This HLA allele is most commonly shared by individuals with seronegative spondyloarthropathies.
What is HLA-B27?
Both rheumatoid arthritis and seronegative spondyloarthropathies present with morning sickness > 30 min that improves with activity.
What is True?
Inflammatory arthritis
Name 3 extra-articular manifestations of rheumatoid arthritis.
Dermatologic: rheumatoid nodules
Ocular: keratoconjunctivitis, scleritis, episcleritis
Pulmonary: interstitial lung, pleuritis, effusion
Cardiac: pericarditis, myocarditis, MI, stroke
Vascular: Raynaud phenomenon
Hematologic: anemia of chronic disease, neutropenia
MSK: carpal tunnel, tenosynovitis, bursitis
Low hemoglobin and low hematocrit are commonly seen in both RA and SSpAs?
Anemia of chronic disease
This is the initial imaging test ordered for a patient suspicious of polyarticular arthritis.
What is x-ray?
Ultrasound and MRI are more sensitive in showing inflammation and erosion.
This form of polyarticular arthritis is more common in women than in men.
What is rheumatoid arthritis?
This form of polyarticular arthritis occurs in an asymmetric manner.
What are seronegative spondyloarthropathies?
Psoriatic Arthitis, Ankylosing Spondylitis, IBD-Associated, Reactive Arthritis
Seronegative spondyloarthropathies have pain in this characteristic region.
What is lower back pain with sacroiliitis?
This is the most specific antibody for rheumatoid arthritis.
What is anti-CCP? anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide
RA: interstitial tissue proteins undergo post-translational modification that involves the conversion of arginine to citrulline (citrullination)
This is most likely an x-ray image of this polyarticular arthritis.
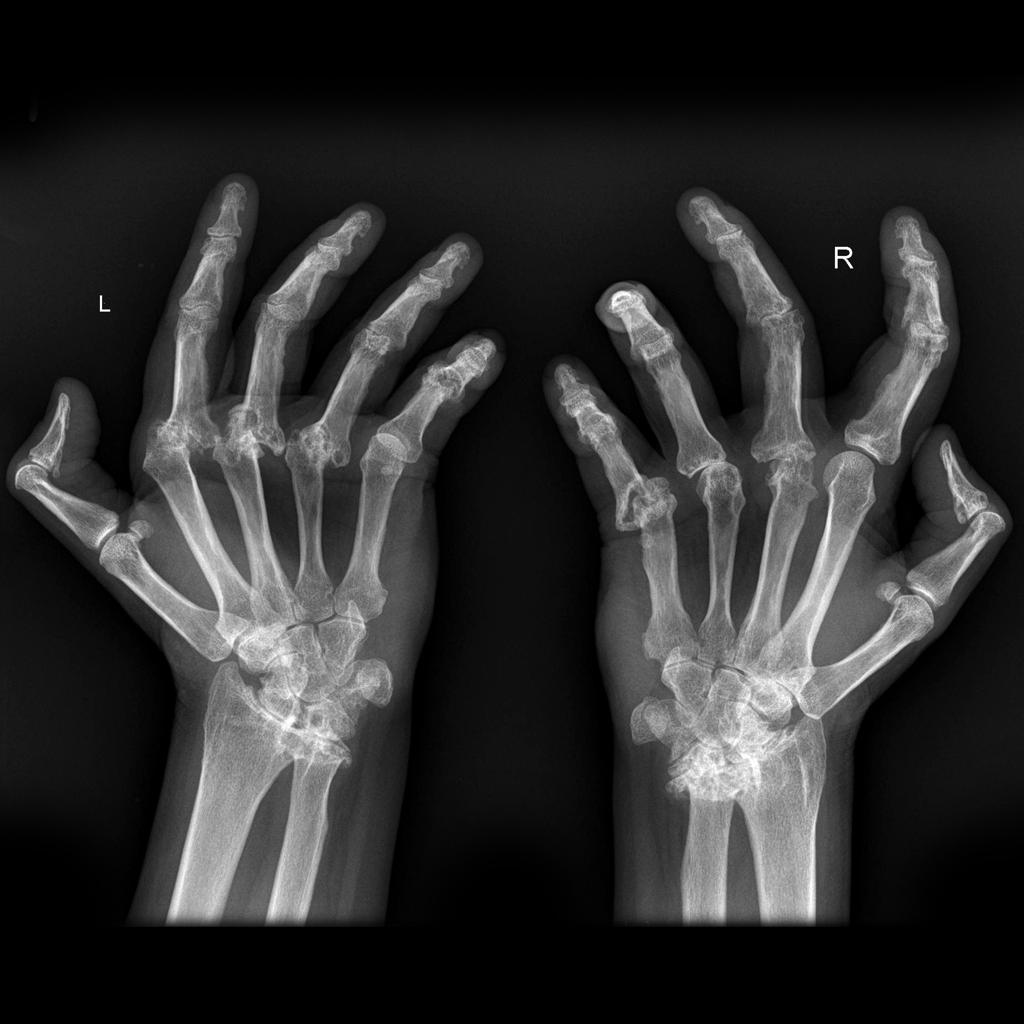
What is rheumatoid arthritis?
Soft-tissue swelling, osteopenia, marginal erosions
Ulnar deviation of MCPs; radial deviation of wrist
This form of polyarticular arthritis is more likely to occur before age 45.
What are seronegative spondyloarthropathies?
Rheumatoid arthritis: >65 yrs
These hands joints are most commonly affected in rheumatoid arthritis. (name all)
What are PIPs, MCPs, wrist* joints?
Also, knees
This classic triad is seen in reactive arthritis.
What is arthritis, conjunctivitis, urethritis?
Reactive arthritis: autoimmune condition that occurs after GI or urinary tract infectionCan't see, can't pee, can't climb a tree.
RF is an antibody that targets this molecule. (be specific)
What is the Fc portion of IgG?
RF attempts to remove autoantibodies and immune complexes. Individuals with RF are more likely to develop extra-articular manifestations.
Bamboo vertebrae and syndesmophytes are characteristic of this form of arthritis.

What is ankylosing spondylitis?
These HLA alleles are most commonly shared in individuals with rheumatoid arthritis.
This is an image of joint deformity.

What is Boutonniere deformity?
Boutonniere = PIP flexion DIP hyperextension
Swan neck = PIP hyperextension DIP flexion
Felty syndrome includes these 3 features.
What is arthritis, splenomegaly, and neutropenia?
This is the most common bacterial pathogen implicated in post-urethritis reactive arthritis.
What is Chlamydia?
Post-enteritis: Shigella, Campylobacter, Yersinia, Salmonella
She cherishes cooking yummy salmon.
This pencil-in-cup deformity is characteristic of this form of arthritis.

What is psoriatic arthritis?