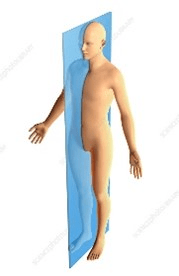
Sagittal Plane - An anatomical plane that divides the body in to left and right
Name 3 compartments of Knee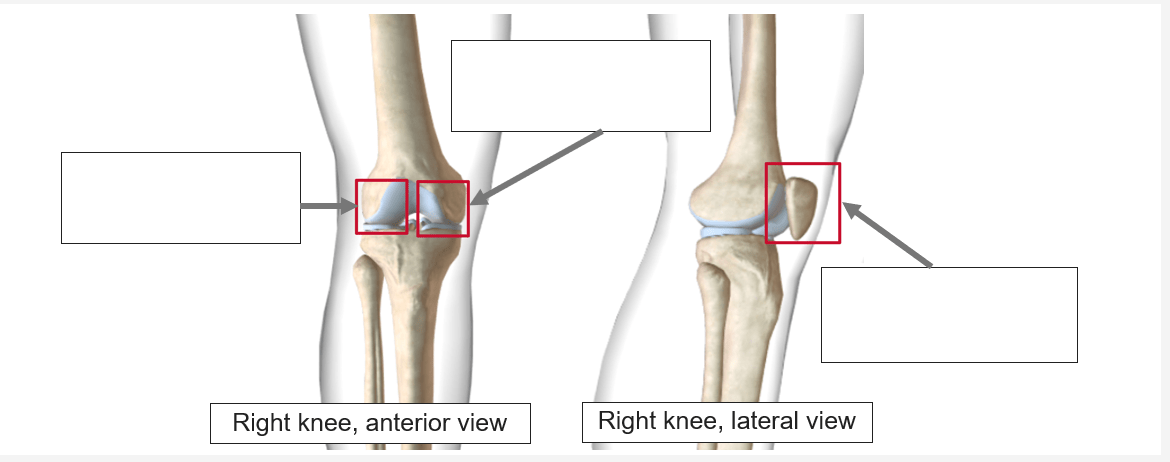
Lateral tibiofemoral ligament
Medial tibiofemoral ligament
Patellofemoral ligament
What blue line represent on this femur?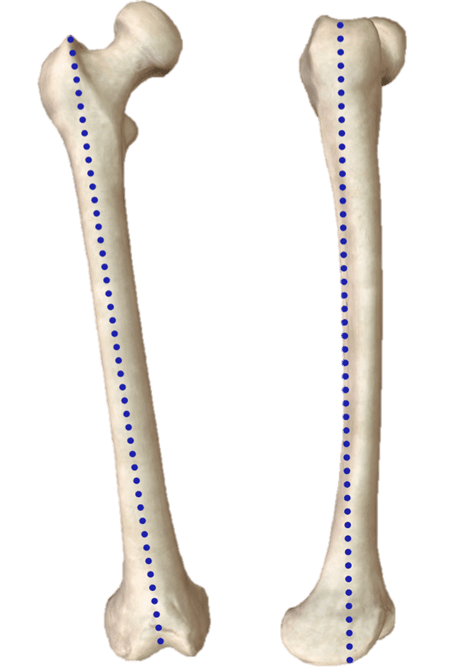
Anatomical Axis
This instrument allows the surgeon to make the Anterior, Posterior, and Chamfer cuts on the femur.
4-in-1 Cutting Block
Shoulder is ---------------- to Elbow
Proximal - Shoulder is closer to the trunk of the body as compared to Elbow
The weight bearing axis also known as -------------------
Mechanical Axis
...............increases the surface area of the tibiofemoral joint, aids in shock absorption, and helps guide femoral movement.
Meniscus
Which deformity is shown in X- ray?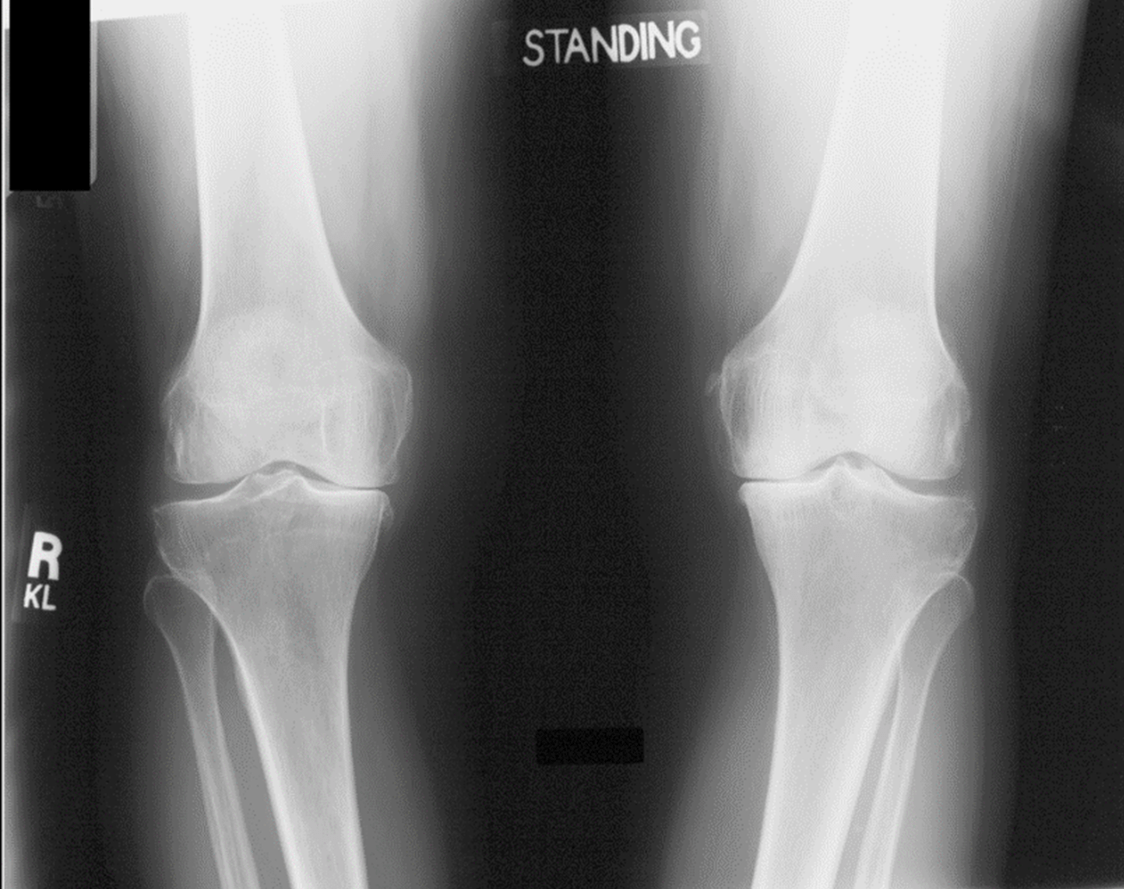
Varus
The distal cutting jig recommended starting resection is _ mm
9
The anatomical plane divides the body in to anterior and posterior sections and is used to assess abduction and adduction movements
Coronal Plane
Why is cancellous bone more susceptible to fractures than cortical bone?
Cancellous bone's porous structure makes it less dense and weaker than cortical bone, making it more susceptible to fractures under stress.
This specific type of stress test is used to evaluate the integrity of the medial collateral ligament by applying Valgus force to the knee
Valgus Stress Test
Label the areas on X-ray
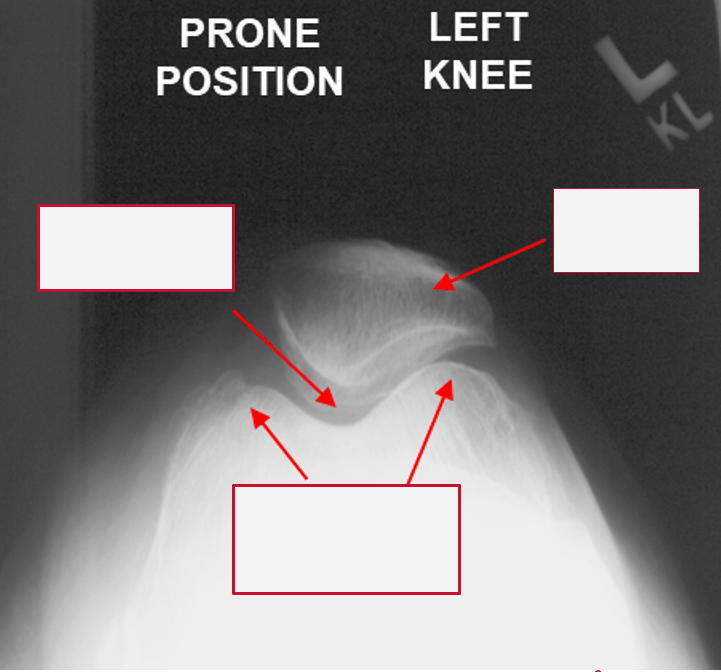
1. Patella Articulation
2. Patella
3. Femoral Condyles
This surgical technique balances soft tissues in flexion and extension during TKR to avoid instability or stiffness
