This small muscle (only 1 head) causes extension at the elbow.
What is anconeus?
This technique is contraindicated when your client has paresthesia due to a nerve lesion.
What is stroking or pincement?
Name this test and state what it is assessing: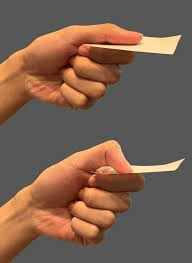
What is Froment's Sign. Assessing the strength of the Adductor Pollicis mm.
This muscle is tested by having your client prone with the ankle plantar flexed and your client is resisting dorsiflexion (applied by you).
What is the gastrocnemius mm.
A condition that begins as fever and may lead to motor weakness of the legs.
What is polio?
This muscle causes external rotation at the hip with the leg in neutral and abduction when the leg is flexed 90 degrees.
What is piriformis?
This condition (be specific) is a contraindication to all hydrotherapy treatments.
What is nerve lesion causing loss of autonomic function?
Name the test and what is being assessed:
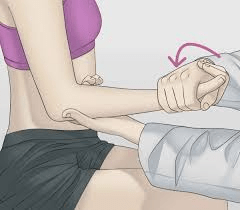
What is the pronator teres test? Assessing for hypertonic pronator teres as the site of impingement of the Median nerve.
These muscles are tested by having your client prone, with the knee flexed 80 and the hip slightly internally rotated and flexed. The client resists the therapist doing knee extension. (2)
What are Semimembranosus & Semitendinosus?
A condition that causes thickening of the palmar fascia; presents as nodules then progresses to a flexion contracture of the fingers.
What is Dupuytren's Contracture?
This muscle assists with flexion of the wrist and does lateral deviation at the wrist.
What is Flexor Carpi Radialis?
These techniques are contraindicated when a client has osteoporosis.
What are tapotement (heavy hacking & pounding) & compressions (deep)?
What is the test and what is being assessed?
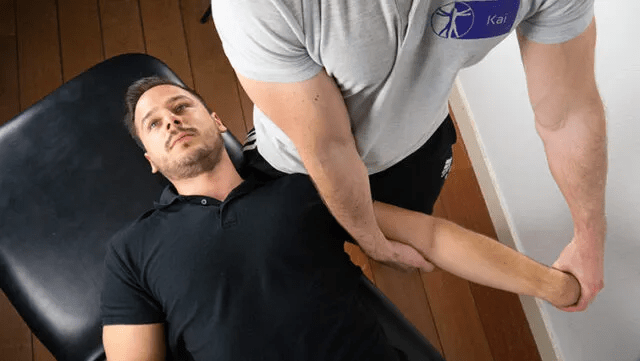
What is ULTT #3, assessing the radial nerve.
This muscle is tested by having the client in a supine position with the ankle plantar flexed and inverted. The client resists the therapist doing dorsiflexion/eversion.
What is Tibialis Posterior?
A condition that causes night pain, altered sensation in the palmar aspect of the first 3 digits, and potential loss of grip strength.
What is Carpal Tunnel Syndrome?
This muscle acts on the shoulder causing extension, adduction and internal rotation.
When a client has this condition PRROM is contraindicated. (name the condition and direction of PRROM, and when the CI is removed).
What is nerve lesion? PRROM CI'd in a direction that stretches the nerve until muscle function returns.
Name the test and what it is assessing for: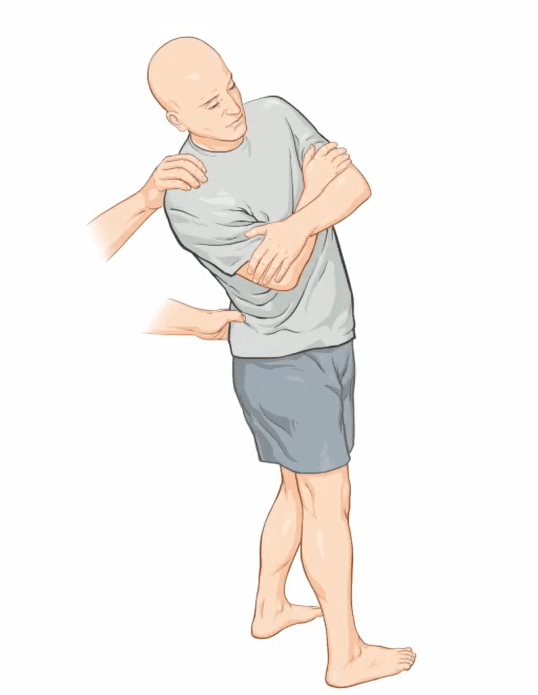
What is Lumbar Quadrant test? It assesses for the presence of nerve root impingement in the lumbar spine.
