidosis, carbon dioxide increases in the plasma, decreasing the pH, and decreasing the ratio of bicarbonate to carbon dioxide.
True or false. If false, correct the statement.
During respiratory acidosis, carbon dioxide increases in the plasma, decreasing the pH and decreasing the ratio of bicarbonate to carbon dioxide.
What gland releases parathyroid hormone (PTH)?
What is the stimuli for its release?
What are its target organs, and what is the overall effect?
The parathyroid gland releases PTH.
PTH is secreted in response to a decrease in the plasma calcium concentration.
The action of PTH is increasing blood calcium levels.
PTH acts:
-on the kidneys (specifically the loop of Henle and distal tubules) to increase calcium reabsorption and thus decrease calcium excretion
-Stimulates activation of functional vitamin D3, which stimulates calcium absorption in GI tract and calcium reabsorption in kidneys
-stimulates resorption of bone
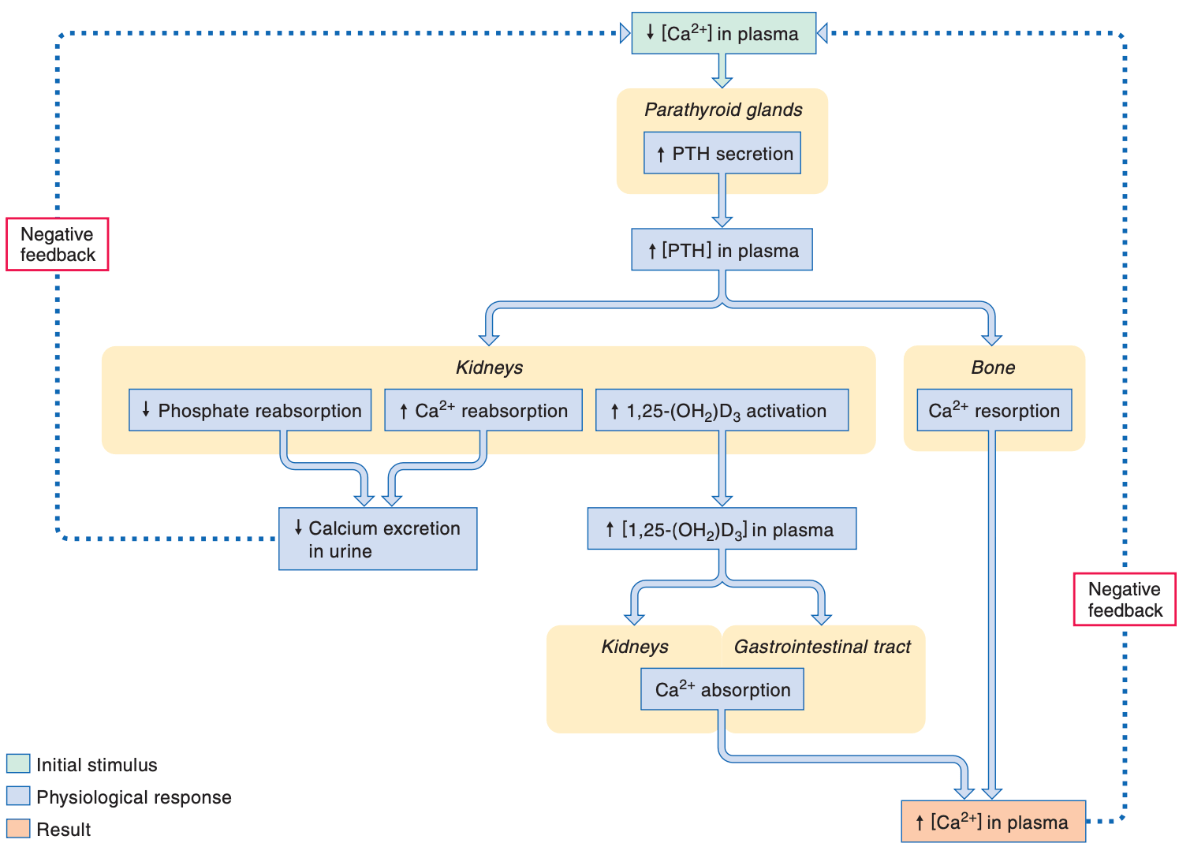
The stimuli for its release is
_____ is the average volume of an erythrocyte. Units?
____ is the average amount of hemoglobin in an erythrocyte? Units?
_____ is the proportion of hemoglobin per erythrocyte measured as a percent.
Mean corpuscular volume is the average volume of an erythrocyte. Units - femtoliters
Mean corpuscular hemoglobin is the average amount of hemoglobin in an erythrocyte. Units - picograms
Mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration is the proportion of hemoglobin per erythrocyte measured as a percent.
