Pneumonia is a clinical diagnosis based on the presence of these three classic findings.
What is a fever, respiratory symptoms, and/or abnormal lung sounds?
This antibiotic class is listed as first-line therapy for outpatient CAP by the 2007 IDSA/ATS guidelines.
What are macrolides (e.g., azithromycin)?
This is the most common bacterial species associated with atypical pneumonia, often treated with macrolides.
What is Mycoplasma pneumoniae?
The two scoring systems recommended for use with clinical judgment to determine patient disposition for CAP.
What are the CURB-65 Score and the Pneumonia Severity Index (PSI)?
A major risk factor for aspiration pneumonia and lung abscess that increases the bacterial load of aspirated substances.
What is poor oral hygiene?
The two pneumonia mimics most critical for an emergency medicine resident to identify and treat in the ED.
What are Congestive Heart Failure and Pulmonary Embolism?
This is the most common atypical symptom in elderly patients with CAP, occurring in over 50% of cases.
What is confusion or altered mental status?
The IDSA/ATS guidelines recommend considering alternatives if S. pneumoniae resistance exceeds this fraction.
What is one-quarter (or 25%)?
This is the first-line imaging modality for suspected CAP in patients ≥65 or those with abnormal vital signs.
What is Chest X-ray (CXR)?
A CURB-65 score of 2 or greater typically favors this patient disposition.
What is Admission?
6yo F with cough and fever. Your interpretation?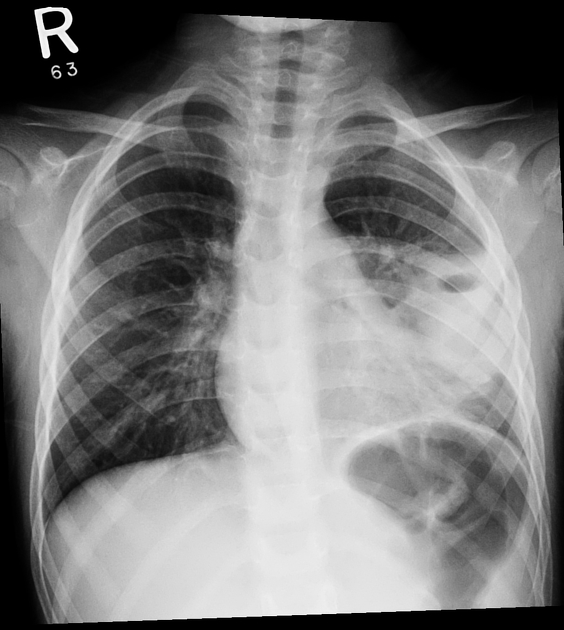
What is a left lower lobe infiltrates associated with cavitary lesion with an air-fluid level or lung abscess?
This single vital sign finding has the highest positive likelihood ratio (3.47) for CAP from a 2019 meta-analysis.
Respiratory Rate >20
*RR > 20 has the highest positive likelihood ratio (3.47) for CAP from the 2019 meta-analysis.
- Fever ≥38°C had a positive LR of 3.21
- HR>100 had a positive LR of 2.79
Name the three most common typical bacteria causing CAP.
What are S. pneumoniae, H. influenzae and M. catarrhalis?
This pair of bacteria are cited as the two main Typical Pathogens for CAP.
What are S. pneumoniae and H. influenzae?
HIV+ Male with cough and SOB. Diagnosis?
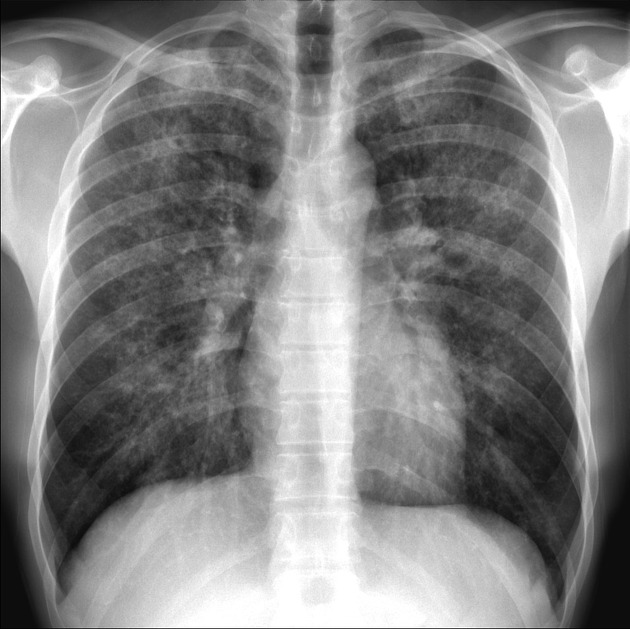
What is Pneumocystis pneumonia or Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia?
