Which structure is used for a large surface area for photosynthesis in plants?
What are leaflets?
Meristems are made up of
Stem cells
Cells that create the stomata
Guard cells 
The 3 cell types found in ground tissue
Roots that penetrate host plants
Parasitic roots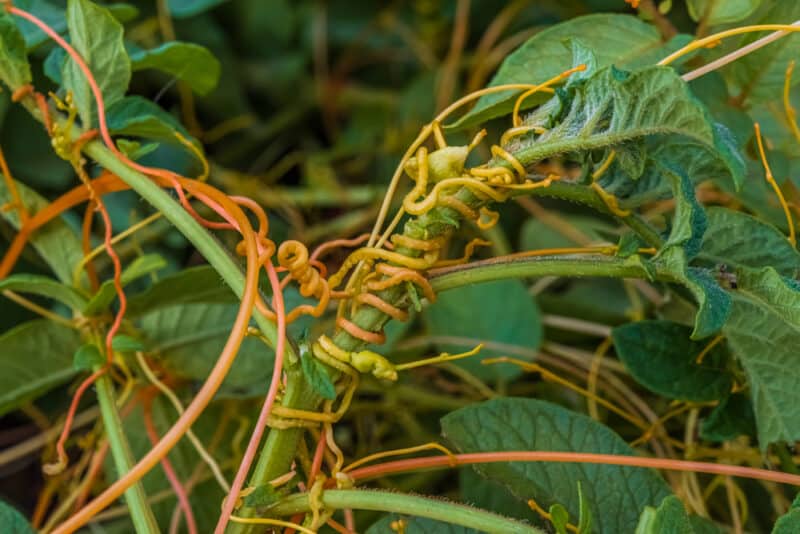
The structure that is above ground in the plant
What is the shoot?
The structure that protects the root from damage as it pushes down
The root cap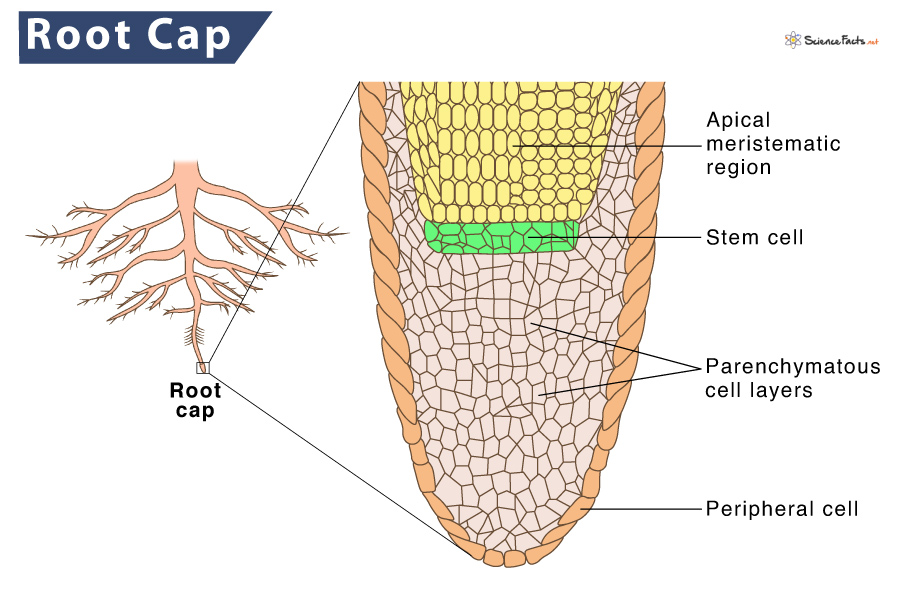
Tubular extensions that form before the formation oflateral roots. Has a single cell structure with no vascular system. Increases the surface of absorption
What are root hairs? 
The cell type that is used for storage, photosynthesis, and secretion. Have chloroplasts and are the most common of the ground tissue
Parenchyma
Roots that keep the plant upright
Prop roots
The structure indicated by question marks
What is the stipule?