Type I - epithelial (simple squamous) cells lining alveoli that participate in gas exchange
Type II - produce surfactant;
Type III cells - alveolar macrophages; engulf foreign particles and pathogens inhaled into the lungs
__________ is the total air that enters the respiratory system and includes air that is not involved in gas exchange
Minute Ventilation is the total air that enters the respiratory system and includes air that is not involved in gas exchange
Which is more soluble in water, and thus is more effectively transported in water? Oxygen or CO2?
CO2; carbon dioxide is nearly 20 times more soluble in blood than is oxygen
What ventilation pattern is the result of decreased blood PCO2 levels?
Hypocapnia
_____ refers to movement of filtered solutes and water from the lumen of the tubules back into the plasma. ______ refers to the movement of molecules from the plasma of peritubular capillaries into the renal tubules to become part of the filtrate.
Reabsorption refers to movement of filtered solutes and water from the lumen of the tubules back into the plasma. Secretion refers to the movement of molecules from the plasma of peritubular capillaries into the renal tubules to become part of the filtrate.
Hyperventilation ______ (increases/decreases) arterial PCO2, thereby ________ (increases/decreases) the ratio of bicarbonate to carbon dioxide.
What type of acid-base disturbance is this?
(metabolic acidosis/alkalosis, respiratory acidosis/alkalosis)
What type of compensation would occur to return to homeostasis?
(Renal compensation or respiratory compensation)
Hyperventilation decreases arterial PCO2, thereby increasing the ratio of bicarbonate to carbon dioxide
This would be an example of respiratory alkalosis.
To bring the ratio back to normal, the kidneys decrease the reabsorption of bicarbonate ions and secrete fewer hydrogen ions (renal compensation)
The lungs cannot compensate for the imbalance because that is where the problem developed initially (unless the hyperventilation was voluntary).
Which hormone regulates potassium secretion?
What are some stimuli for the release of this hormone?
What portion of the renal tubules secretes potassium?
Aldosterone regulates potassium secretion.
Stimuli for the release of aldosterone include:
-angiotensin II/RAAS
-increased plasma potassium levels
The distal tubules secretes potassium.
What is the term for erythrocytes that are smaller than normal? Larger than normal? Normal-sized?
Microcytic - smaller than normal
Macrocytic - larger than normal
Normocytic - normal-sized
What is internal respiration?
Cellular respiration; use of oxygen within mitochondria to generate ATP by oxidative phosphorylation
If you have low forced expiratory volume, this is an indication you have ____
a. Restrictive pulmonary disease
b. Obstructive pulmonary disease
c. Asthma
d. Chronic bronchitis
a. Restrictive pulmonary disease
What is the respiratory quotient?
The ratio of the amount of carbon dioxide produced by the body to the amount of oxygen consumed is called the respiratory quotient.
The ___ is a percentage of the forced vital capacity that can be exhaled in a certain time period
The forced expiratory volume (FEVx) is a percentage of the forced vital capacity that can be exhaled in a certain time period
The volume of plasma filtered per unit time is the _______.
The sum of the Starling forces in the renal corpuscle is called the _____.
What is the equation to calculate this?
The volume of plasma filtered per unit time is the glomerular filtration rate (GFR).
The sum of the Starling forces in the renal corpuscle is called the glomerular filtration pressure (GFP).
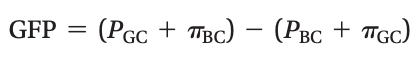
The clearance of which two substances can be used to estimate the GFR?