Gap Balancing technique (Ligament Balancing)
A surgeon makes an incision on the knee closer to the midline of the body to repair a torn structure. Using anatomical direction , describe the location of the incision with respect to the body's midline.
Medial side of the Knee
In a road traffic accident, a patient's tibia is forced medially relative to the femur. Which ligament is most likely to be compromised, and on which side of the knee?
Medial collateral ligament on the medial side of the knee
Excessive genu varum alignment increases compressive loading on this compartment of the knee, accelerating osteoarthritic changes
Medial Compartment
This angle measured on a weight - bearing AP Knee X-ray, helps evaluate Varus or Valgus malalignment and guides surgical correction in osteotomies
Hip-Knee-Ankle Angle
The polyethylene component sits between the femoral and tibial implants and acts as the new weight-bearing surface of the knee
Tibial Insert
Discuss the role of the coronal plane in the assessment of dynamic knee stability
The coronal plane is critical in evaluating dynamic knee stability during cutting, pivoting, and lateral movements. Biomechanical imbalances in the coronal plane, such as excessive knee valgus or varus alignment, can lead to altered load distribution across the knee joint.
A 35 year old runner presents with pain localized just above the patella, worsened by stair climbing and squatting. This condition involves micro-tears in tendons of which muscle group
Quadriceps
During normal gait, the knee experiences this complex rotational movement combining flexion-extension with slight internal-external rotation esp during terminal extension called ----------------
Screw-Home Mechanism