Approximate age of planet earth
4.5 billion years
The layer of the earth where we live
Crust
The two factors that cause plate movements
Convective currents in the mantle
Gravity
One type of plate boundaries
Convergent
Divergent
Transform
It is solid, inorganic, naturally occurring, and has a definite chemical composition and crystalline structure
A mineral
Mineral group that contains only atoms of one element
Native elements
A naturally occurring solid composed of one or more minerals
A rock
..... is the type of igneous rocks high in silica mineral content
Felsic
This causes magma to melt
Change in temperature
Change in pressure
Addition of volatiles
broken down by processes of weathering
and erosion
Sediment
Scientist behind continental drift theory
Alfred Wegner
The largest mineral content of the inner core
Iron
The plate where we are right now
North American plate
A land form along convergent continental plate boundaries
mountain
plateau
The picture below is a type of mineral. True or False

Building block of sulfide minerals
Sulfide ion S2-1
Molten rock that makes it to the surface
Lava
True or false: Mafic rocks have a low Iron and magnesium content
This is an example of a volatile that causes rock melt
water
carbondioxide
The first process in the sedimentary rock formation cycle
Weathering
A mathematical equation that describes or predicts a natural phenomenon
Scientific Law
The thinnest layer of the earth
Crust
A type of plate boundary where the oceanic plate rides over the continental plate
Convergent
A feature that forms along divergent oceanic plate boundaries
Mid-ocean ridge
This is a mineral. True or false
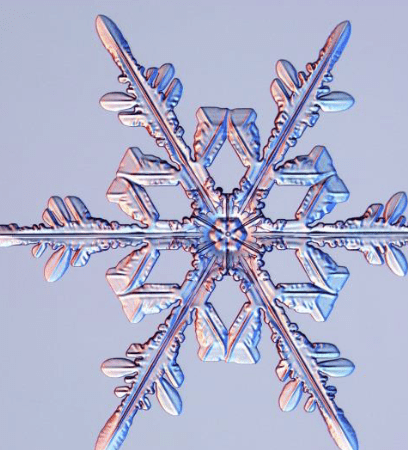

True
Pyrite with chemical formula FeS2 belongs to which mineral class
Sulfide
A rock that forms from solidification and crystallization of molten rock
An igneous rock
Ultramafic igneous rocks have a ............ melting point
high
The first minerals to melt are high in Silica
True
Frost wedging is a type of ...............weathering
Physical
The first step in the scientific method process
OBSERVE
The thickest layer of the earth
Mantle
Evidence that supports plate tectonics
Shapes of continents match or plates fit back together
Presence of similar fossils at different plates
Close match in mountain ranges
Feature A that forms along the plate boundary in the picture

Rift valley
This is a mineral

False
The building block for carbonate minerals is
Carbonate ion (CO32-)
A rock is ............ grained if the minerals can be seen by naked eyes
Coarse grained
True or false: Felsic rocks are dark in color
False
True or false: The last minerals to crystallize are ultramafic.
False
The type of weathering in the photo is called.....

Root wedging
These have passed all tests and failed none!!
Scientific theories
The mechanical layer of the earth where we live
Lithosphere
This is a ....................... boundary

Transform
It forms on the ocean side along convergent plate boundaries
Trench
Property of a mineral that causes resistance to scratch
Cuprite CU2O belongs to the ............ class of minerals
oxide
A rock that forms when magma intrudes and solidifies deep in the Earth’s crust.
Intrusive
A Pluton that runs parallel to existing structures
A sill
Decompression rock melting is common along ...........plate boundaries
Divergent
Deposition
The geologic theory that continents were once part of a supercontinent that broke apart.
Continental drift theory
The largest mineral component in the earth's crust
Oxygen
The principle that the processes we see in action on Earth today have worked in much the same way throughout the geologic past
Uniformitarianism.
One feature that is common along convergent oceanic plate boundaries
Island arc
Trench
Property of a mineral that determines the way it reflects light
Luster
Bismuth B is belongs to the .......... class of minerals
Native element
True or false: This rock is intrusive.

False
Sill or dike?

Dike
A process by which blocks of parent rock fall into and dissolve in magma.
Assimilation
The number one transporting agent of sediments
water
Human activities and natural changes are responsible for the changes in global temperature. This statement is an example of a ..........
Scientific Hypothesis
The liquid layer of the earth
Outer core
The type of plate boundary
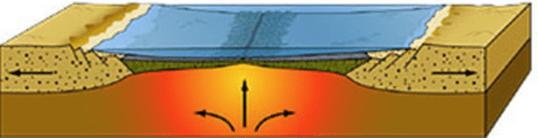
Divergent continental boundary
The hazard(s) that form along convergent continental-oceanic plate boundaries
Earth quakes
Volcanos
Color of a mineral when crushed on unglazed porcelain
Streak
Mineral specimen that have been cut, shaped and polished
Gems
Rocks that have zero or no grains at all have a ......... texture
glassy
Igneous rocks common along convergent continental-oceanic boundaries: Felsic or Mafic?
Felsic
A factor that affects magma/lava composition
Initial rock composition
Partial melting
Fractional crystallization
Assimilation and contamination
Magma mixing
The process that rounds off sediment edges as they tumble and strike one another during transportation
Abrasion
General procedure for discovering how the universe works through systematic observations and experiments.
Scientific method
The earth layer(s) that commonly melt at plate boundaries
Crust, mantle
The names of the two plates that converged to form the Himalayan mountains
Eurasian and Indian plates
This hazard doesn't occur along convergent continental-continental boundaries
Volcano
Property of a mineral in the picture

Cleavage
Sylvite with chemical formular KCl belongs to the ..... class of minerals
Halide
This rock is made of minerals including quartz, feldspar and biotite
Granite
An example of an ultramafic rock
Peridotite
Komatiite
True or false: Silica-rich magmas are thick and viscous
True
The last stage in sedimentary rock formation
Diagenesis
Lithification