One liter of water weighs ______ kg.
What is 1 kg?
FAHN 9th ed. Ch. 18 p. 492
One lb. water weighs 2.2 lbs., or 1 kg.
1 kg = 2.2 lbs.
*** So, when the patient is upset about having to be awakened for their daily weight, it is important because it is really a measurement of fluid balance. Each addition or subtraction of a kg in weight represents liter(s) of water.
This is the normal range for sodium.
This is the normal range for potassium (K+).
What is 3.5 - 5.0 mEq/L ?
This is the normal range for magnesium (Mg++).
See SCC School of Nursing Lab Values sheet.
This is the normal range for Calcium (Ca++).
What is 9.0 - 10.5 mEq/L?
See SCC School of Nursing Lab Values sheet.
If the client's Na+ is high, would you encourage the client to drink water or would you put them on a fluid restriction?
What is the nurse would encourage them to drink water?
This is necessary because sodium and water are best friends. Where one goes, the other goes- just like teenage girls to a bathroom.
In order to bring the sodium level down, the patient should dilute it by drinking water if possible or either via IV hydration. The nurse should carefully monitor the Na+ values and watch the patient for signs and symptoms of hyper and hyponatremia.
This passive transport process involves the diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane in the presence of at least one impermeable solute.
*An example of this is when water molecules diffuse into and out of cells, through the cellular selectively permeable membrane, correcting imbalances in water concentration.
What is osmosis?
FAHN 9th ed. Ch. 18 p. 492-494
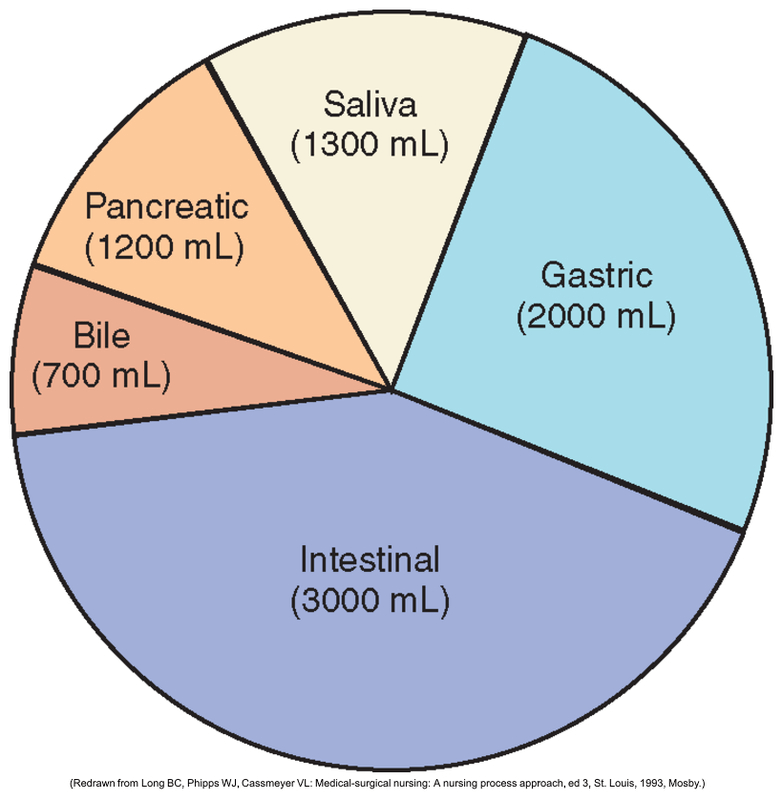
Your body produces internal secretions every day. During a 24 hour day, more than ________ liters of sodium containing fluids are produced.
What is 8 liters?
If the potassium level is high or low, the nurse should monitor for _______ side effects as a priority.
What are cardiac side effects?
FAHN 9th ed. Ch. 18 p. 496-497
Always think HEART with potassium imbalances!
Hypomagnesemia is often seen in patients with _____________.
What is alcoholism?
FAHN 9th ed. Ch. 18 p. 501
Patients who are truly alcoholics will choose drinking alcohol over eating food every time, if that is the choice they are faced with making. Once the alcoholism takes over their body, they are often malnourished at the expense of feeding their unquenchable need for alcohol. Hypomagnesemia goes hand in hand with chronic malnourishment/ under-nourishment.
