This static wrist–hand–finger orthosis immobilizes the wrist, fingers, and thumb in neutral to slight wrist extension with MCP flexion of 70–90 degrees and full IP extension, a position chosen to maintain collateral ligament length, reduce future capsular contracture, and allow functional opposition and three-jaw chuck pinch.
What is a resting hand splint?
In preparation for the residual limb to accept a prosthesis, which of the following is the ideal shape of the residual limb following a transtibial amputation?
Cylindrical
Bonus: Transfemoral - Conical
This partial foot amputation removes all tarsal and metatarsal bones, leaving only the talus and calcaneus intact.
What is a Chopart amputation?
A 53 year-old male with a history of diabetes and hypertension develops sudden-onset severe foot pain. He denies trauma. On exam you notice swelling of the great toe. Synovial fluid analysis reveals crystal deposition with a negative birefringence pattern. What is the most appropriate initial treatment?
Indomethacin
A patient with sickle cell disease who has experienced chronic episodic left hip/groin pain will most likely suffer from which pathology later in his life?
Hip avascular necrosis
Which of the following is the most common cause of upper extremity amputation?
Trauma
What amputee K levels describes a patient who is capable of unlimited household ambulation and limited community ambulation at a fixed cadence?
K2
At what age should the first prosthesis be fitted in a child with otherwise normal development who has a congenital left lower extremity deficiency?
9 months - child is able to pull to stand
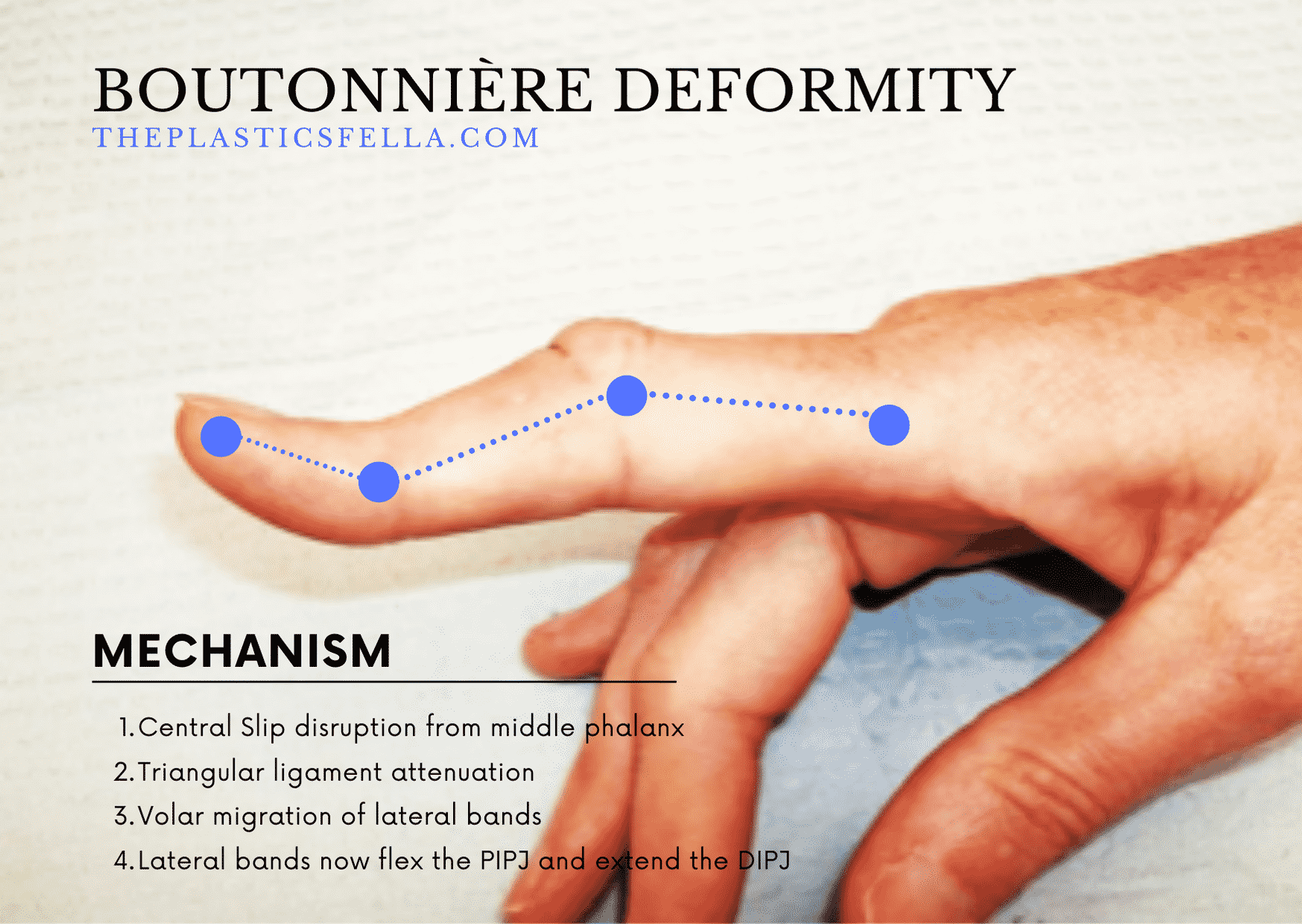
Describe Boutonniere's Deformity
MCP hyperextension, PIP flexion, DIP hyperextension
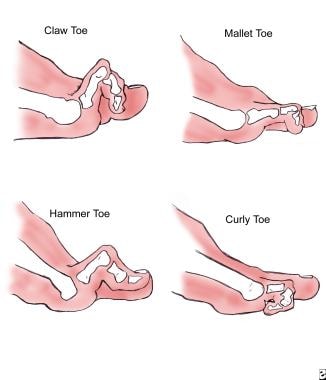
Describe Hammertoe
MTP extension, PIP flexion, DIP extension
Following orthoses would be most appropriate for an unstable bony fracture at C4?
Halo vest
Impaired venous outflow in the residual limb due to an ill-fitting (too tight) socket constricting blood flow; this can lead to red and firm/indurated skin at the residual limb
What is venous venous choke syndrome
A 6 year-old boy undergoes a transtibial amputation for a malignant bone tumor in his distal tibia and is fitted with a below-knee prosthesis. At his current age, how often can his prothesis be replaced?
