Umbilical arteries
Delivers oxygen, nutrients, and hormones to the baby from the placenta
Umbilical Vein
What does the ductus arteriosis become after birth?
Ligamentum arteriosum
90% of cord insertions are either ____________ or ____________
Central or eccentric
Usually defined as < 2 cm between the cord and placental edge
Marginal insertion
Increase of the size of the placenta
Placentomegaly
The Ductus Venosus becomes what after birth?
Ligamentum venosum
Occurs when the placenta partially or totally covers the cervix
Placenta previa
Placental Accreta, Increta, and Percreta can be detected as early as ______ to ________ weeks in most at-risk patients by visualization of irregular ___________ spaces within the placenta
15 - 20; vascular
This type of placenta anomaly is rarely associated with fetal malformation and ususally has no clinical significance
Circummarginate placenta
This type of placental abruption is between the amnion and chorion
pre-placental abruption
A ___________ insertion may evolve into a ________________ insertion during pregnancy
marginal; velamentous
Placental grading has been found to correlate to
fetal lung maturity
Shunts most of the umbilical vein blood flow directly to the IVC
Ductus Venosus
Where do the umbilical arteries branch from?
Internal Iliac Arteries
Allows blood to enter the left atrium from the right atrium
Foramen Ovale
A normal placenta will appear:
smooth with a granular echo pattern
When does placental calcification often occur with increasing gestational age?
~ 29 weeks
An early progression to a grade 3 placenta is concerning and sometimes associated with this
Placental Insufficiency
Placental accreta, increta, and percreta happen when the placenta attaches itself too far into what?
Myometrium
Succenturiate placenta is caused by abnormal
Distributions of the chorionic villi
This type of placental abruption is also known as subchorionic
marginal placental abruption
The umbilical cord is normally made up of how many vessels? What are they?
3; AVA (2 umbilical arteries and 1 umbilical vein)
Premature aging of the placenta can indicate
placental insufficiency
The umbilical cord inserts into the fetal membranes outside the placental margin and travels between the amnion and chorion to the placenta
velamentous insertion
When is the placenta apparent on ultrasound
9-10 weeks
Maximum thickness of the placenta at any stage of pregnancy should not exceed
4 cm
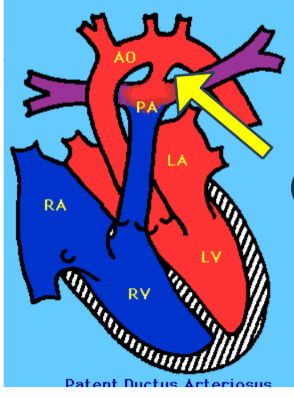
Connects the pulmonary artery to the proximal aorta and allows most of the blood from the right ventricle to bypass the fetus's fluid-filled non-functioning lungs
Ductus arteriosis
One of the biggest concerns of placenta previa
Risk of hemorrhage during labor, deliver, or the first few hours after delivery
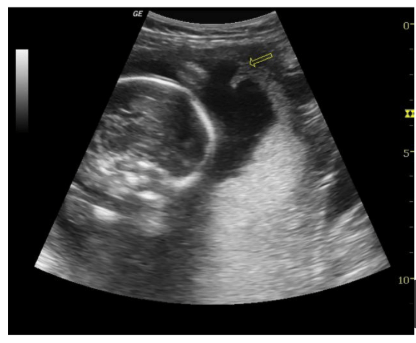
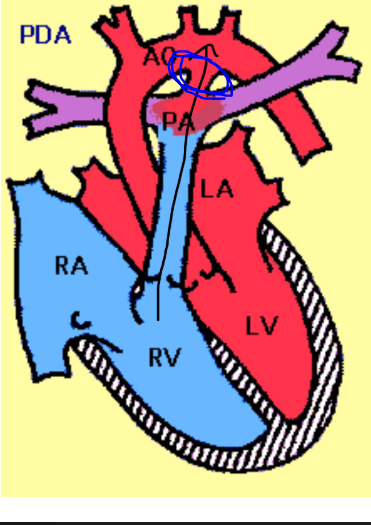 What is this structure in the fetal heart?