Inulin and creatinine
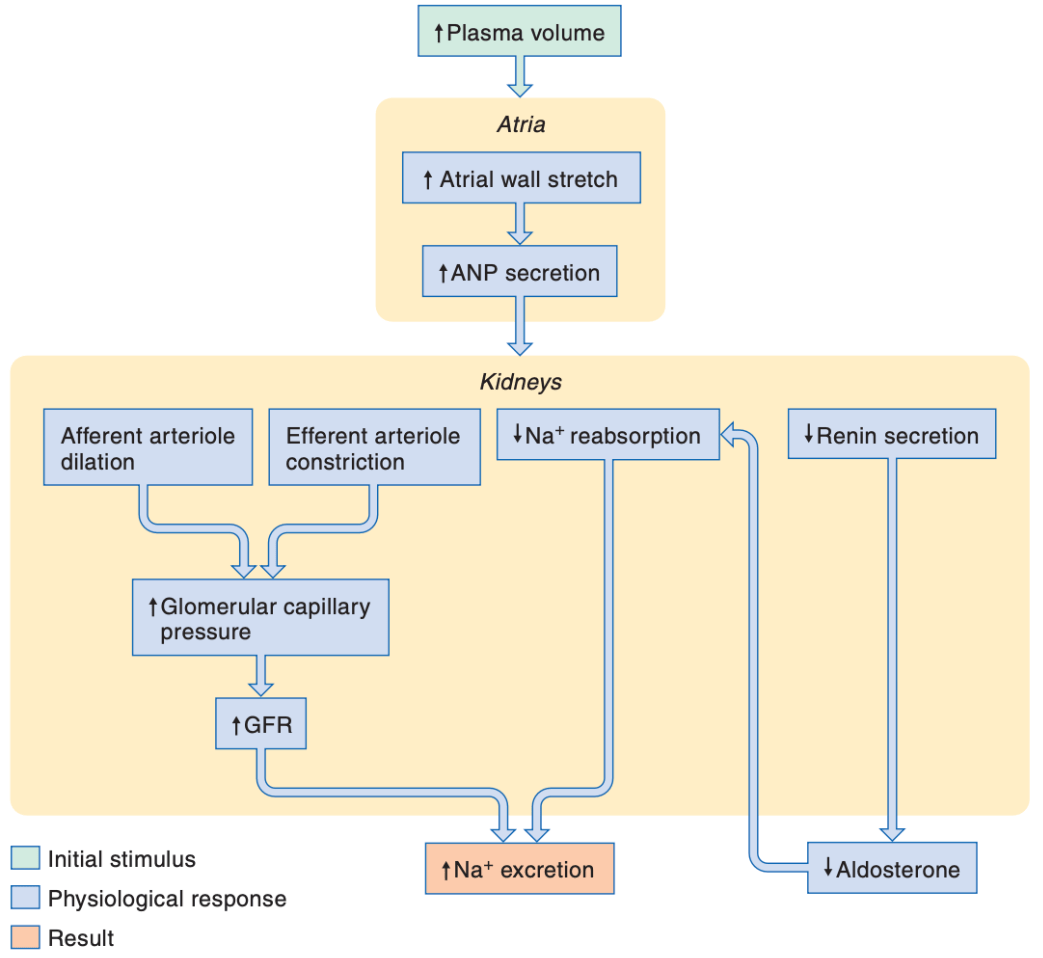
True or False: If false, correct the statement
ANP increases potassium excretion by increasing the glomerular filtration rate and by decreasing potassium reabsorption.
ANP increases sodium excretion by increasing the glomerular filtration rate and by decreasing sodium reabsorption.
What does the Tallquist test measure?
The Tallquist test uses a colored hemoglobin scale to estimate the anount of hemoglobin in the blood.
What are the four aspects of external respiration?
Pulmonary ventilation - the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the atmosphere and body tissues, which involves both the respiratory and circulatory systems.

The ___ is a percentage of the forced vital capacity that can be exhaled in a certain time period
The forced expiratory volume (FEVx) is a percentage of the forced vital capacity that can be exhaled in a certain time period
At rest, the cells of the body consume approximately _____ mL of oxygen and produce approximately _____ mL of carbon dioxide each minute when at rest
At rest, the cells of the body consume approximately 250 mL of oxygen and produce approximately 200 mL of carbon dioxide each minute when at rest
The normal ratio of bicarbonate concentration to carbon dioxide concentration in arterial blood is
20:1
Define the terms transport maximum and renal threshold.
Transport maximum (Tm) is the rate of transport by carrier proteins when carriers are 100% saturated
Renal threshold is the plasma concentration of solute at which the transport maximum is exceeded and excess solute appears in the urine
If the clearance of molecule X is greater than the GFR, was X reabsorbed or secreted in the renal tubules?
