Layer of the Earth that plates are made of and where we live.
Crust
In investigations, the independent variable is what we _____a_____. The dependent variable is what we ____b______.
a. Change; modify; test; compare
b. Measure
At this type of boundaries plates are pulling apart
Divergent
What type of landform occurs at continental - continental convergent boundaries?
Mountains
What is it called when one plate goes under another plate?
subduction
Layer of the Earth where convection cells are found, which move the plates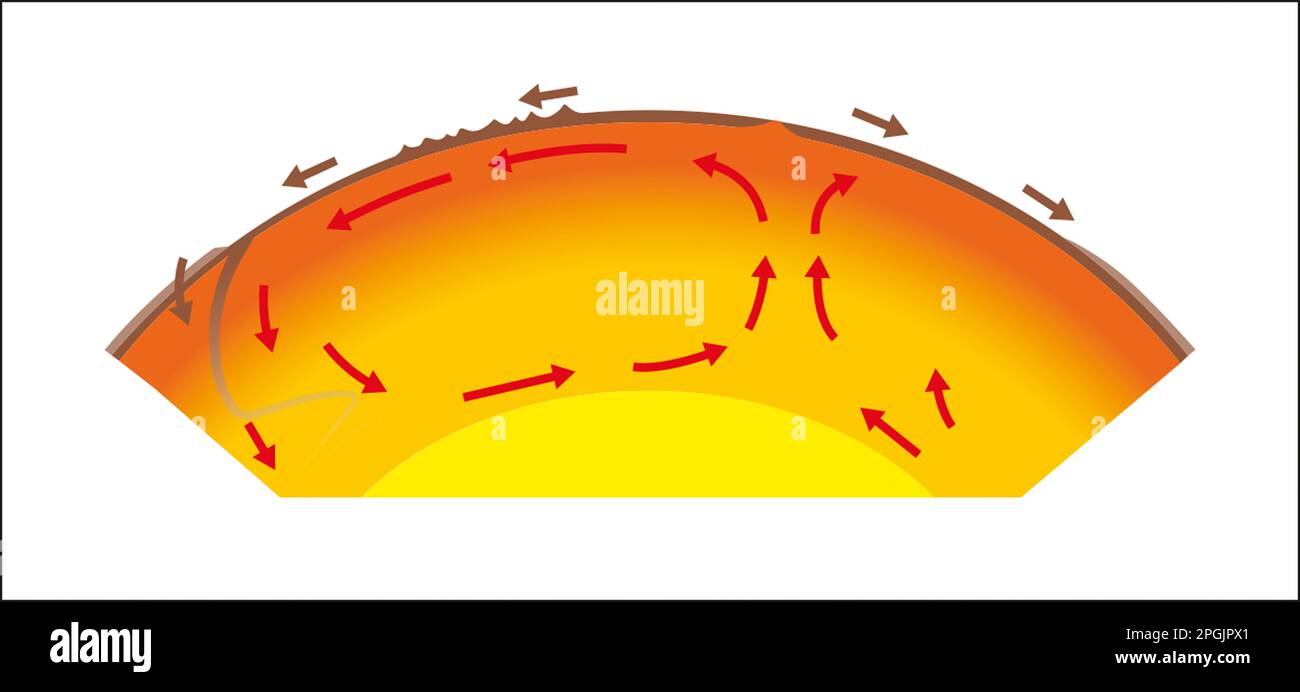
"How does soil type affect how fast it erodes in a river?
The IV is...
The DV is...
DV: Erosion rate/how fast it erodes
At this type of boundary plates are sliding against each other (100). What processes can happen at these boundary types (100)?
Transform, earthquakes
New crust forms at ____a_____ plate boundaries to form a mid-ocean _____b______.
a. divergent
b. ridge
Renewable resources are ___________ as fast as they are used.
Once we use non-renewable resources, we cannot ___________ quickly.
Renewable - replaced as fast as they are used
Non-renewable- once used, they are gone
One of the main types of rock you would DEFINITELY at a divergent plate boundary
Igneous
What were the independent variables we tested in the Copper Extraction lab?
concentration of copper sulfate, temperature of copper sulfate, voltage (#of batteries)
Country X experiences many earthquakes. There are several large volcanoes along its shoreline with the ocean.
What type of plate boundary is it likely found on (with crust types)?
Convergent - Continental / Oceanic
Model 2 convection cells at a plate boundary where new crust is formed.

a. Natural resources come from...
b. Natural resources are used...
a. the Earth
b. by humans
100 points per answer:
In the mantle, plastic rock that is ___a____ _______ will rise towards the Earth's ___b____. As it cools, it will ____c____ towards the Earth's hotter ___d____ _____.
a. less dense; b. crust; c. sink; d. outer core
"How does the type of crust a boundary affect the number of earthquakes at the boundary?"
What is the independent and dependent variable?
IV: Crust type
DV: number of earthquakes
What causes Earth's plates to move?
Convection currents in the mantle drag the plates around on the surface.