What is this structure in the fetal heart?
Ductus Arteriosis
 What type of placenta is shown here
What type of placenta is shown here
Succenturiate Placenta
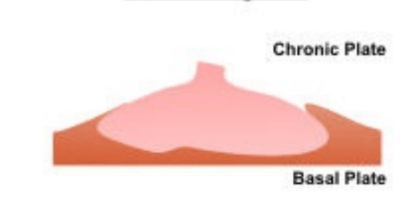 What type of placenta is shown here
What type of placenta is shown here
Circummarginate placenta
2 primary neoplasms of the placenta (nontrophoblastic)
1. chorioangioma
2. teratomas
Succenturiate placenta may be confused with
myometrial contraction
The umbilical cord does not insert centrally; common and not considered an abnormality; still in the meaty part of the placenta
eccentric insertion
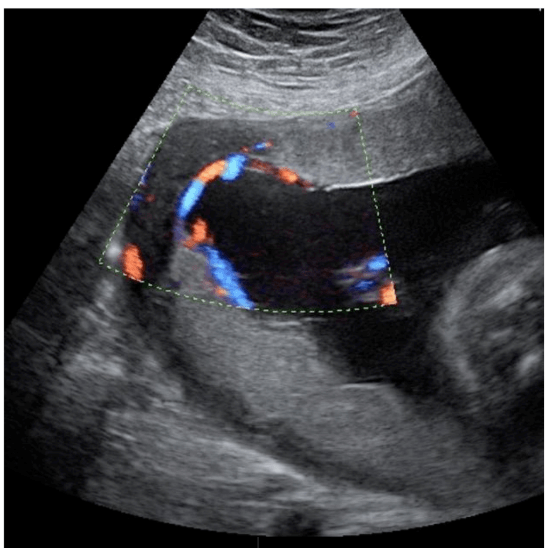
Can occur as a result of velamentous insertion; the vessels traverse the internal os trapping them between the fetus and opening of the birth canal
Vasa Previa
In this situation the cord insertion is too close to the edge of the placenta
Marginal insertion
Painless, bright red vaginal bleeding during the second half of pregnancy; may have contractions
Placenta previa
 This is an image of
This is an image of
Placentomegaly
Occurs when the placenta goes into the myometrium but does not penetrate uterine muscle
Accreta
Placental Accreta, Increta, and Percreta have an increased incidence with: (4)
2. previous C-section deliveries
3. Women over 35 (AMA)
4. Multiple pregnancies
Occurs when the placenta penetrates through the entire uterine wall and invades other organs such as bladder and rectum
percreta
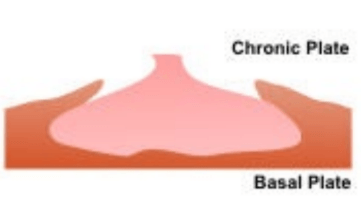 What type of placenta is shown here
What type of placenta is shown here
Circumvallate Placenta
This type of placental abruption is the most common
marginal placental abruption
Types of cord insertion (4)
1. Eccentric
2. Marginal
3. Velamentous
4. Normal/central
Types of Placenta Previa:
1. low lying
2. marginal
3. complete
What is the fetal circulation adaptation that allows blood to flow from the right atrium to the left atrium of the heart?
Foramen Ovale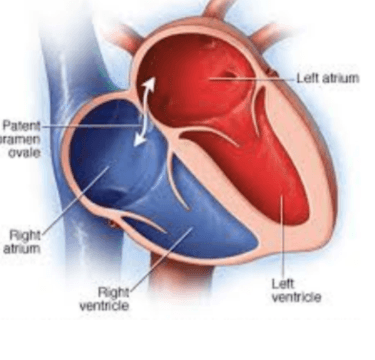
At about _____ weeks the ________________________ opposite the implantation site will begin to produce a smooth membrane
What is the fetal circulation adaptation that allows blood to bypass the liver and go straight to the IVC?