If the clearance of molecule X is greater than the GFR, X was secreted in the renal tubules
______ occurs when bone is broken down to liberate calcium ions, increasing blood calcium levels.
Resorption occurs when bone is broken down to liberate calcium ions, increasing blood calcium levels.
Which of the red blood cell indices would allow you to determine that erythrocytes are microcytic?
Which of the red blood cell indices would allow you to determine that erythrocytes are hypochromic?
Mean corpuscular volume would allow you to determine that erythrocytes are microcytic.
Mean corpuscular hemoglobin would allow you to determine that erythrocytes are hypochromic.
Where does the conduction zone begin and end?
Where does the respiratory zone begin?
The conduction zone begins with the larynx and ends with the terminal bronchioles.
The respiratory zone begins with the respiratory bronchioles
How do you calculate the alveolar ventilation
(Tidal volume – anatomical dead space) x the respiratory rate
In ______, alveolar ventilation exceeds the demands of the tissues; causing arterial PCO2 to decrease and PO2 to increase
In hyperventilation, alveolar ventilation exceeds the demands of the tissues; causing arterial PCO2 to decrease and PO2 to increase
The effect that pH has on the hemoglobin-oxygen dissociation curve is referred to as the _____
The effect that pH has on the hemoglobin-oxygen dissociation curve is referred to as the Bohr Effect
Between _____ mm Hg and _____ mm Hg, intrinsic mechanisms are sufficient to regulate and maintain a relatively constant GFR.
What are the three intrinsic mechanisms?
Between 80 mm Hg and 180 mm Hg, intrinsic mechanisms are sufficient to regulate and maintain a relatively constant GFR.
The three intrinsic mechanisms for regulating GFR:
1. Myogenic regulation - alters resistance via arteriolar smooth muscle contraction
2. tubuloglomerular feedback - alters arteriolar smooth muscle after detecting concentration of filtrate in distal tubule by the macula densa
3. mesangial cell contraction (changes permeability of filtration barrier)
Usually the net effect of potassium transport in the kidney is _______________
Usually the net effect of potassium transport in the kidney is reabsorption
The medullary osmotic gradient does not dissipate because the capillary system known as the __________ is permeable to both water and solutes.
The medullary osmotic gradient does not dissipate because the capillary system known as the vasa recta is permeable to both water and solutes.
What is the volume of intrapleural fluid within the intrapleural space?
approximately 15 mL
What is the equation to calculate pulmonary (minute) ventilation?
What is the equation for alveolar ventilation?
Pulmonary ventilation is the product of tidal volume (TV) x respiratory rate (RR)
Alveolar ventilation is the (tidal volume - anatomical dead space) x respiratory rate
- Alveolar ventilation is the volume of air reaching the gas exchange area per minute
_____ is at a higher concentration in the alveoli and diffuses into the blood, whereas ______ is at a higher concentration in the blood
Oxygen is at a higher concentration in the alveoli and diffuses into the blood, whereas carbon dioxide is at a higher concentration in the blood
At which body sites does the partial pressure of carbon dioxide exceed the partial pressure of oxygen?
Indicate whether the GFR will tend to rise or fall in response to an increase in each of the following:
a) the glomerular filtration pressure
b) the glomerular capillary hydrostatic pressure
c) the glomerular capillary osmotic pressure
d) the hydrostatic pressure in Bowman’s capsule
e) the osmotic pressure in Bowman’s capsule
f) the concentration of proteins in the plasma.
Indicate whether the GFR will tend to rise or fall in response to an increase in each of the following:
a) GFR will increase in response to increase in GFP
b) GFR will increase in response to increase in glomerular capillary hydrostatic pressure
c) GFR will decrease in response to increase in the glomerular capillary osmotic pressure
d) GFR will decrease in response to increase in the hydrostatic pressure in Bowman’s capsule
e) GFR will increase in response to increase in the osmotic pressure in Bowman’s capsule
f) GFR will decrease in response to increase in the concentration of proteins in the plasma.
True or False. If False, correct the statement
Intrinsic control of glomerular filtration rate (GFR) can occur when mean arterial pressure falls below 80 mm Hg
Intrinsic control of glomerular filtration rate (GFR) can occur:
-through myogenic regulation
-via tubuloglomerular feedback
Extrinsic control of glomerular filtration rate (GFR) can occur:
-when mean arterial pressure falls below 80 mm Hg
-due to an increase in sympathetic input
Describe the three lines of defense against changes in acid-base balance.
