 Traces of an ancient organism preserved in rock.
Traces of an ancient organism preserved in rock.
What is a fossil?
 The process which adds more crust to the ocean floor.
The process which adds more crust to the ocean floor.
What is sea-floor spreading?
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-483766933-56c6e7fd3df78cfb37869a63.jpg)
The point where two plates move apart from each other.
What is a divergent boundary?
 The force that acts on rock or crust to change its shape or volume.
The force that acts on rock or crust to change its shape or volume.
What is stress?
Vibrations in the ground that result from movement along faults.
What are Earthquakes?
 Volcanoes form mostly at these types of plate boundaries.
Volcanoes form mostly at these types of plate boundaries.
What are convergent boundaries?
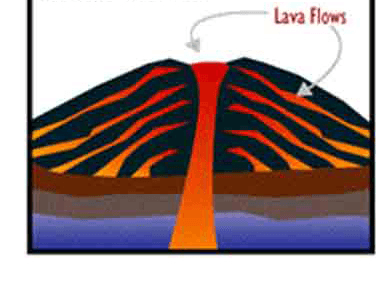 These form when lava flows out gradually building wide, gently sloping mountains.
These form when lava flows out gradually building wide, gently sloping mountains.
What are shield volcanoes?
 The person who made the hypothesis which sparked the idea of Pangea.
The person who made the hypothesis which sparked the idea of Pangea.
Who is Alfred Wegener?
 These form long chains of mountains that rise up from the ocean floor.
These form long chains of mountains that rise up from the ocean floor.
What are Mid-Ocean Ridges?
The point where two plates move together (toward each other.)
What is a convergent boundary?
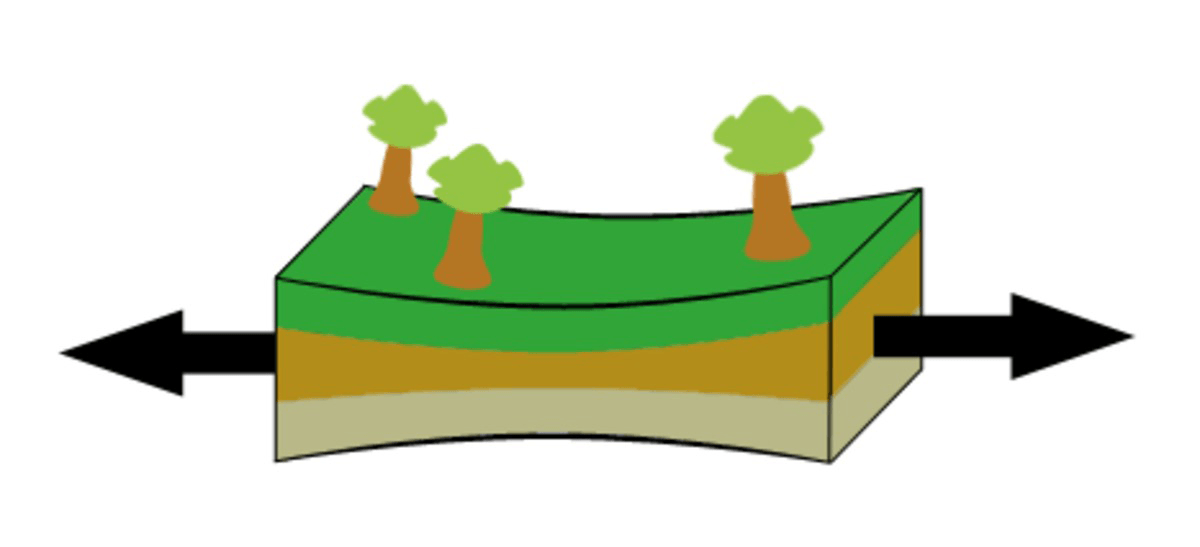 When the crust is pulled apart, stretching the rock.
When the crust is pulled apart, stretching the rock.
What is tension?