Ductus Venosus
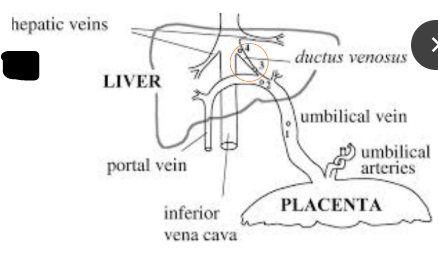
With ________ previa the placenta will usually move away from the cervix as the uterus grows and stretches
marginal
Occurs when the placenta does penetrate into the uterine muscle
Increta
What is the fetal circulation adaptation that allows blood to bypass the lungs and go straight to the aortic arch?
Ductus Arteriosis
 What kind of placenta is this
What kind of placenta is this
Circumvallate placenta
3 secondary neoplasms of the placenta
1. melanoma
2. carcinoma of breast
3. carcinoma of lung
This type of placental abruption is where the placenta is detaching from the wall of the uterus
retro-placental abruption
One or more accessory lobes connected to the placenta by blood vessels
Succenturiate placenta
Most common form of placenta attaching into myometrium
Accreta
Premature aging of the placenta can cause _______ and is associated with: (4)
IUGR:
1. smoking
2. chronic HTN
3. Lupus
4. Diabetes
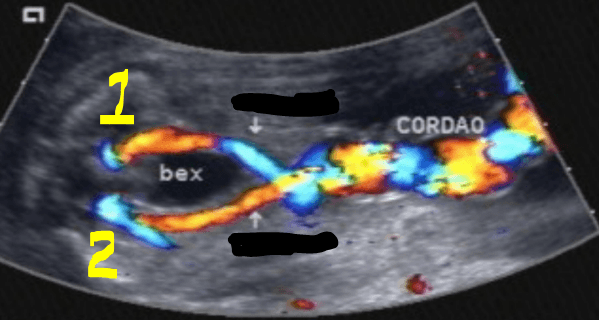
What are 1 and 2 in this image? And what are they going around?
umbilical arteries; bladder
Risk factors of Placenta previa: (3)
1. C-section
2. surgery to remove fibroids
3. D & C
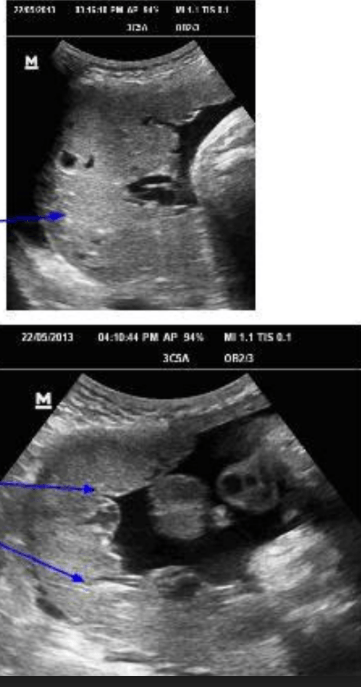 Placenta Grade _____
Placenta Grade _____
II
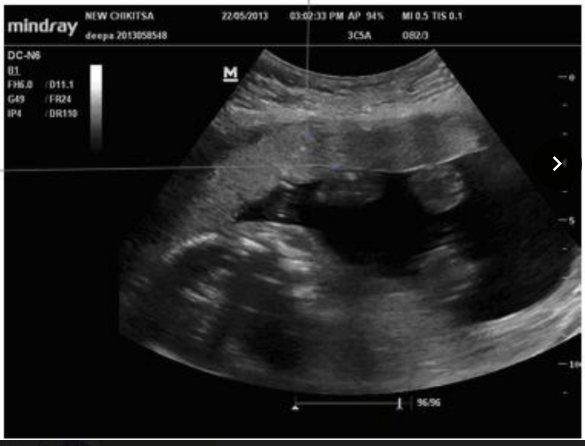 Placenta grade ____
Placenta grade ____
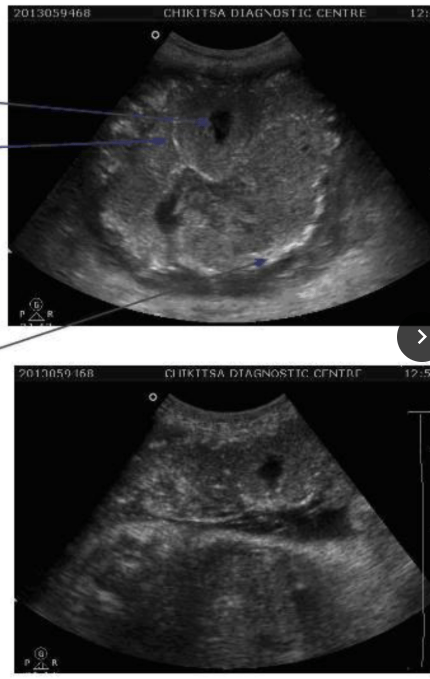 Placental Grade ____
Placental Grade ____
III
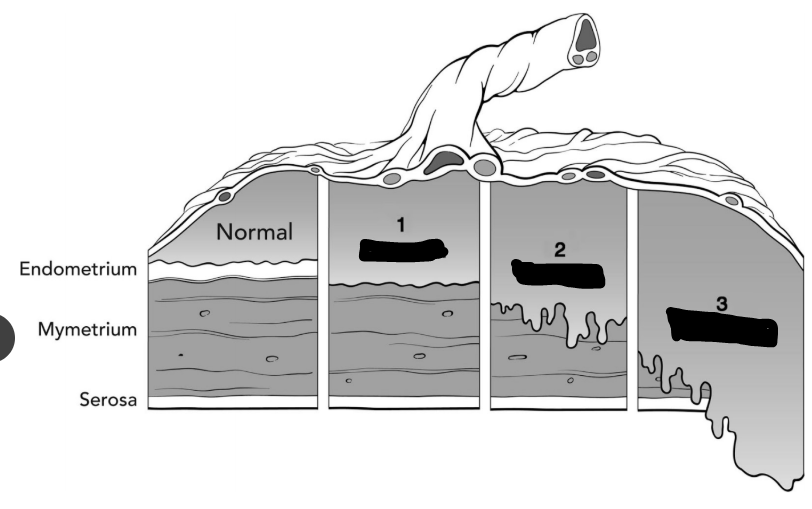 Label 1, 2, and 3
Label 1, 2, and 3
1. Accreta
2. Increta
3. Percreta
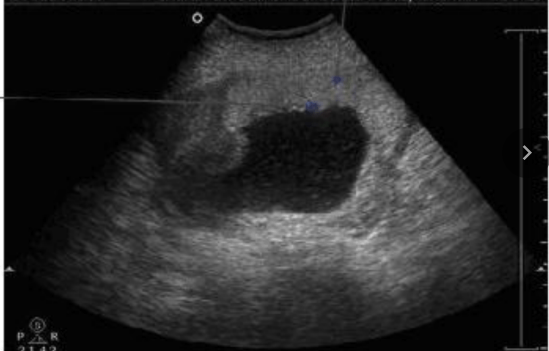
 What type of placental abruption is this?
What type of placental abruption is this?