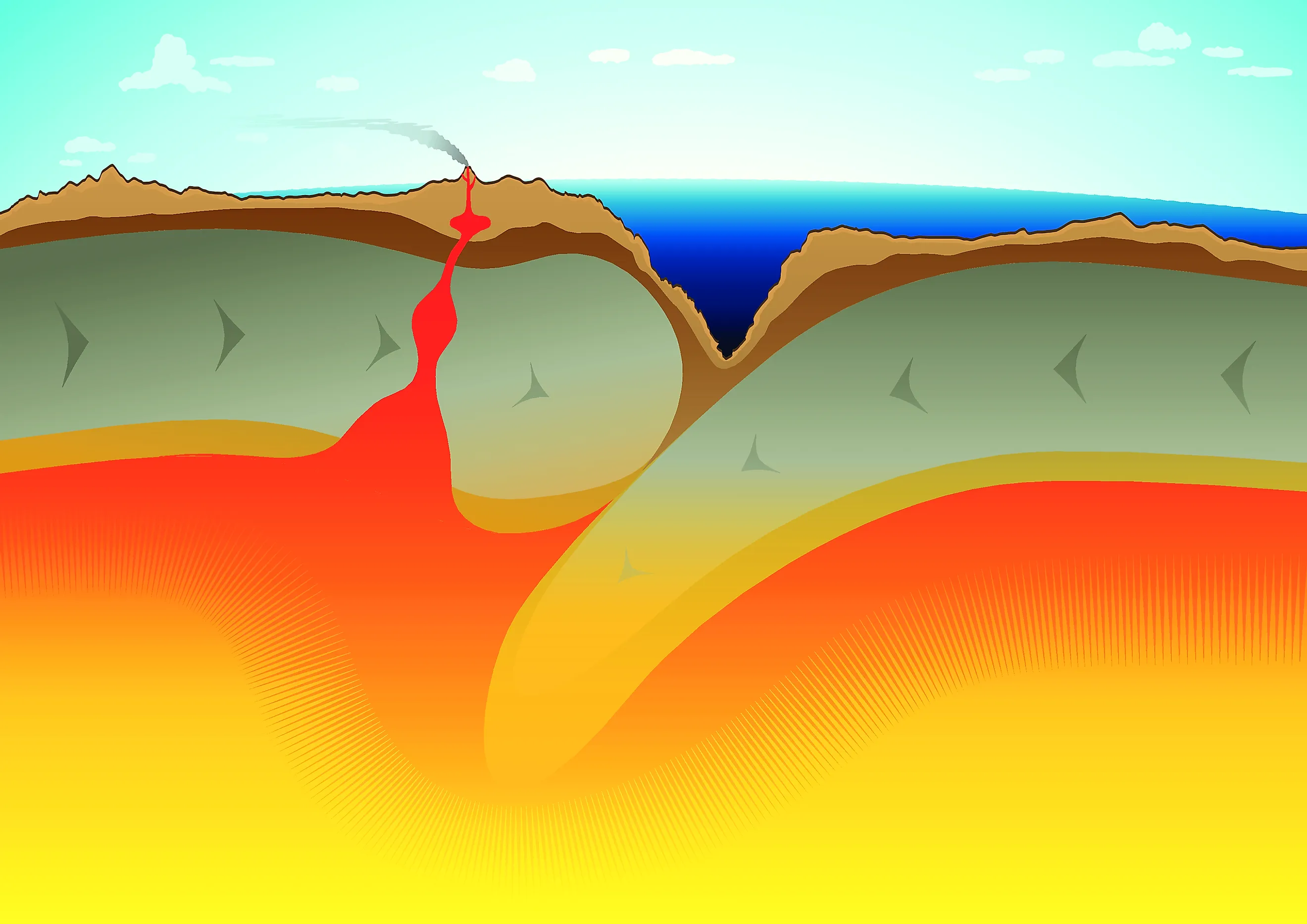
Model a subduction zone.
Include labels: rising magma, volcano, trench, convection cell
What are the three types of heat transfer? Which one is most important in plate movement?
conduction, convection, radiation / Conduction
Which type of boundary are the deepest earthquakes located (100)? Why (400)?
Convergent. The subducting plate continues to slide against the other plate deep under the surface.
Design an investigation involving Komodo dragons.
RQ (100):
IV (100):
DV (100):
3 Constants (200): 
RQ: How does food type affect how wide a Komodo dragon opens its mouth?
IV: Food type
DV: Angle of jaw; length from top to bottom of mouth
Constants: Amount of food; time food is shown to dragon; location
How can plates be created and destroyed at the same time? Explain or model.
Plates are created a divergent boundaries and destroyed at convergent boundaries. 
What type of landform occurs at a continental-oceanic convergent boundary? Describe why.
Volcanoes. The subducting plate melts as it sinks into the mantle. Magma rises to the surface and escapes as a volcanic eruption.
Name three piece of evidence that support the theory of continental drift.
shapes of continents, same fossils AND rocks AND glacier evidence on different continents
