This structure reflects ultrasound waves.
What is bone?
Commonly occurs after antibiotic treatments.
What is C. dif?
Longest muscle in the human body.
What is sartorius?
Most common liver disease in Canada. 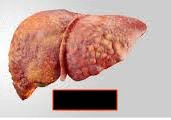
What is non-alcoholic fatty liver disease?
What is chronic bronchitis?
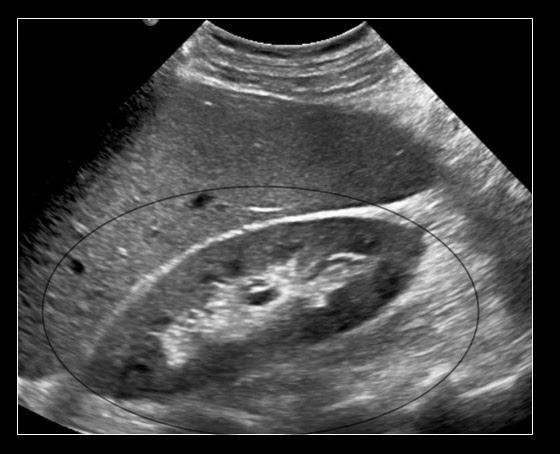
What is kidney
Common viral cause of gastroenteritis.
This is the red structure. 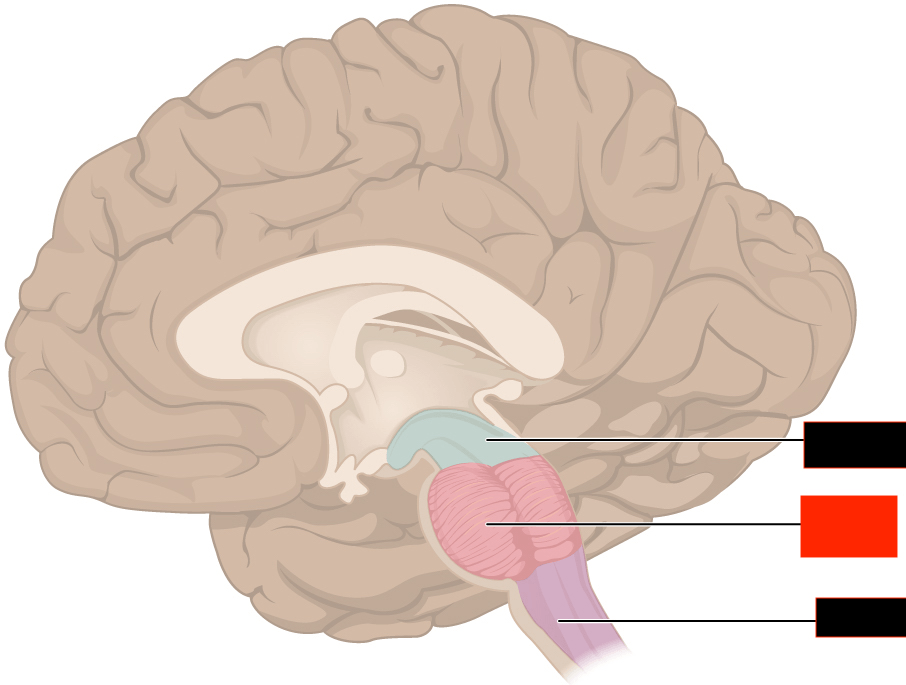
What is the pons?
This esophageal cancer is commonly associated with GERD.
What is adenocarcinoma?
LABA and a LAMA is the combination treatment for this disease.
What is COPD?
This probe is also called a convex probe.
What is a curvilinear probe?
Gram positive bacteria that commonly causes lung infections.
What is Strep Pneumoniae?
This is the 8th cranial nerve.
What is the vestibulocochlear nerve?
Presents with bronzing of the skin.
Characterized by eosinophilic inflammation.
What is asthma?
Low frequency probes are used to identify these type of structures.
What is superficial?
Organism ingested from uncooked poultry.
What is campylobacter jejuni?
This bone in the red box.