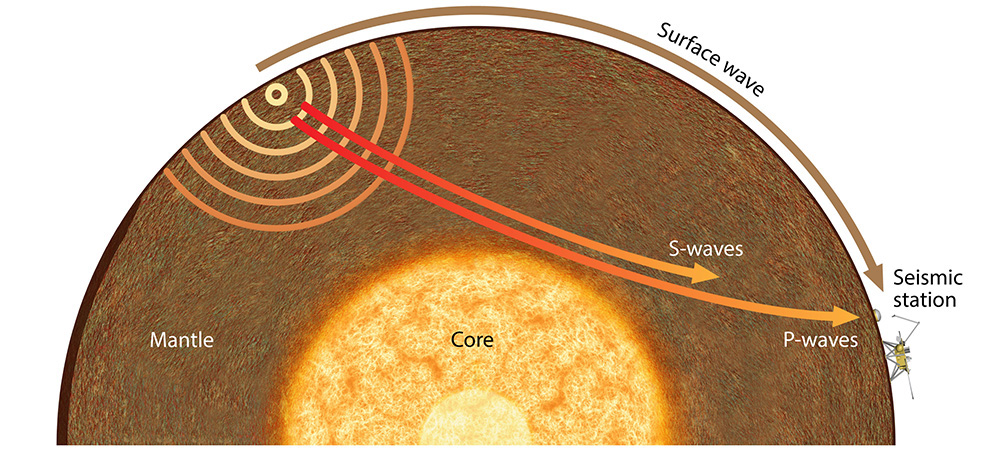 Waves that carry the energy of an Earthquake away from the focus.
Waves that carry the energy of an Earthquake away from the focus.
What are seismic waves?
 The type of eruption that has magma high in silica with trapped gases that build up pressure until it explodes with incredible force creating a pyroclastic flow, or an eruption that hurls out ash, cinders, and magma bombs.
The type of eruption that has magma high in silica with trapped gases that build up pressure until it explodes with incredible force creating a pyroclastic flow, or an eruption that hurls out ash, cinders, and magma bombs.
What is explosive eruption?
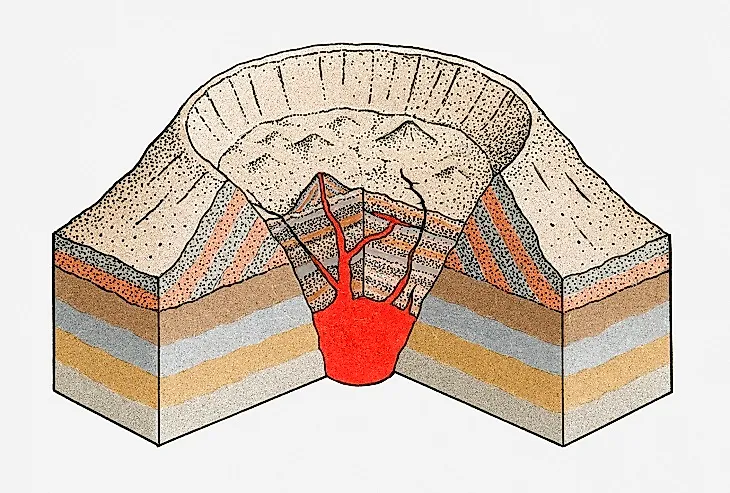 A huge hole left by the collapse of a volcanic mountain.
A huge hole left by the collapse of a volcanic mountain.
What is a caldera?
 The idea that the continents slowly moved away from each other.
The idea that the continents slowly moved away from each other.
What is continental drift?
 This is a deep under-water canyon found at a subduction zone.
This is a deep under-water canyon found at a subduction zone.
What is Deep-Ocean Trench?
The point where two plates slip past each other.
What is a transform boundary?
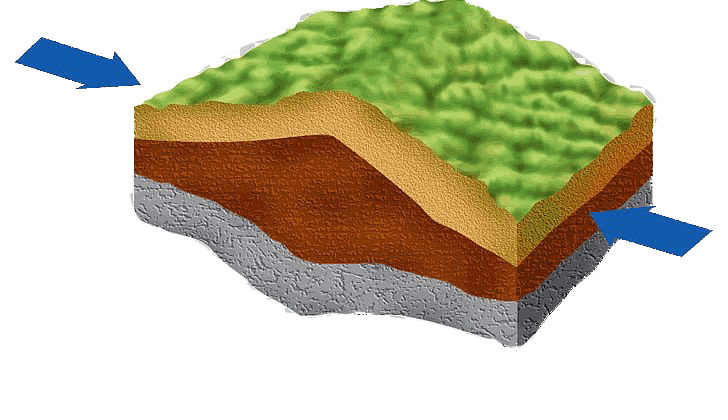 When rock or crust is squeezed until it folds or breaks.
When rock or crust is squeezed until it folds or breaks.
What is compression?
 The point beneath Earth’s surface where rock under stress breaks to cause an Earthquake.
The point beneath Earth’s surface where rock under stress breaks to cause an Earthquake.
What is Focus?
 The point where a volcano is formed in the middle of a plate instead of as a result of plates converging.
The point where a volcano is formed in the middle of a plate instead of as a result of plates converging.
