In what organelle does cellular respiration occur? Describe it's structure.
Mitochondria
- Double membrane → outer and inner membrane
- Porins found on the outer membrane
- Matrix → fluid filled space inside the mitochondria
Which kinds of organisms undergo cellular respiration?
All organisms!!
In what organelle does photosynthesis occur? Describe its structure.
Chloroplast
- Double membrane → outer and inner membrane
- Porins found on the outer membrane
- Thylakoids and thylakoid lumen
- Stroma
- Grana
Which kinds of organisms undergo photosynthesis?
- Plants
- Algae
- Photosynthetic bacteria / cyanobacteria
What is the chemical equation for cellular respiration?
C6H12O6 + 6O2 -> 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy (ATP)
How many net ATP are generated in glycolysis? How many ATP is generated at the end of cellular respiration (range is fine)?
Glycolysis: 2 net ATP are generated (2 were used in phase 1, and 4 were generated → 4-2 = 2)
Overall: 36-38 ATP molecules
What is the chemical equation for photosynthesis?
Light energy + 6CO2 + 6H2O -> C6H12O6 + 6O2
What role does NADPH play in photosynthesis?
NADP+ / NADPH acts as an electron carrier to bring electrons to the stroma so that the Calvin Cycle can take place
What happens in the 3 steps/phases of glycolysis? Where does glycolysis occur in the cell?
1. Priming reactions: Glucose gets phosphorylated with the help of ATP (this helps make it easier to cut glucose into 2 molecules for the next phase)
2. Cleavage: The 6 carbon molecule from phase 1 gets split/cut/cleaved into 2 molecules (G3P)
3. Oxidation and ATP Formation: Both G3P molecules get oxidized and these electrons and protons are transferred to NAD+ to make NADH. Phosphate is also taken from a sugar and added to ADP to make ATP. Pyruvate is made as a result.
Products: 2 net ATP, 2 NADH, and 2 pyruvate
What role does O2 play in the electron transport chain during cellular respiration?
It acts as an electron acceptor. When it accepts the electron, it gets converted to H2O.
Electron acceptors like O2 are necessary, since if we didn't have them, electrons could wreak havoc on the cell and cause damage
What are the general steps of photosynthesis and where do they occur in a plant cell?
Light dependent: occur in thylakoid membrane
1. Light harvesting
2. NADPH and ATP synthesis
Light independent / dark reactions: occur in the stroma
3. Carbon fixation / Calvin Cycle
What would happen to ATP and NADPH production if PSII was inhibited?
No ATP or NADPH would be made since electrons can't flow through the photosystem
What are the 3-4 general steps of cellular respiration and their location within the cell?
1. Glycolysis - cytosol
2. Pyruvate oxidation - mitochondria
3. Citric acid cycle / Krebs cycle - mitochondria
4. Oxidative phosphorylation - mitochondria
What role does NADH play in the electron transport chain?
NAD+ / NADH are electron carriers that help carry the electrons that will go through the electron transport chain to help establish the proton electrochemical gradient
Without it, no electrons would go through the electron transport chain → no ATP would be made
What are the products of the light dependent reactions? How are they used in the light independent reactions?
Light dependent reactions release ATP and NADPH that will be used to create sugar in the Calvin Cycle
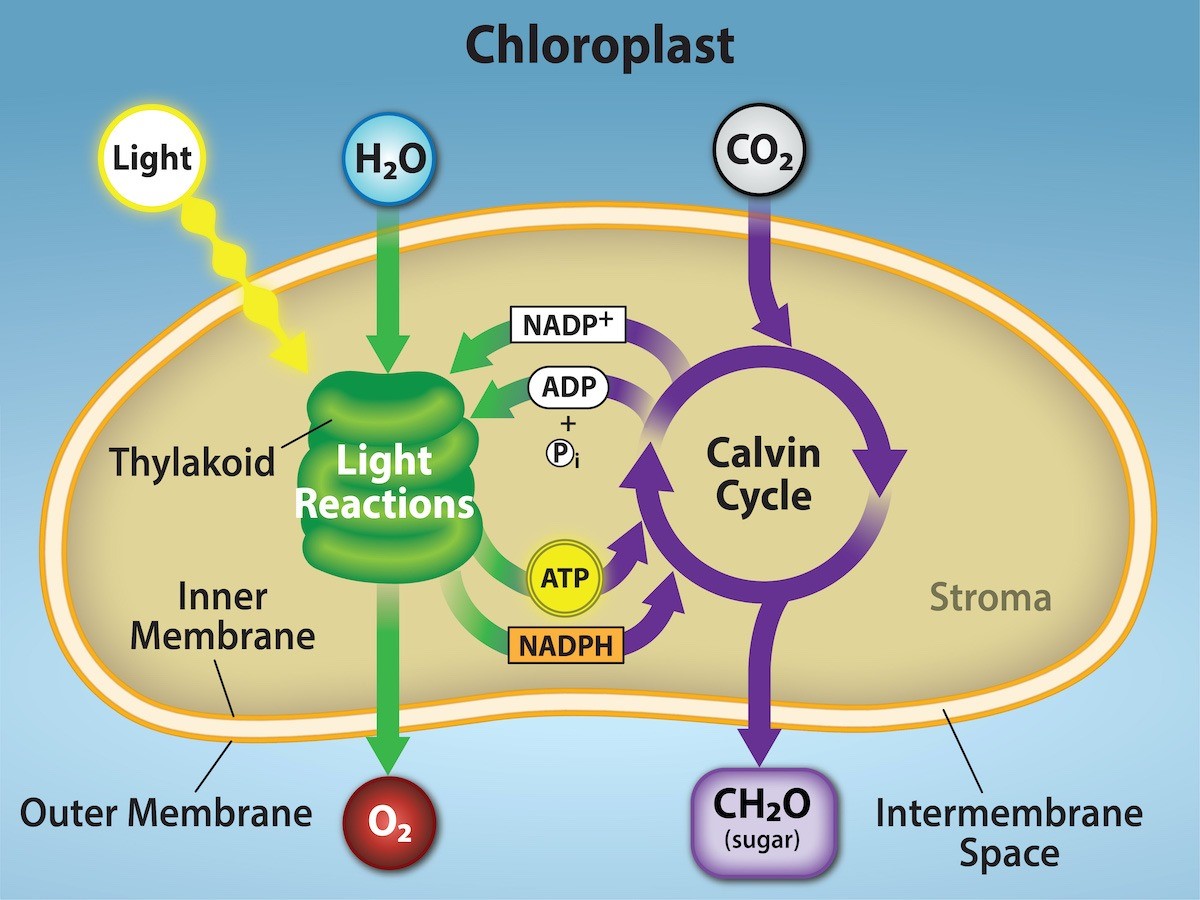
Why is CO2 important in the Calvin Cycle?