Marginal
This is the most common maternal malignant tumor to metastasize to the placenta
Melanoma
2 complications of vasa previa
1. vessels may rupture causing significant blood loss
2. vessels easily become compressed which causes heart rate to drop
< 18 weeks:
uniform echogenicity
smooth chorionic plate
Grade 0
PLACENTA GRADE: > 39 weeks
significant calcification
chorionic plate interrupted by indentations
Grade III
PLACENTAL GRADE:
18-29 weeks:
occasional hyper-echoic area/calcification
chorionic plate well defined
Grade 1
3 classifications of placental abruption
1. pre-placental
2. marginal placental
3. retro-placental
 Placental grade ____
Placental grade ____
0
Least common and most dangerous form of placenta attaching into myometrium
Percreta
PLACENTAL GRADE:
> 30 weeks:
basal echoed in the placenta are a hallmark
grade II
Relatively common; benign vascular tumor; usually asymptomatic and small
chorioangioma
A benign non-trophoblasic tumor composed of mixture of epithelial, adipose, skeletal, and connective tissues
teratoma
Similar to cirumvallate placenta, but the membrane ring is thinner
circummarginate placenta
5 Fetal adaptations from video:
1. Umbilical vein
2. Umbilical artery
3. Ductus Venosus
4. Foramen Ovale
5. Ductus Arteriosus
Types of placental positioning (7)
2. Anterior
3. RT Lateral
4. LT Lateral
5. Fundal
6. Combination
7. Covering OS
Causes of placentomegaly: (7)
2. maternal diabetes
3. chromosomal abnormalities
4. hydrops
5. inutero infection
6. Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome
7. Hydatidiform mole
Placenta previa is more common among women who (6)
1. have already delivered at least one baby
2. had placenta previa in past
3. are carrying multiples
4. AMA
5. Asian
6. Smoke
Circumvallate placenta is associated with (4)
1. Placental abruption
2. Oligohydramnios
3. Preterm birth
