Monocot or Eudicot root?
Eudicot root.
How many seeds do Eudicots have?
2
How many seeds do Monocots have?
1
What is a Bryophyte?
small flowerless green plant
What helps plants survive?
Monocot or Eudicot?
Monocot
True or False. Eudicot has scattered vascular bundles.
False
What type of root does a Monocot have?
Fibrous
What are examples of Bryophytes?
Mosses, Hornworts, Liveworts.
Flowers use adaptations such as thorns for___
protection.
This is an example of a _______
Bryophyte.
How many cotyledons do i have?
2
Monocots flower parts in groups of _________
3 or Multiples of 3
Bryophytes are vascular plants. True or False.
False, they are nonvascular.
Without the bright colors of nature there would not be as much ______ occuring.
Pollination
What kind of seed is this?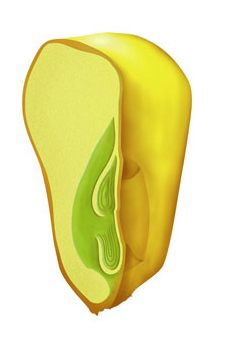
Monocot Seed.
Why is this a Eudicot?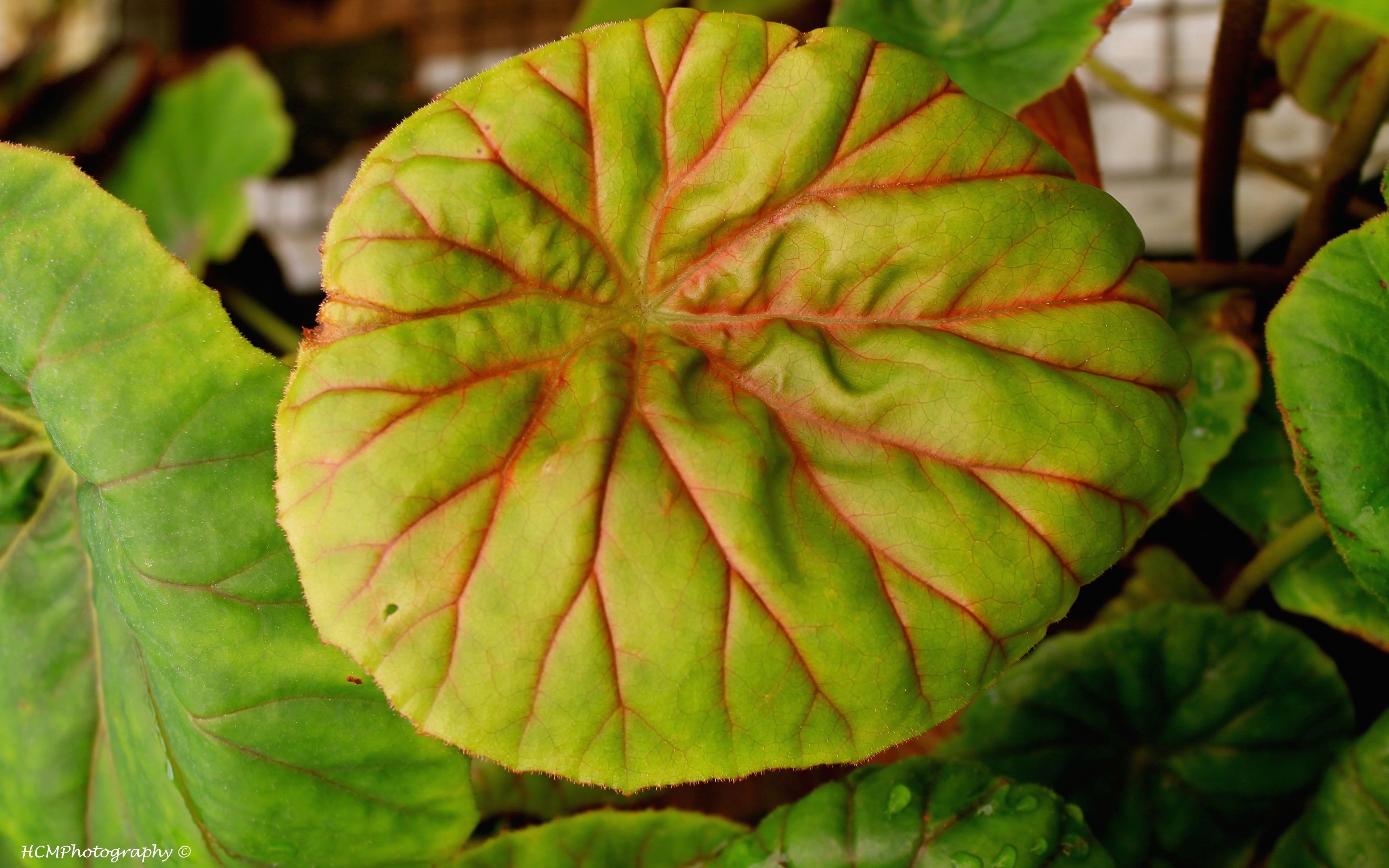
Germination is _________
The process by which a seed begins to grow
Describe alternation of generation.
A life cycle in which there is both a multicellular diploid form, the sporophyte, and a multicellular haploid form, the gametophyte.
How do deep roots help desert plants adapt?
Helps them conserve/store water.
What kind of seed is this?
Eudicot.
Root difference from monocot is _____
Taproot is usually present in eudicot, whereas in monocot it has fibrous roots.
How can you identify this is a Monocot?
The parallel veins in the leafs.
What are the characteristics of bryophytes?
Their sporophytes are unbranched and they do not have a true vascular tissue containing lignin.
Waxy Cuticle
Protects plant from water loss