This is the most reliable indicator of fluid status.
What is daily weights?
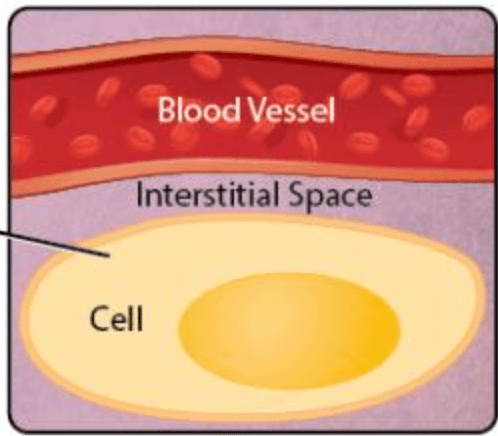
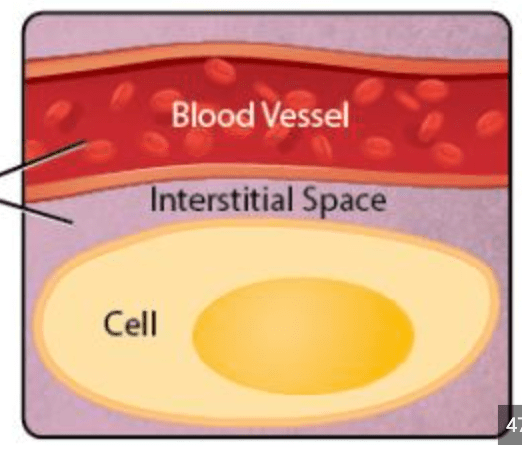
This fluid is inside the cells.
What is intracellular fluid?
Calculate:
The drip rate for 1000 mL of fluid to infuse over 8 hours using a drop factor of 20 gtts/mL.
What is?
1000 mL / 8 hr X 1 hr / 60 min X 20 gtts / min = 41.6 gtts/mL = 42gtts/min
- Convert hours to minutes: 8 hours × 60 minutes/hour = 480 minutes.
- Divide total volume by total time: 1000 mL ÷ 480 minutes ≈ 2.08 mL/min.
- Multiply by the drop factor: 2.08 mL/min × 20 gtts/mL = 41.6 gtts/min.
- Round to the nearest whole number: 42 gtts/min.
Figure: pH 7.25, PaCO2 55, HC03 25.
What is respiratory acidosis uncompensated?
Step 1 – pH 7.25 is Acidic
Step 2 – match PaCO2 with partner, PaCO2 is 55 = Acidic
Our HCO3 25 is WNL
Step 3 – Compensated or Uncompensated? No balance was found, so it’s Uncompensated
These are the specific actions a nurse takes to help a patient achieve their care goals.
What are nursing interventions?
Name this alternative option for the administration of medication or fluids subcutaneously.
What is hypodermoclysis?
This fluid is outside the cells.
What is extracellular fluid?
Calculate:
The drip rate for 1500 mL of Lactated Ringer's over 12 hours using a drop factor of 15 gtt/mL.
What is?
1500 mL / 12 hr X 1 hr / 60 min X 15 gtts / min = 31.3 gtts/mL = 31gtts/min
- Convert hours to minutes: 12 hours × 60 minutes/hour = 720 minutes.
- Divide total volume by total time: 1500 mL ÷ 720 minutes ≈ 2.08 mL/min.
- Multiply by the drop factor: 2.08 mL/min × 15 gtts/mL = 31.2 gtts/min.
- Round to the nearest whole number: 31 gtts/min.
Figure: pH 7.57, PaCO2 25, HCO3 22.
What is respiratory alkalosis uncompensated?
Step 1 – pH 7.57 is Base
Step 2 – match PaCO2 with partner, PaCO2 is 25 = Base
Our HCO3 22 is WNL
Step 3 – Compensated or Uncompensated? No balance was found, so it’s Uncompensated
List four primary nursing interventions for patients with a fluid overload diagnosis.
What are monitor positioning, oxygen therapy, drug therapy, and diet therapy?
Name the condition that may develop when a patient is receiving a hypertonic solution and develops an elevated blood pressure.
What is circulatory overload?
The primary control of water in the body is through pressure sensors in the vascular system that stimulate or inhibit the release of the is hormone.
What is antidiuretic hormone (ADH)?
Calculate:
The drip rate for 300 mL of Ampicillin Sodium 500 mg to infuse over 40 minutes using a drop factor of 20 gtt/mL.
What is?
300 mL / 40 min X 20 gtts / min = 31.3 gtts/mL = 150 gtts/min
- Multiply volume by drop factor: 300 mL x 20 gtts = 6000 gtts
- Divide total volume by total time: 6000 gtts ÷ 40 minutes = 150 gtts/min.
Figure: pH 7.21, PaCO2 39, HCO3 19.
What is metabolic acidosis uncompensated?
Step 1 – pH 7.21 is Acid
Step 2 – match PaCO2 with partner, PaCO2 is 39 = WNL
Our HCO3 19 = Acid
Step 3 – Compensated or Uncompensated? No balance was found, so it’s Uncompensated
List the primary nursing interventions for patients with a dehydration diagnosis.
What are assessing fluid status, preventing further loss, and restoring hydration through oral or intravenous means per provider orders?
These solutions can worsen hypertension because they leave the intravascular space and enter cells, causing cardiovascular collapse and increasing intracranial pressure
What are the hypotonic solutions?