This sign of hypocalcemia is elicited by inflating a BP cuff to induce a carpal spasm.
What is Trousseau's sign?
FAHN 9th ed. Ch. 18 p. 500
To rapidly correct a hypocalcemic state, the LPN should anticipate the RN to administer intravenous ________ _________.
What is IV calcium gluconate?
FAHN 9th ed. Ch. 18 p. 499
This is the body's state of balance; what the body tries to self-correct into to achieve.
What is homeostasis?
FAHN 9th ed. Ch. 18 p. 491

1. Is Sodium an intracellular or an extracellular ion?
2. The primary excretion route for Sodium is/are the __________.
1. What is an extracellular ion?
2. What are the kidneys?
Name three foods rich in potassium.
FAHN 9th ed. Ch. 18 Box 18.3 p. 496
What are: (any 3)
1. Apricots
2. Bananas
3. Cantaloupe
4. Dried fruits
5. Grapefruit
6. Honeydew melon
7. Broccoli
8. Cabbage
9. Tomatoes
10. Potatoes (especially skins)
11. Spinach
12. Beef
13. Chicken
14. Oranges/ Orange juice
The majority of magnesium is found stored in the ___________.
What are the bones?
FAHN 9th ed. Ch. 18 p. 500
This sign of hypocalcemia is the contraction of facial muscles which is elicited when the nurse taps over the facial nerve in front of the ear (cheek).
What is Chvostek's sign?
CHvostek = CHeek tapping
FAHN 9th ed. Ch. 18 p. 500
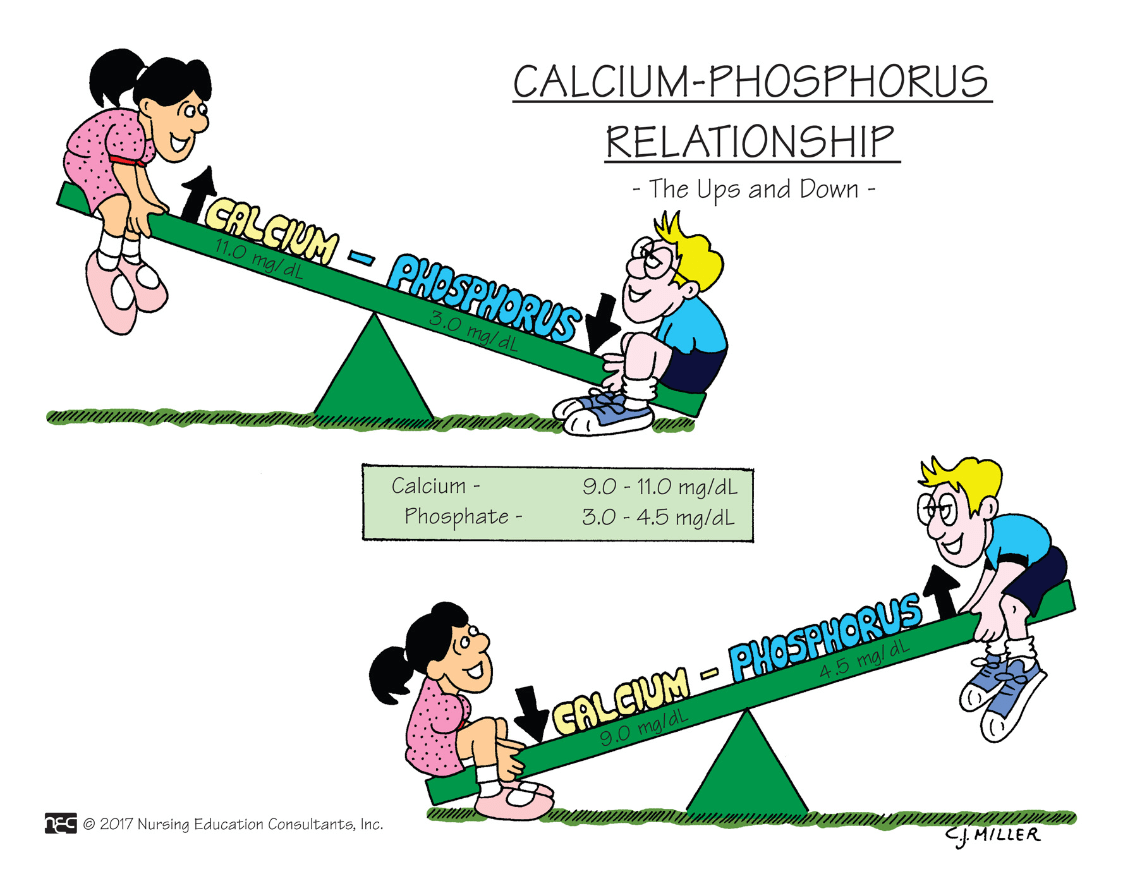
Calcium is in an inverse relationship with ________. What this means is that when one value is up, the other is down.