Until age 5, a prosthetic device should be replaced annually. From age 5-12, a prosthetic device can be replaced every 18 months. A prosthetic device can be replaced every 2 years from age 12-21.
Which of the following imaging studies will be most helpful for diagnosing ankylosing spondylitis - pelvis XR vs lumbar spine XR ?
Pelvis x-rays - To identify b/l sacrolitis
Bonus: What is treatment?
Firm mattress, sleep in position to keep spine straight/prevent spine flexion deformity—lie prone
Which of the following juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA) subtypes requires ophthalmology referral?
- Polyarticular
- Oligoarticular
Oligoarticular
In a patient with a congenital terminal left transradial limb deficiency, which of the following points in time would be most appropriate to first prescribe a prosthesis?
6 months
What is the most common lower extremity amputation in dysvascular disease (the most common cause of lower limb amputations)?
Transmetatarsal fx - dysvascular disease tends to affect the limb or proximally > distally
This prosthetic control system offers improved cosmesis and stronger grasp force with less harnessing but is heavier, more expensive, less durable, and requires daily battery charging.
What is a myoelectric prosthetic control system?
A 55 year-old female presents with bilateral shoulder pain and stiffness over the past 6 months. Labs reveal elevated ESR and CRP. Which of the following additional symptoms is most likely present in this patient?
Jaw pain - Polymyalgia Rheumatica
Radiographic findings of patchy osteopenia and ground glass appearance are found in?
CRPS (Sudeck's Atrophy)
What is the benefit of a figure 9 transradial harness suspension system over a figure 8 (O-ring) harness system?
It is lighter and provides a greater freedom and comfort by the elimination of the usual front support strap and triceps pad or cuff.
Which gait phase has the highest center of gravity?
Midstance
Bonus: The body has the lowest COG during loading response.
Name the 6 determinants of gait
Pelvic Rotation
Pelvic Tilt
Knee Flexion in Stance
Foot Mechanisms
Knee Mechanisms
Lateral Displacement of the Pelvis
Which type of dermatomyositis is associated with malignancy?
Type III (5-8%)
For acutely inflamed joints in rheumatoid arthritis, which of the following is the most appropriate type of exercise?
Isometric - as it limits the damage that can be done to the joint via range of motion (ROM) exercises