Which most rapidly corrects changes in blood pH?
Which takes the longest to compensate for imbalances?
1. Buffering of hydrogen ions - fastest
The most important buffer in the extracellular fluid is bicarbonate; its response time is limited only by the time required for buffers to bind or release hydrogen ions.
2. Respiratory compensation - acts within minutes
-regulates pH by increasing or decreasing alveolar ventilation, which tends to raise or lower pH, respectively
3. Renal compensation - hours to days
- The kidneys regulate the pH of arterial blood by regulating the renal excretion of hydrogen ions and bicarbonate, and by producing new bicarbonate
If the hydrogen ion concentration in the blood increases, the kidneys increase hydrogen ion secretion and bicarbonate reabsorption and synthesize new bicarbonate; if hydrogen ion concentration in the blood decreases, kidneys decrease hydrogen ion secretion and bicarbonate reabsorption.
True or false:
At rest, the chest wall is compressed and tends to recoil inward; (as would a compressed spring), whereas the lungs are stretched and tend to recoil outward like an inflated balloon
False
At rest, the chest wall is compressed and tends to recoil outward; (as would a compressed spring), whereas the lungs are stretched and tend to recoil inward like an inflated balloon
Decide whether each of the following parameters will increase, decrease, or not change in the situations given.
a. airway resistance with bronchodilation
b. intrapleural pressure during inspiration
c. air flow with bronchoconstriction
d. bronchiolar diameter with increased PCO2
e. tidal volume with decreased compliance
f. alveolar pressure during expiration
Decide whether each of the following parameters will increase, decrease, or not change in the situations given.
a. airway resistance with bronchodilation (decrease)
b. intrapleural pressure during inspiration (decrease)
c. air flow with bronchoconstriction (decrease)
d. bronchiolar diameter with increased PCO2 (increase)
e. tidal volume with decreased compliance (decrease)
f. alveolar pressure during expiration (increase)
What structures make up the respiratory membrane?
type I epithelial cells in the alveolar wall and endothelial cells in the capillary wall “sandwiched” around their fused basement membranes
A(n) (increase/decrease) in the levels of carbon dioxide during (hyperventilation/hypoventilation) lead to respiratory alkalosis.
A(n) decrease in the levels of carbon dioxide during hyperventilation lead to respiratory alkalosis.
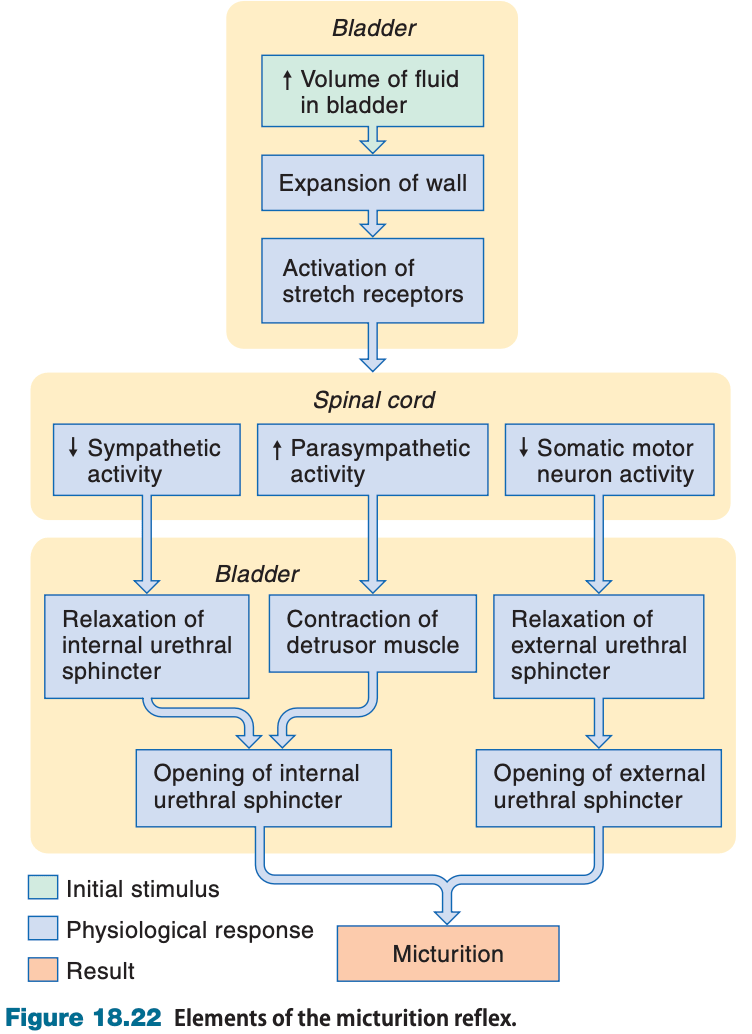
In the micturition reflex, which muscle is innervated by sympathetic fibers, which muscle is innervated by parasympathetic fibers, and which muscle is innervated by somatic nervous system fibers?