What is phosphorus?
The minimum urine output (UOP) should be ______ per hour.
What is 30 mL per hour?
FAHN 9th ed. Ch. 18 p. 492
Give two signs of hyponatremia.
Review Box 18.1 p. 495 FAHN 9th ed.
What are: (any 2)
1. Abdominal cramps
2. Apathy/ Apprehension
3. *SEIZURES*
4. Fatigue
5. Headache
6. Irritability
7. Muscle weakness, twitching, tremors
8. N/V
9. Postural hypotension
List two conditions that can cause hypokalemia.
FAHN 9th ed. Ch. 18 pp. 496-7
What are: (any 2)
1. Decreased K+ intake
2. GI losses (vomiting, diarrhea, suctioning)
3. Loss from cells (burns, trauma, fistulas)
4. Ileostomy
5. Conditions causing large urine output
True or False?
The kidneys conserve magnesium.
TRUE!
FAHN 9th ed. Ch. 18 p. 501
The kidneys conserve magnesium. They conserve it so much, they do it at the expense of potassium. So, if you see any elevated electrolyte value, always check all values, to make sure one isn't high while another one is lowered.
If not otherwise contraindicated, the patient with hypercalcemia should drink _______ liters of water per day, to prevent the formation of renal stones.
What is 3 to 4 liters of water per day?
FAHN 9th ed. Ch. 18 Box 18.7
Though the kidneys filter the blood at a rate of 125 mL/ minute, the body only typically produces _________ liters of urine per day.
What is 1-2 liters of urine per day?
FAHN 9th ed. Ch. 18 p. 491-2
This type of solution expands the body's fluid volume without causing a fluid shift from one compartment to another.
What is an isotonic solution?
FAHN 9th ed. Ch. 18 p. 494
Give two nursing interventions for hypernatremia.
See Box 18.2 FAHN 9th ed. p. 496
What are: (any 2)
1. Decrease sodium intake in the patient's diet (take the salt shaker out of the room- even the hidden one in the bedside table!)
2. Monitor V/S, especially BP, pulse, and RR
3. Monitor I & O
4. Monitor Serum Sodium level
5. Monitor water loss from fever/ infection *insensible losses count*
6. Provide a safe environment for a confused or agitated patient
7. Weigh the patient daily (looking for fluid loss)
The antidote for hyperkalemia is ___________.
What is sodium polystyrene (Kayexalate)?
This can be given orally or as an enema.
FAHN 9th ed. Ch. 18 Box 18.5 p. 498
Pregnant patients may lose deep tendon reflexes if their magnesium level is _________.
Choose one:
greatly elevated
or
greatly depleted
What is (greatly) elevated?
In hypermagnesemic states, the loss of deep tendon reflexes, often from excessive magnesium administration, can severely restrict nerve & muscle activity. This is a dangerous state because respiratory depression and cardiac arrest can follow. Patients may need emergent dialysis to remove the excess magnesium.
FAHN 9th ed. Ch. 18 p. 501
The most life-threatening symptom of hypocalcemia is __________.
FAHN 9th ed. Ch. 18 Box 18.6 p. 499
List 4 functions of water in the body.
What are: (any 4)
1. carries nutrients to cells and waste products away
2. provides a medium for chemical reactions (metabolism)
3. tissue lubricant
4. maintains acid-base balance
5. assists in heat regulation via evaporation