Examples: 0.45% NS, 0.25% NS, D5W
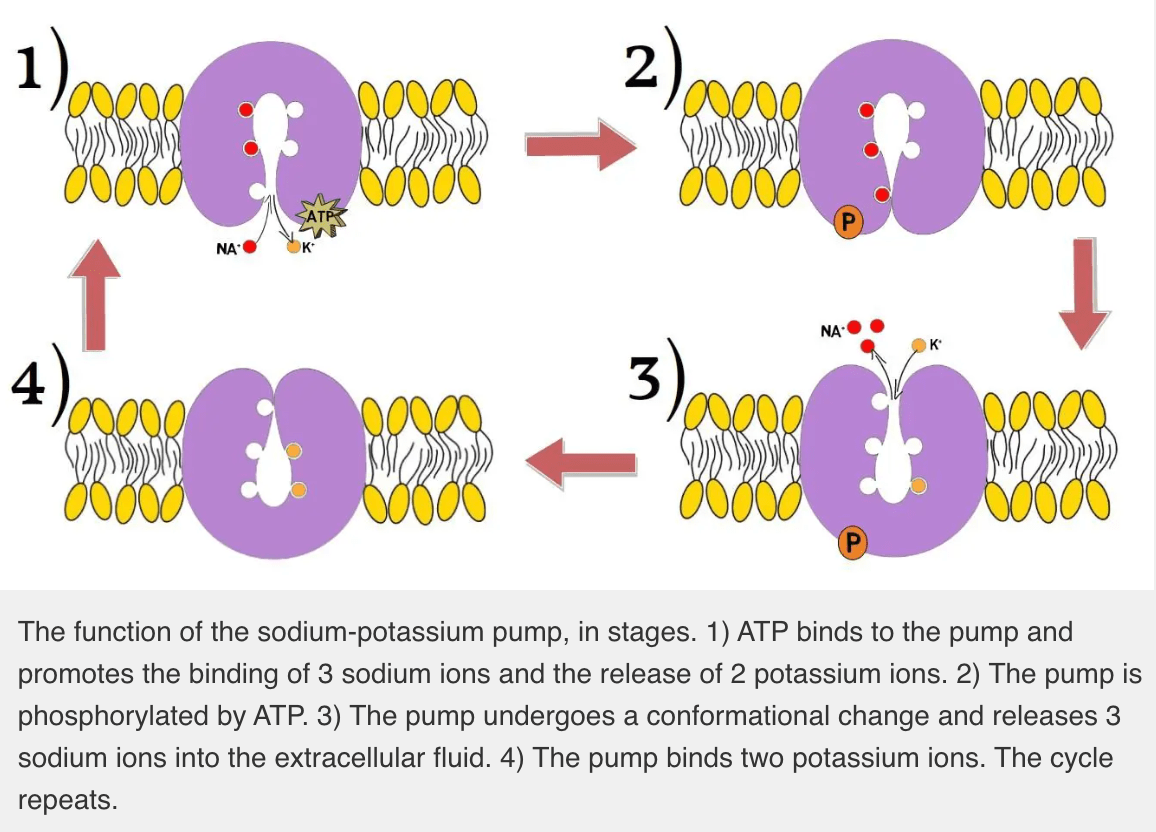
Name this critical pump vital for maintaining homeostasis by regulating two essential ions inside and outside of the cells.
What is the sodium-potassium pump (aka Na+/K+ ATPase)?
Calculate:
The drip rate for 650 mL of D5W to infuse over 6 hours using a drop factor of 10 gtt/mL.
What is?
650 mL / 6 hr X 1 hr / 60 min X 10 gtts / min = 18.1 gtts/mL = 18 gtts/min
- Convert hours to minutes: 6 hours × 60 minutes/hour = 360 minutes.
- Divide total volume by total time: 650 mL ÷ 360 minutes ≈ 1.81 mL/min.
- Multiply by the drop factor: 1.81 mL/min × 10 gtts/mL = 18.1 gtts/min.
- Round to the nearest whole number: 18 gtts/min.
Figure: pH 7.48, PaCO2 36, HCO3 28.
What is metabolic alkalosis uncompensated?
Step 1 – pH 7.48 is Base
Step 2 – match PaCO2 with partner, PaCO2 is 36 = WNL
Our HCO3 28 = Base
Step 3 – Compensated or Uncompensated? No balance was found, so it’s Uncompensated
List the nursing actions needed for hypercalcemia.
What are rehydration, promoting calcium excretion, ensuring patient safety, and addressing the underlying cause?
The dynamic steady state that the body strives to achieve every day.
What is homeostasis?
Filtration is promoted by this type of movement between areas in the body?
What is hydrostatic pressure?
Calculate:
The drip rate for 500 mL of D5 1/2 Normal Saline with 10 meq of potassium chloride to infuse over 5 hours using a drop factor of 10 gtt/mL.
What is?
500 mL / 5 hr X 1 hr / 60 min x 10 gtts /min = 17 gtts/min
- Convert hours to minutes: 5 hours × 60 minutes/hour = 300 minutes.
- Divide total volume by total time: 500 mL ÷ 300 minutes ≈ 1.67 mL/min.
- Multiply by the drop factor: 1.67 mL/min × 10 gtts/mL = 16.7 gtts/min.
- Round to the nearest whole number: 17 gtts/min.
Figure: pH 7.45, PaCO2 46, HCO3 27.
What is respiratory acidosis compensated?
Step 1 – pH 7.45 is WNL
Step 2 – match PaCO2 with partner, PaCO2 is 46 = Acidic
Our HCO3 27 = Base
Step 3 – Compensated or Uncompensated? Balance was found, so it’s compensated
List the primary nursing interventions for clients with hypomagnesia.
What are correcting the magnesium deficit, monitoring for dangerous complications, ensuring patient safety, and addressing the underlying cause?