These are the elements found in a lipid.
What are carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen (CHO)?
What DNA stands for.
What is deoxyribonucleic acid?
This domain does not have a nucleus and is found everywhere that life exists.
What is Bacteria?
The use of DNA as a template to make a strand of mRNA.
What is transcription?
This is the type of microscope produces low-power, 3D images like the one shown:
What is a dissecting microscope?
This macromolecule provides short-term energy for cellular respiration.
What are carbohydrates?
These are the base-pair rules for DNA replication.
What is A-T and G-C
This domain includes four kingdoms.
What is Eukarya?
The ribosome is responsible for this process.
What is translation?
This microscope is found in high school biology classrooms and can view the inside of microscopic subjects.
What is a compound light microscope?
These are the monomers of a protein.
What are amino acids?
These proteins untwist and unzip DNA during DNA replication.
What are enzymes?
This kingdom includes multicellular organisms that have cell walls and chloroplasts.
What is Plantae?
This is the complementary strand of mRNA for the following strand of DNA: TAT GCA TAG.
What is AUA CGU AUC
This microscope produced the image shown:

What is a compound light microscope?
These monomers follow the A-T, C-G base-pair rules.
What are nucleotides?
These segments of DNA code for individual proteins.
What are genes?
This kingdom is considered a "grab bag" and can have traits from all of the other Eukaryotic kingdoms.
What is Protista?
A change in DNA that does not result in a misshapen protein.
What is a silent mutation?
This microscope is the highest powered microscope and creates a 2D image of the inside of a subject.
What is a transmission electron microscope (TEM)?
DNA mutations affect these macromolecules by changing their shape.
What are proteins?
This is the complementary strand of DNA with bases TAA GCG AGT.
What is ATT CGC TCA?
This trait sets the salmon apart from the other organisms on this cladogram:

What are lungs?
This is the amino acid coded for by the following mRNA codon: GAC
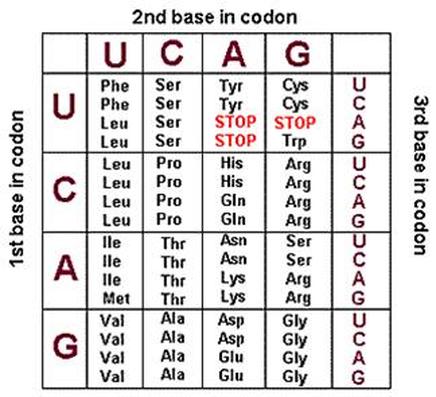
What is Asp?
This microscope created the following image:

What is a scanning electron microscope (SEM)?