The enlarged ovary of the flower that protects the developing seeds.
What is fruit?
Farmers water their crops using a system of large pipes and sprinklers which can cause soil to become salty.
What is irrigate and salinization?
What are 3 pests groups and how do they harm crops?
Weeds: steal nutrients from the crop
Fungus: spread disease
Insects: eat the crop
What are 3 different ways to asexually reproduce plants? Which one is the one where soil covers the stem and a new plant grows? 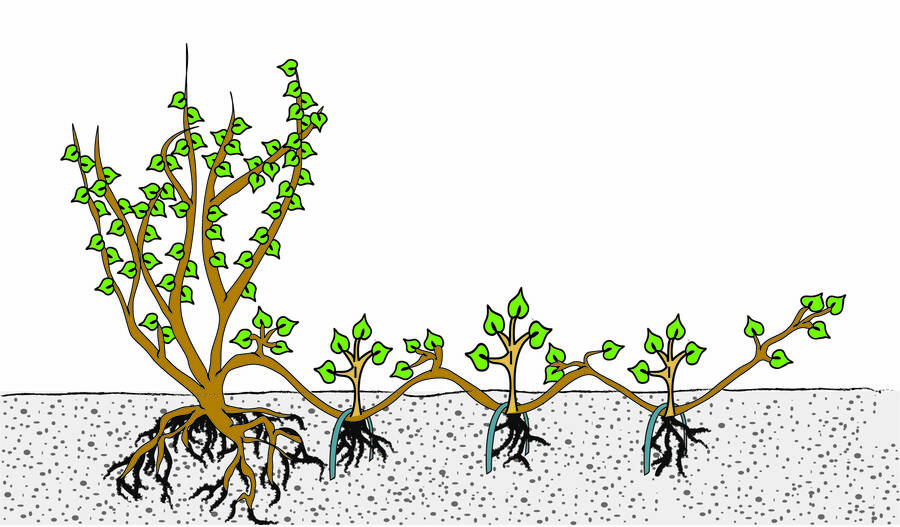
Grafting, cutting, and layering. Layering is where soil covers the stem running on the ground and a new plant is formed.
Name ways to conserve the quality of the soil and prevent erosion.
Cultivate less often and use a wide-shoveled cultivator (disturbs less soil)
Plant shelter belts and forages.
Practice zero-tillage.
Irrigate less
- Seeding and reshaping waterways
A substance used to control insects or other organisms that are harmful to plants or animals. Can harm non-target organisms, can create resistant pest species, can build up in soil as chemical residue.
What is a pesticide?
The part of a cell that controls the organism's characteristics is called the gene. When scientists change genes of plants, they can add desirable characteristics.
What are genetic modification?
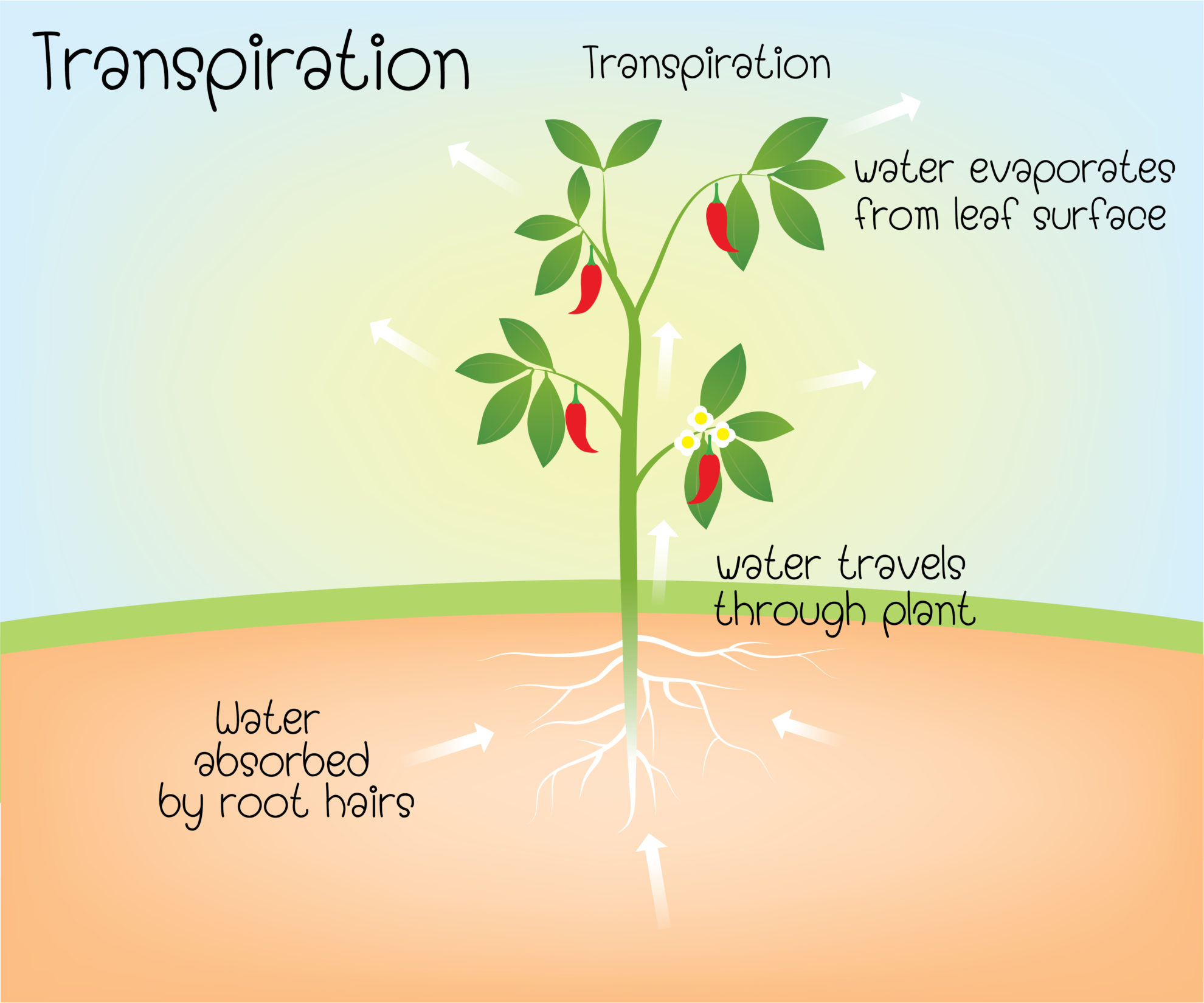
How does water move into and out of a plant?
It is pulled by transpiration and pushed by osmosis.
Heartwood, xylem, cambium, phloem, and bark are ____________. The growing part is the _____________.
What are the 5 layers of a tree stem and the cambrium
Pollutant concentration increasing higher up the food chain.
What is biomagnification?
What is germination and the best conditions for it?
The development of a seed into a new plant. Plants germinate best in warm, moist and dark places.
 What are the three nutrients labelled as numbers on a bag of fertilizer?
What are the three nutrients labelled as numbers on a bag of fertilizer?
Nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium.
The of decomposer in the soil the mixes, aerates, and digests the soil.
What are earthworms?