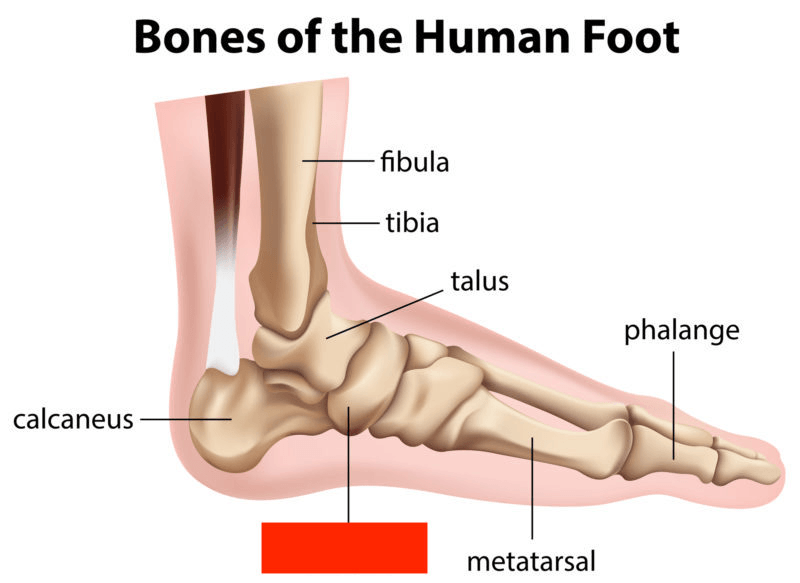
What is the cuboid?
This pathology. 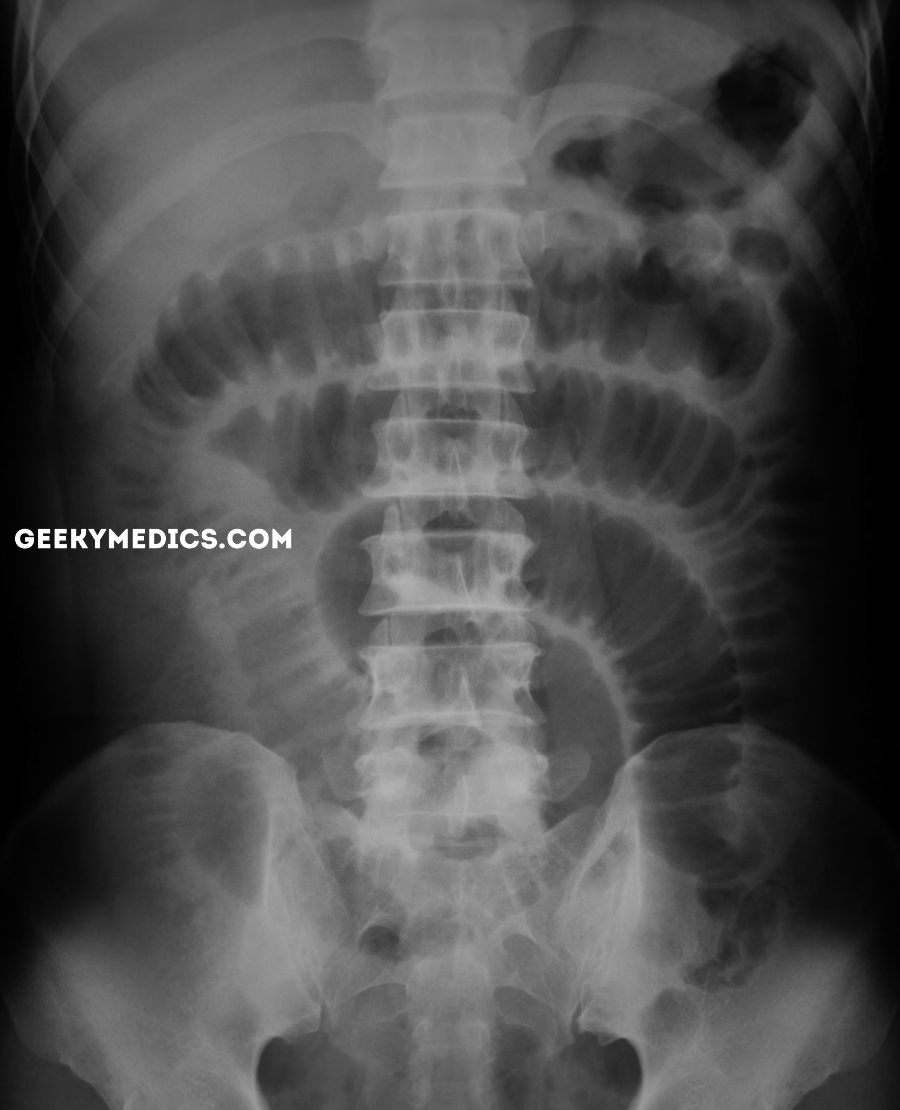
What is a small bowel obstruction?