Detrusor muscle - parasympathetic
Internal urethral sphincter - sympathetic
External urethral sphincter - somatic
Describe the pathway of filtrate flow from the renal corpuscle to elimination from the body.
From renal corpuscle, filtrate flows to the PCT to the proximal straight tubule to the descending thin limb of loop of Henle, to the ascending thin limb of the loop of Henle, to the ascending thick limb of the loop of Henle to the distal convoluted tubule to the connecting tubule to the collecting duct to the ureter to the bladder to the urethra
What enzyme converts angiotensinogen to angiotensin I? What organ synthesizes angiotensinogen? What synthesizes the proteolytic enzyme in question?
What enzyme converts angiotensin I to angiotensin II? What organ synthesizes the proteolytic enzyme in question?
What are the four actions of angiotensin II? Identify the target organs and their effect to increase MAP
Renin converts angiotensinogen to angiotensin I.
The liver synthesizes angiotensinogen. The juxtaglomerular cells/granular cells in the afferent arteriole of the kidney release renin.
Angiotensin Converting Enzyme (ACE) converts angiotensin I to angiotensin II. The lungs release ACE.
1. Angiotensin II stimulates vasoconstriction of systemic arterioles, which by increasing the total peripheral resistance increases mean arterial pressure.
2. Angiotensin II stimulates the adrenal cortex to secrete aldosterone, which by increasing sodium reabsorption increases water reabsorption.
3. Angiotensin II stimulates the posterior pituitary to secrete ADH, which by increasing water reabsorption minimizes fluid loss and maintains plasma volume, thereby maintaining mean arterial pressure.
4. Angiotensin II activates hypothalamic neurons to stimulate thirst and fluid intake, which by increasing plasma volume increases mean arterial blood pressure.
Put the events of inspiration* in the correct order
a. Pip decreases
b. Transpulmonary pressure increases
c. Diaphragm and intercostals contract
d. Palv decreases to less than Patm
c. Diaphragm and intercostals contract
a. Pip decreases
b. Transpulmonary pressure increases
d. Palv decreases to less than Patm
Under normal conditions, if respiring tissues consume oxygen at a rate of 250 mL/min, at what rate does oxygen diffuse from the alveoli to blood?
250 mL/min
Remember:
(1) oxygen moves from alveolar air into the blood at the same rate it is consumed by the tissues
(2) carbon dioxide moves into alveolar air from the blood at the same rate it is produced in the tissues
The binding of one oxygen molecule to hemoglobin _______ the affinity of the hemoglobin molecule for oxygen and, therefore, _______ the likelihood that another oxygen will bind with hemoglobin.
the binding of one oxygen molecule to hemoglobin increases the affinity of the hemoglobin molecule for oxygen and, therefore, increases the likelihood that another oxygen will bind with hemoglobin.
The clearance of what substance is used to calculate renal plasma flow?
How do you calculate renal blood flow?
Clearance of PAH is used to calculate renal plasma flow.
Renal blood flow = Clearance of PAH / 1-Hematocrit
Which structures make up the juxtaglomerular apparatus?
Where are they located?
Macula densa - distal convoluted tubule
Juxtaglomerular cells/granular cells - afferent arteriole
What are the stimuli for the release of renin?
Stimuli for renin release
1.Decreased pressure in afferent arteriole
2.Baroreceptor reflex/Renal sympathetic nerve activity
3.Macula densa - Decreases in Na+ and Cl– in distal tubule filtrate