A provider orders 500 mg of a drug PO. If the pharmacy sends 250 mg tablets, this is the number of tablets you will administer.
What is 2 tablets?
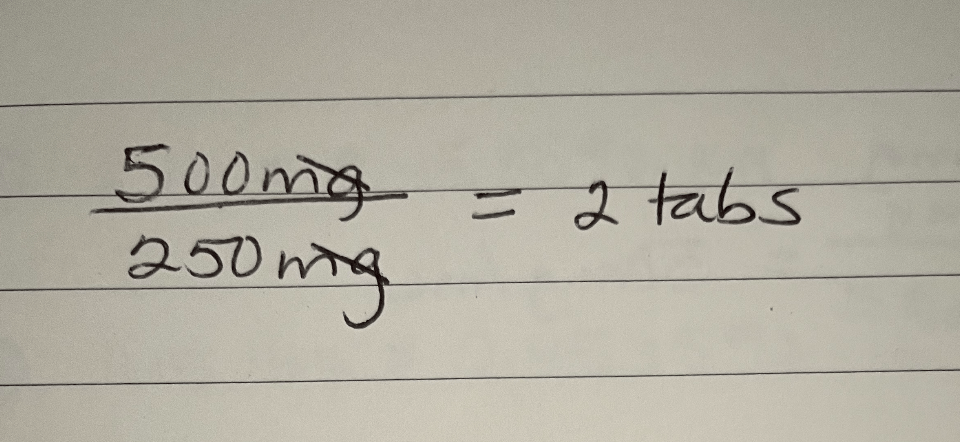
This term describes the mechanical act of moving air in and out of the lungs.
What is ventilation?
This mnemonic stands for Where, How, Aggravating/Alleviating, Timing, Severity, Useful data, and Perception.
What is WHAT’S UP?
This device is used post-operatively to promote deep breathing and prevent atelectasis.
What is an incentive spirometer?
This is the highest priority action for a nurse whose patient suddenly becomes cyanotic while on a nasal cannula.
What is check the oxygen tubing connection?
To convert 3 fluid ounces to the metric system, the nurse calculates this many milliliters (mL).
What is 90 mL?
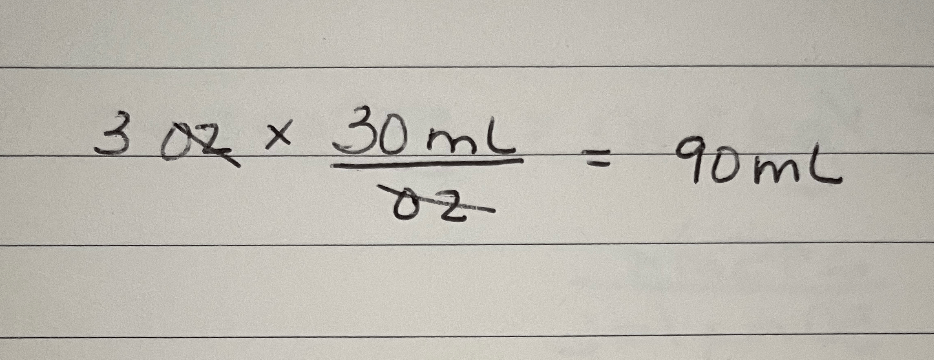
This waste product is the most important chemical regulator of the respiratory rate.
What is carbon dioxide (CO₂)?
This is the first step a nurse should take if they hear an adventitious breath sound in only one lung lobe.
What is ask the patient to cough and then listen again?
To thin thick secretions for easier expectoration, the nurse should encourage the patient to increase this.
What is fluid intake (hydration)?
After a bronchoscopy, the nurse must confirm this has returned before allowing the patient to drink water.
What is the gag reflex?
This is the standard rounding rule for a calculated dose of 1.028 mL when asked to record to one decimal place.
What is 1.0 mL?
This process involves the exchange of gases between the alveoli and the blood.
What is external respiration?
When assessing a patient in acute respiratory distress, the nurse should defer a full history and perform this type of rapid assessment instead.
What is a focused assessment?
This position involves the patient sitting at the edge of the bed and leaning over a bedside table to facilitate easier breathing.
What is the tripod (or orthopneic) position?
Following a lung biopsy, the nurse should place the patient in this specific position to help prevent bleeding and ensure stability at the biopsy site.
What is the side-lying position on the affected side?
An IV is set to run at 125 mL/hr. If the drop factor is 15 gtt/mL, this is the flow rate in drops per minute (gtt/min).
What is 31 gtts/min?