Meristems have the ability to become a variety of different cell types. This ability is known as being ________________________
Pluripotent
When the stomata is open, this is happening to the guard cells
Inflation, half moon shape
The cells that are used for support and protection and allow for bending without breaking in the plant
Collenchyma
The purpose of pneumatophores
Facilitation of oxygen uptake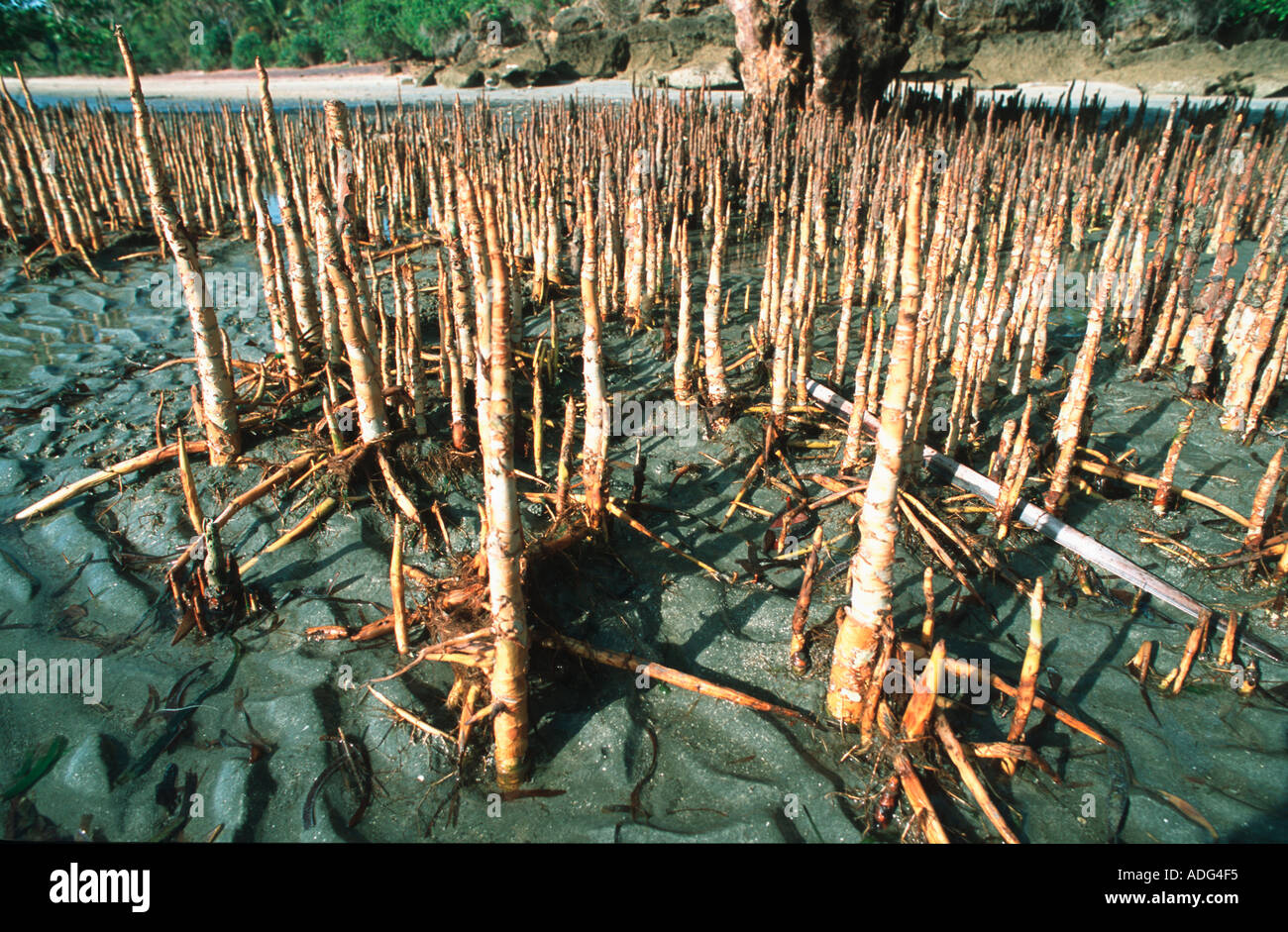
These structures are extensions of a leaf. They are typically found on flimsier plants such as sweet peas and tomatoes. They are used to attach to and curl around other things for support.
The three types of meristems
Apical meristem, lateral meristem, intercalary meristem
A structure like an umbrella to protect from UV radiation and reduce evaporation.
 Trichomes
Trichomes
Schlerenchyma
Roots that pull the plant further into the soil
 Contractile roots
Contractile roots
The point at which part of the plant diverges from the stem
What is the petiole?
The 3 types of meristems allow growth in what directions
Apical: up and down
Lateral: to the sides, becoming thicker
Intercalary: becoming thicker and bushier
The structure in which some secrete smelly or bitter substances to deter herbivores from eating them
Trichomes
Which cells of the ground tissue are still living? Which are dead? (There are 3 cell types)
Roots that obtain water from the air
 Aerial roots
Aerial roots