This scoring system is superior to the old HCAP criteria in sensitivity, specificity, and both predictive values for predicting risk of MDR organisms.
What is the DRIP Score (Drug Resistance in Pneumonia Score)?
A lung abscess that is a result of hematogenous spread or pre-existing lung disease, which has a higher mortality, is referred to as this type.
What is a secondary lung abscess?
The required minimum oxygen saturation on room air for a patient with a PSI score >70 to be considered suitable for outpatient discharge from the ED.
O2 sat > 92%
The overgrowth of normal pulmonary flora is thought to be triggered by environmental disruptions, most commonly this type of illness.
What is a viral illness?
82 yo F with fatigue and AMS? Your interpretation?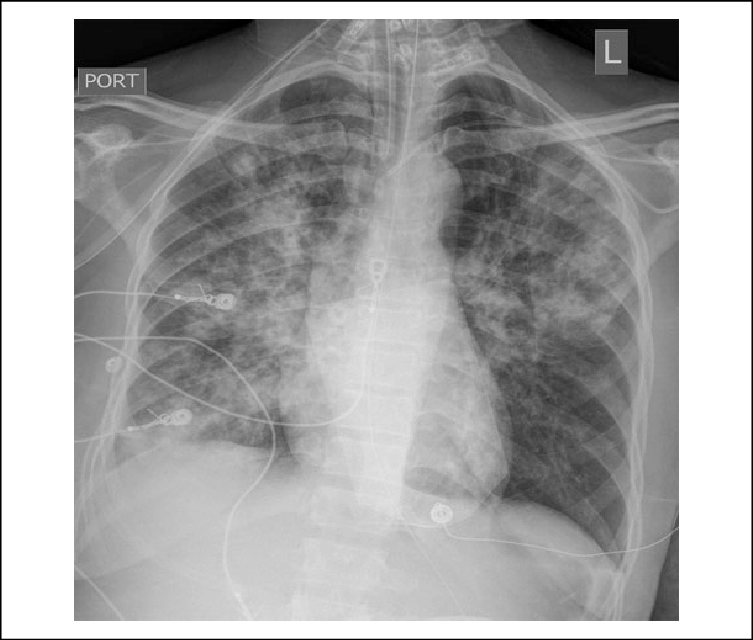
What is bilateral pulmonary infiltrates with more confluent opacity in the right lung, consistent w/ multilobar pneumonia?
The treatment for pneumonitis should primarily focus on this, as prophylactic antibiotics are generally not effective.
What is supportive care (thorough suctioning and respiratory support)?
A patient with CAP and a Pneumonia Severity Index of 135 points would be categorized as this risk level and disposition.
CT is recommended for critically ill patients with respiratory symptoms or a negative CXR, particularly since pneumonia is the most common cause of this life-threatening syndrome.
What is sepsis (or septic shock)?
The fluid of choice for septic shock patients with CAP, based on the SALT-ED and SMART trials.
What is Ringer’s Lactate?
The percentage of patients who have infiltrates on a CT who will have a negative CXR, demonstrating that a negative film does not rule out CAP.
What is within 30%?
The goal for giving appropriate antibiotics is preferably within this timeframe, expressed in hours, once bacterial infection is identified.
What is 4 hours?
The specific antibiotic that can be added to the regimen for community-acquired aspiration pneumonia if high suspicion for anaerobes exists.
What is Clindamycin?
The three or more criteria a patient must meet from the 9 specified list to warrant ICU admission even without intubation or septic shock.
What are confusion, multilobar infiltrates, hypothermia, tachypnea, hypotension requiring aggressive IV fluid resuscitation, PaO2:FiO2 ratio ≤250, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, or uremia?
In a supine patient who aspirates, infiltrates are typically found in these two specific lung segments.
What is the superior lower lobes and/or posterior upper lobes?
The expert consensus for the duration of time that must pass without subjective patient improvement to define treatment failure for CAP.
What is 72 hours?