Name the outcome that a 12-lead ECG provides.
What is shows 12 different views of the heart's electrical activity?
Name the method used for arrhythmia interpretation.
What is the six-step process?
Name the force the left ventricle must generate during a contraction to eject blood into the aorta through the aortic valve.
What is afterload?
This condition is the major cause of right-sided heart failure.
What is left-sided heart failure?
List the earliest symptoms of chronic heart failure.
What are fatigue and weakness?
Name the outcome that an 18-lead ECG provides.
What is shows 18 different views of the heart's electrical activity?
Do this to determine the regularity of a rhythm.
What is the count of the number of small squares between each R wave and/or use a caliper to measure the R-to-R spacing?
Name this medical condition that is a major cause of left-sided heart failure.
What is hypertension?
Name this condition when the right ventricle hypertrophies or fails from disorders of the lung.
What is cor pulmonale?
Name this breathing pattern of shallow respiration that builds to deep breaths followed by a period of apnea.
What is Cheyne-Stokes respirations?
Name the phenomenon represented by the P wave of the cardiac cycle.
What is representing atrial depolarization?
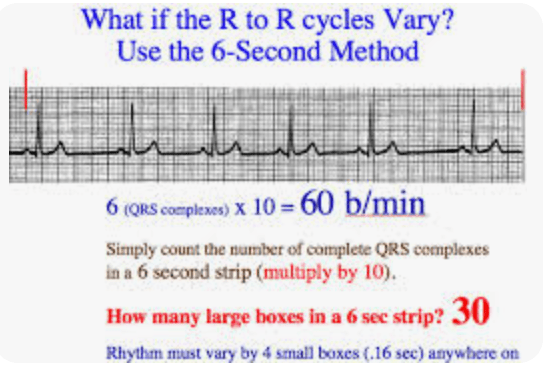
Explain the 6-second method that is used for irregular rhythms, which may also be used to estimate a rapid regular rhythm.
What is count the number of R waves with a 6-second strip?
Name this pressure that influences the force needed to open the aortic valve to pump blood into the aorta.
What is peripheral vascular resistance?
Name the condition when the liver becomes congested.
What is hepatomegaly?
Name this condition that many heart failure patients have due to hemodilution from fluid overload and decreased angiotensin-converting enzyme action, along with reduced ACE action that decreases erythropoietin release, resulting in decreased production of RBCs.
What is anemia?
Name the time represented that it takes for the electrical impulse to travel from the SA node to the AV node.
What is the PR interval?
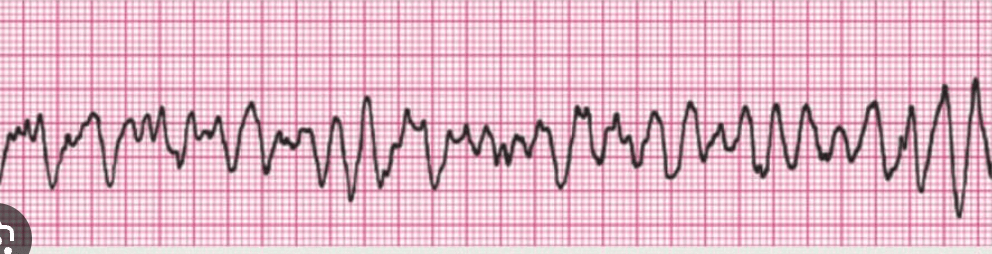
Name this dangerous, life-threatening ventricular rhythm that occurs when many ectopic ventricular foci fire at the same time and are chaotic, with no discernible waves, and the ventricle quivers.
What is ventricular fibrillation?
This is the first location where blood backs up due to left-sided heart failure.
What is the left ventricle into the left atrium?
Name the medical condition when resistance increases from elevated pressure due to the primary effect on the right ventricular workload of the heart.
What is pulmonary hypertension?
List three priority chronic heart failure nursing diagnoses.
What are impaired gas exchange, decreased cardiac output, and excess fluid volume?
Name the outcome that the QRS complex represents.
What is ventricular depolarization?
Name the condition - the silent heart.
What is asystole?
Explain why alveolar edema is serious.
What is reduces gas exchange across the alveolar-capillary membrane, resulting in shortness of breath and cyanosis from decreased oxygenation of the blood?
Name the condition in which systemic venous congestion also leads to splenic distension.
What is splenomegaly?
What is B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP)?