4. Increased risk of fetal demise
Symptoms of placental abruption: (4)
1. vaginal bleeding
2. abdominal tenderness/back pain
3. contractions
4. abnormalities in the baby's heartbeat
Cause is unknown but some risk factors for placental abruption (7)
1. polyhydramnios
2. trauma
3. high blood pressure
4. past pregnancies
5. smoking
6. street drugs
7. AMA
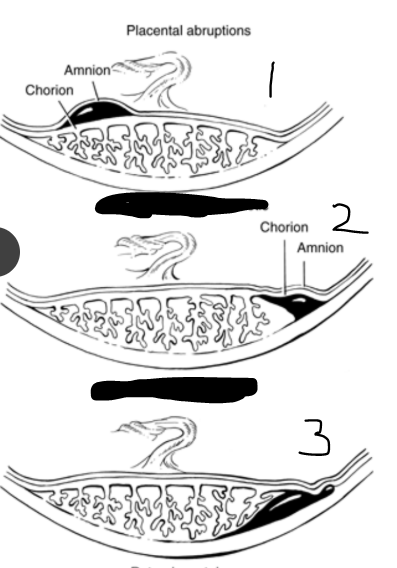 label 1, 2, and 3
label 1, 2, and 3
1. pre-placental abruption
2. marginal placental abruption
3. retro-placental abruption
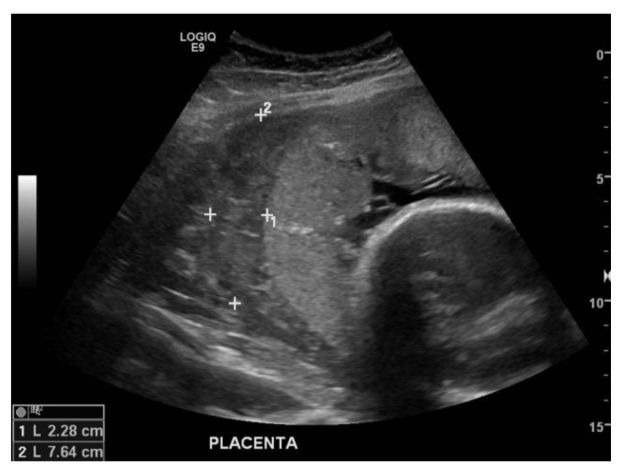
Tend to occur on fetal side of placenta near cord insertion; solid, hypo-echoic, rounded mass with anechoic areas
Chorioangioma
Very rare and benign; almost never associated with congenital deformities
Teratoma
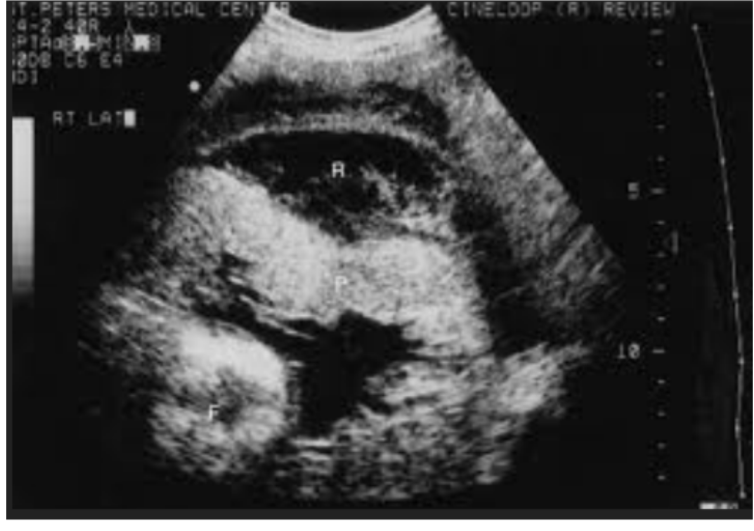 What type of placental abruption
What type of placental abruption
Retro-placental abruption