This muscle is tested with the client supine, elbow flexed 90 degrees, wrist flexed 90 degrees and forearm fully pronated.
What is Flexor Carpi Radialis?
A condition that is secondary to inflammation and hyper (or hypo)mobility and causes pain in the buttocks region.
What is SI joint dysfunction?
Which muscles (name them all) do external rotation of the shoulder?
What are Infraspinatus and Teres Minor?
For this condition exercise and strength training are contraindicated to local regions of the body. Explain why.
What is Post-Polio? Because the motor neuron is over-taxed and fatiguing it with exercise will make the condition worse.
Name the test and what it is assessing for:
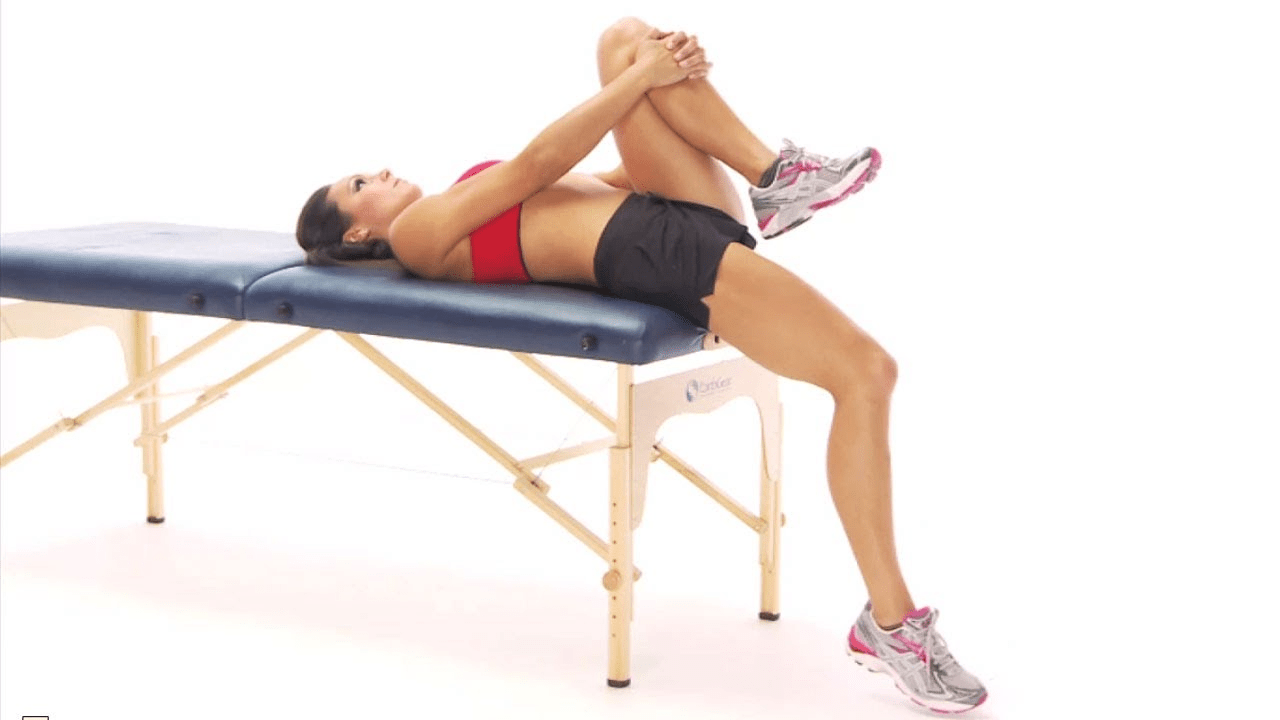
What is Thomas test? Assesses muscle length of the psoas, rectus femoris and TFL mm.
This muscle is tested by having the client in supine, with elbow flexed to 90 degrees and the thenar & hypothenar eminences opposed.
What is Palmaris longus?
A condition that presents with motor weakness in the 4th & 5th lumbricals as well as difficulty forming a fist. The hand presents with extension of the 4th & 5th MCP joints.
What is an Ulnar Nerve Lesion?