What is a hot spot?
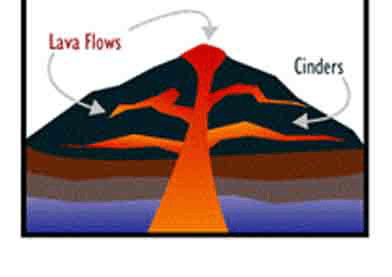 This is a tall cone-shaped mountain in which layers of lava alternate with layers of ash.
This is a tall cone-shaped mountain in which layers of lava alternate with layers of ash.
What is a composite volcano?
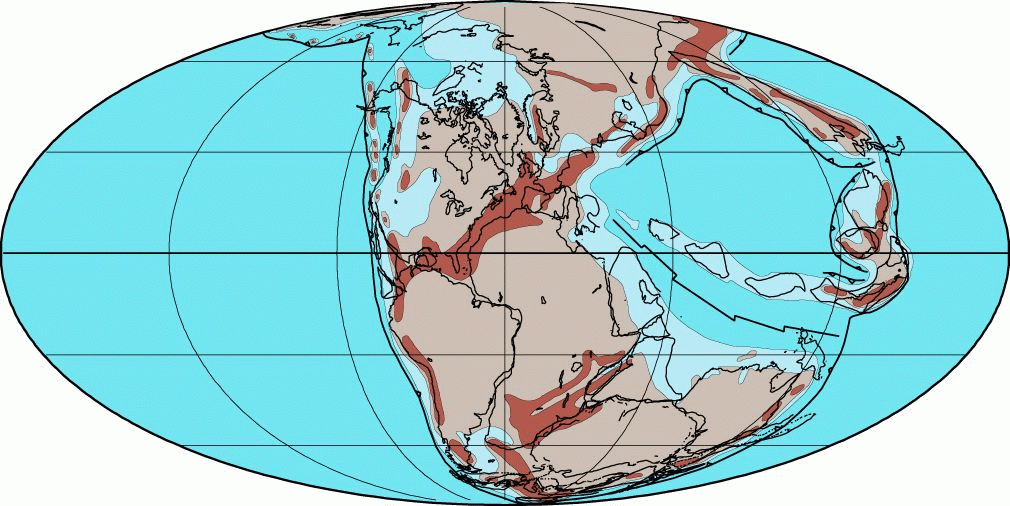 The supercontinent that Wegener suggested occurred on Earth about 300 million years ago.
The supercontinent that Wegener suggested occurred on Earth about 300 million years ago.
What is Pangea?
 A technique that scientists use to map the ocean floor.
A technique that scientists use to map the ocean floor.
What is sonar?
A break in the Earth's crust.
What is a fault?
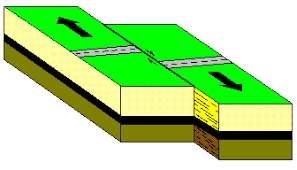 When two slabs of crust are pushed past each other in opposite directions.
When two slabs of crust are pushed past each other in opposite directions.
What is shearing?
 The point on the surface directly above the focus.
The point on the surface directly above the focus.
What is the Epicenter?
 A volcano that is not active, but may become active.
A volcano that is not active, but may become active.
What is a dormant volcano?
 A mass of rock formed when a large body of magma cools inside the crust.
A mass of rock formed when a large body of magma cools inside the crust.
What is a batholith?
 The movement of plates is largely driven by this force.
The movement of plates is largely driven by this force.
What is convection?
 The processes which change the size and shape of the oceans.
The processes which change the size and shape of the oceans.
What are sea-floor spreading and subduction?
 When pieces of Earth's crust diverge on land.
When pieces of Earth's crust diverge on land.
What is a rift valley?
Landforms which are formed by compression.
What are mountain ranges, volcanic arcs, and ocean trenches?
 Compression waves that travel through solids and liquids, compressing and expanding the material they pass through. The first waves to arrive at a seismic center.
Compression waves that travel through solids and liquids, compressing and expanding the material they pass through. The first waves to arrive at a seismic center.
What are Primary Waves (P Waves.)
 This type of eruption is low in silica content, flows easily, and erupts quietly with gases bubbling out gently and lava oozing quietly.
This type of eruption is low in silica content, flows easily, and erupts quietly with gases bubbling out gently and lava oozing quietly.
What is a quiet eruption?
 A fountain of water and steam that erupts from the ground when buildup of pressure is released.
A fountain of water and steam that erupts from the ground when buildup of pressure is released.
What is a geyser?