Perfused by the fetal circulation and may impair fetal cardiac activity if large in size
chorioagnioma
Doppler evaluation of the placenta is useful in diagnosing (3)
1. chorioangioma
2. placenta accreta
3. vasa previa
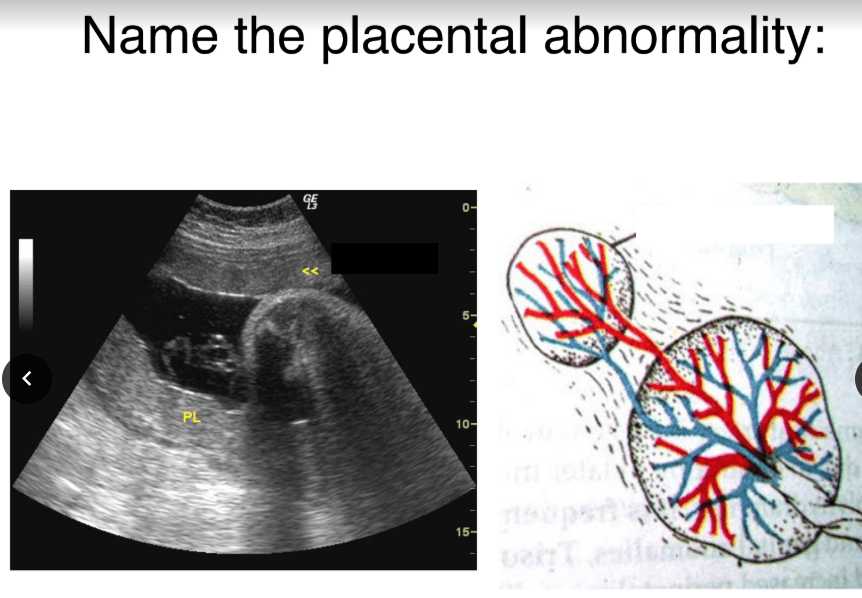
Succenturiate Lobe
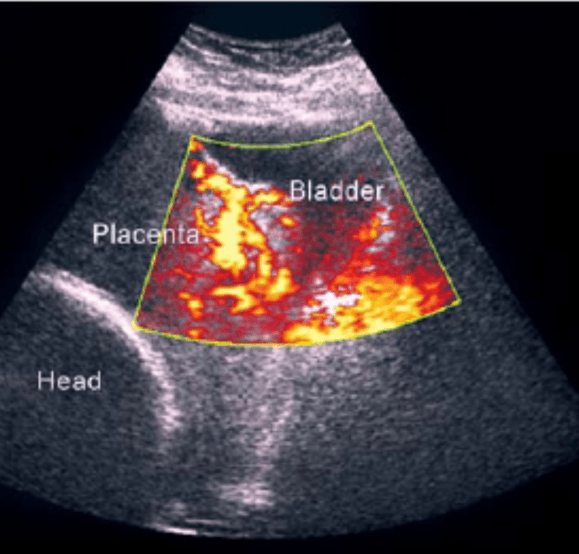
What is this image of
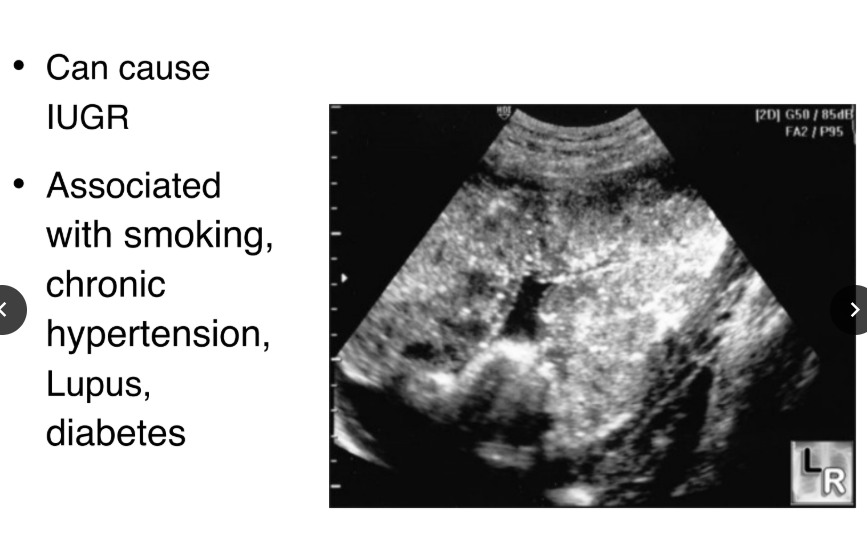
Premature aging of the placenta
The placenta should never measure more than
4 cm
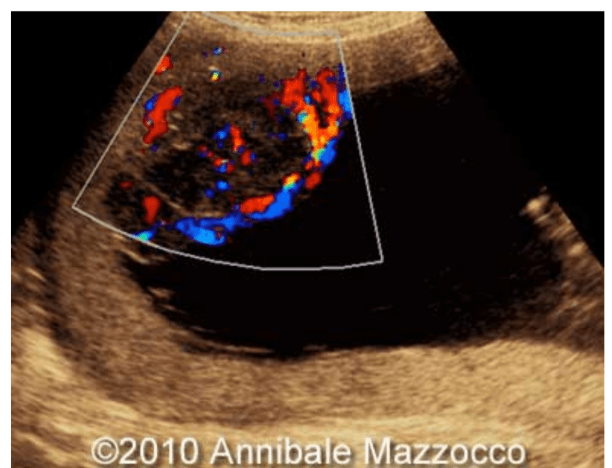 These will present as very vascular with fetal arterial waveforms
These will present as very vascular with fetal arterial waveforms
Chorioangiomas
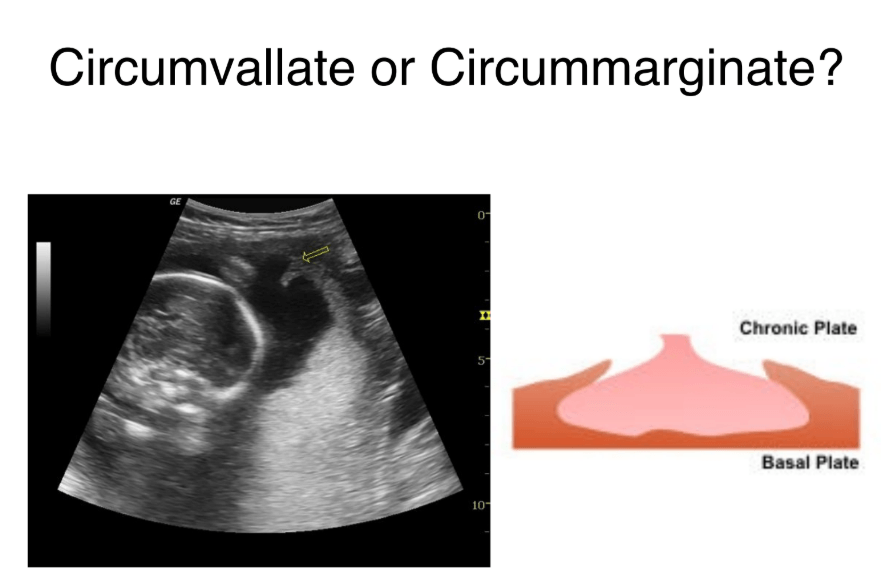
Circumvallate
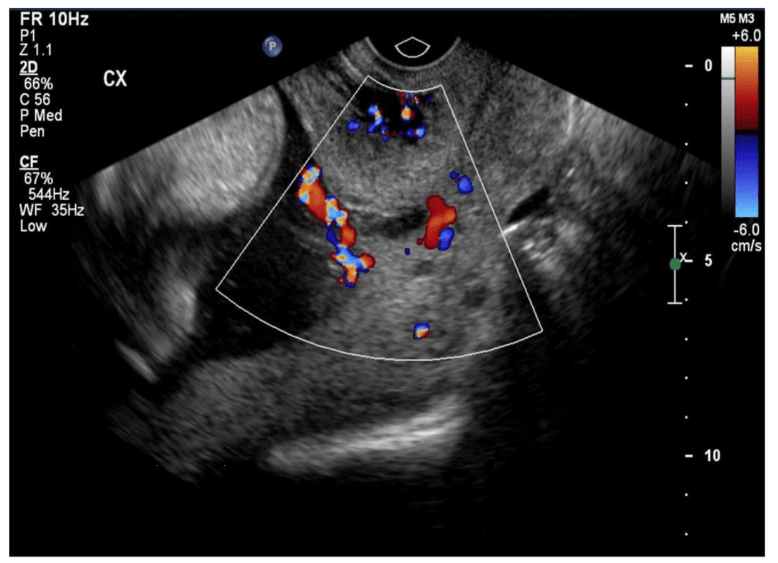
Vasa Previa
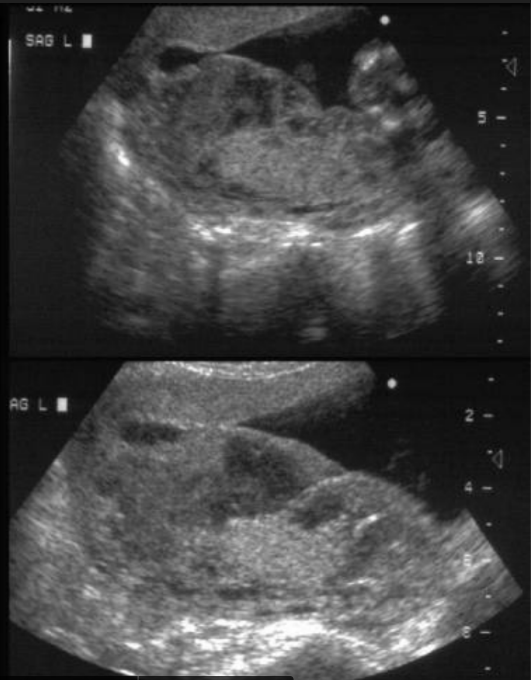
Placental Metastasis (from maternal breast cancer)
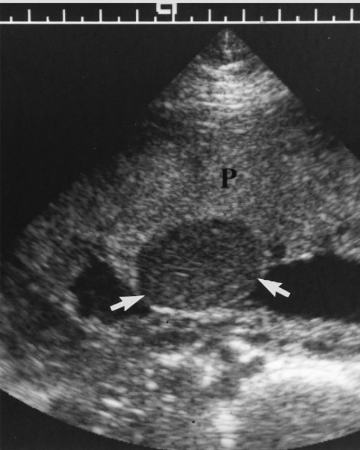 What is this an image of
What is this an image of
Chorioangioma