It acts as a source of carbon that can be used to make the precursors for molecules made of carbon, like glucose (C6H12O6)
Which step of cellular respiration is this diagram showing?
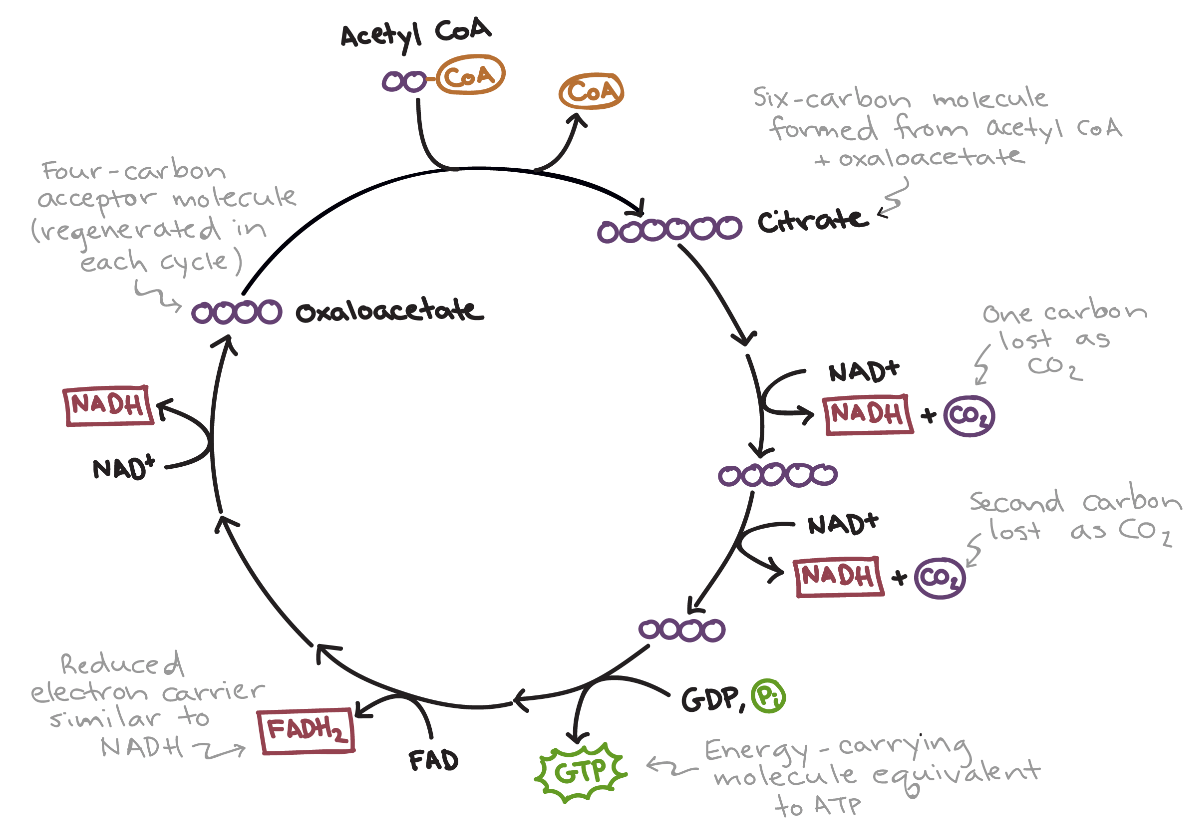
Citric Acid Cycle / Krebs Cycle
What role does the proton (H+) electrochemical gradient play in the last step of cellular respiration?
It stores the potential energy to make ATP, since molecules diffuse from from high to low concentrations, the H+ will naturally want to move down their concentration gradient (low) area through ATP synthase which helps make ATP
What is the primary electron donor in photosynthesis? Why is this electron donor needed?
H2O is the primary electron donor, and it is needed to provide electrons to the chlorophyll pigments in PSII in order to stabilize it and allow electron flow to continue.
It also provides H+ that helps establish the proton electrochemical gradient
Describe what takes place in the 3 steps of the Calvin Cycle.
1. Carbon Fixation: CO2 gets incorporated into a 5 Carbon molecule called ribulose bisphophate (RBP) through the help of Rubisco (enzyme)
2. Reduction: RBP gets reduced (electrons are added to it) through the help of NADPH (it donates its e-)
3. Regeneration: RBP gets regenerated so that the cycle can keep going, while 1 molecule leaves the cycle so that is can be turned into glucose