Divergent Boundary
This is the surface expression or location of an earthquake.
What is the epicenter?
What are P-waves?
Normal faults are caused by this type of stress.
What is tensional stress?
What boundary is this image depicting?
Transform Boundary
This is the measurement that objectively measures the amount of energy that has been released during an earthquake.
What is magnitude?
Seismic waves are measured and reported by this instrument.
What is a seismograph?
This type of stress is often found at convergent boundaries.
What do you call the area where two tectonic plates meet?
Plate Boundary
True or False: A high magnitude earthquake is always a high intensity earthquake.
False.
These waves are the second to arrive and move in a shearing manner.
What are S-Waves?
Normal faults helps to create this geographic feature.
What is a valley (topographic lows)?
What layers of the earth are involved in plate tectonics?
Lithosphere & Asthenosphere
This is the actual location of the earthquake, usually includes longitude/latitude coordinates and depth.
What is the hypocenter?
These waves are the last to arrive and cause the most amount of ground deformation and damage.
This image depicts what kind of fault?
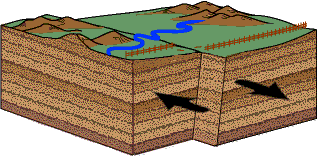
What is a right-lateral strike-slip fault?
A trench and volcanic island arc would be found at which plate boundary?
Oceanic-Oceanic Convergent Boundary
The most destructive earthquakes tend to occur along subduction zones and are referred to as this specific kind of earthquake.
What is a megathrust earthquake?
How do body waves allow us to infer that there is a liquid layer in the interior of our planet?
P and S-wave shadow zones
This type of fault leads to the thickening of continental crust and increases elevation.
What is reverse/thrust faulting?