The five causes of hypoxemia.
What is high altitude, hypoventilation, VQ mismatch, shunt, and diffusion block?
Labelled 2.
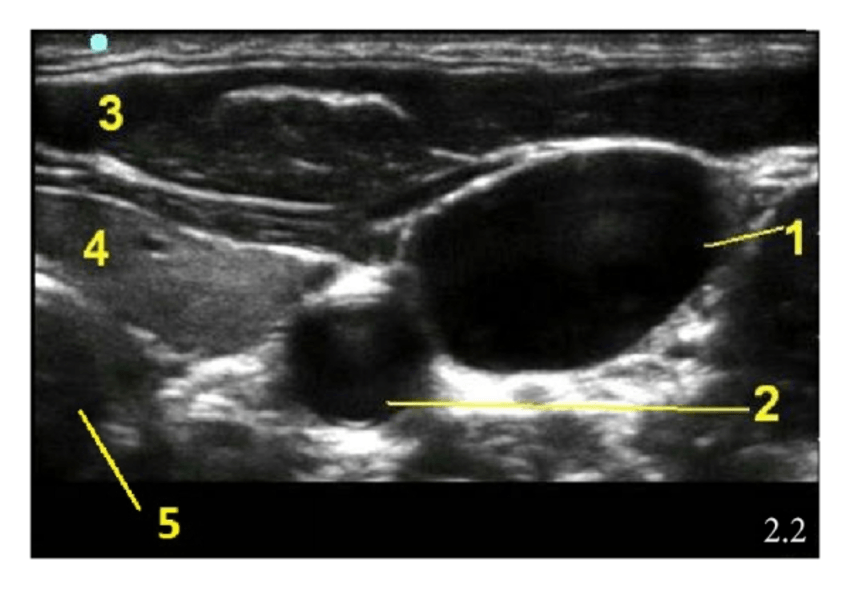
What is the common carotid artery?
Bacteria uniquely seen in HIV patients that cause pneumonia.
What is Pneumocystis jiroveci?
The trigeminal nerve is made up of these three branches.
Treatment of H.pylori requires a combination of 4 drugs.
What is a PPI, amoxicillin, clarithromycin, and metronidazole?
This pathology.
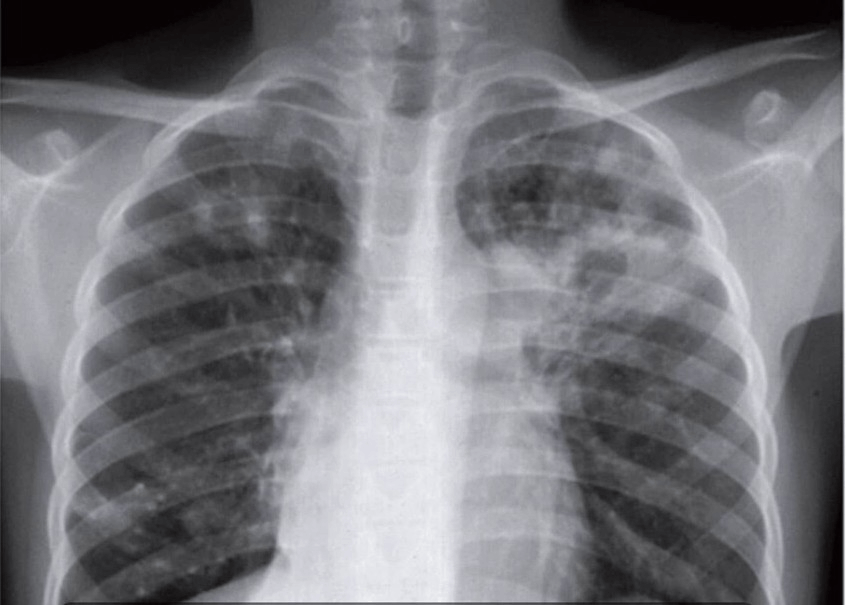
What is TB?