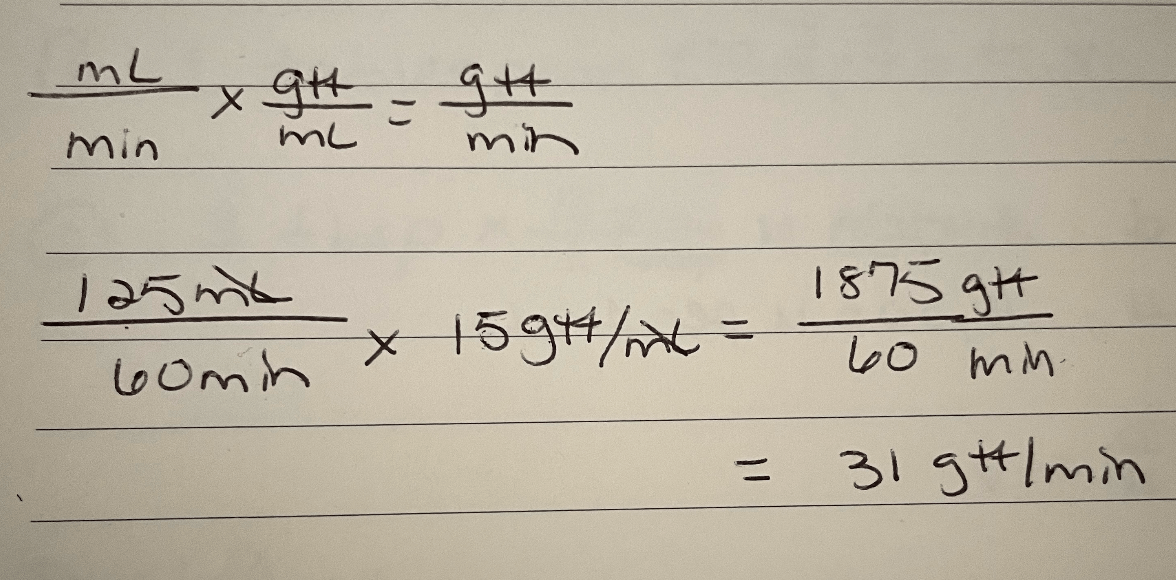
This describes the air remaining in the lungs after a normal, passive expiration.
What is functional residual capacity?
This objective finding, often noted in the fingernails, indicates long-term chronic hypoxia.
What is clubbing?
Prior to suctioning a patient with a tracheostomy, the nurse should perform this action to prevent hypoxia.
What is hyperoxygenate the patient with 100% oxygen?
For a patient with COPD, the nurse knows that an oxygen saturation of 88%–92% is acceptable because a higher level may suppress this.
What is the respiratory drive?
A patient weighing 198 lbs is ordered 15 mg/kg/day divided every 12 hours. This is the mg dose per administration.
What is 675 mg?
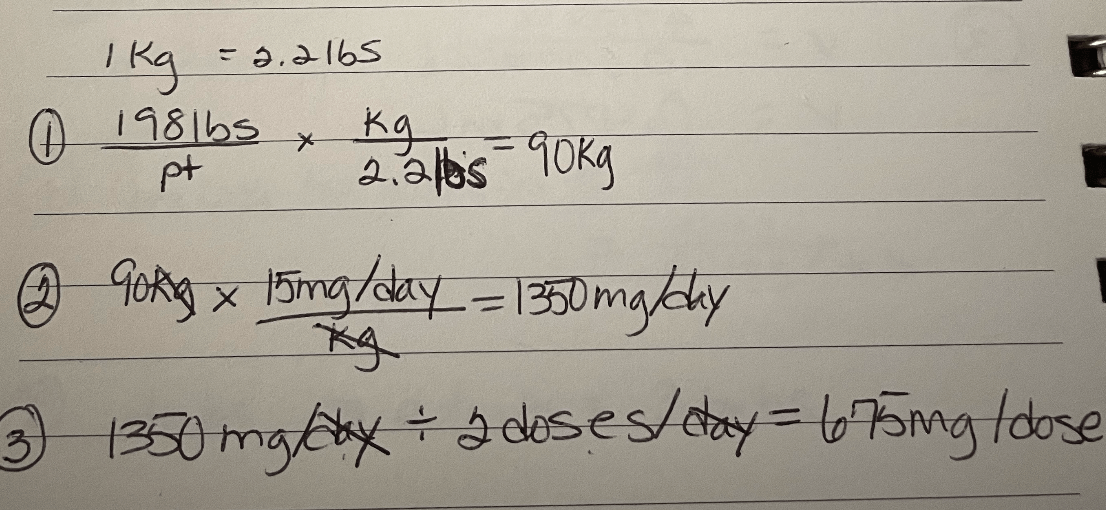
These hair-like structures in the lower respiratory tract are paralyzed by smoking, impairing the lungs' defense mechanisms.
What are cilia?
A nurse finds a patient has "Kussmaul's" respirations; they would expect to see this specific breathing pattern.
What are deep and rapid respirations?
When caring for a patient with a chest tube, the nurse notes continuous bubbling in this specific chamber, indicating a possible air leak.
What is the water seal chamber?
Following a thoracentesis, the nurse must immediately report this finding, which could indicate a pneumothorax.
What is tracheal deviation?