f(x) + 2 Represents this type of transformation
Vertical shift 2 units up
What is the inverse of (2x+3)/4
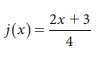
What is 2x-(3/2)
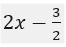
The end behavior of the function y = x^2
As x -> ∞, f(x) -> ∞
As x -> -∞, f(x) -> ∞
What is the equation of the asymptote of the function
f(x) = log (x + 4) ?
x = -4
f(x - 4) Represents this type of transformation
Horizontal shift 4 units right
What is the inverse of 3x+1
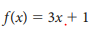
What is (x-1)/3
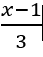
The end behavior of f(x) = -x^3 + 2x^2 - 4x + 1
As x -> -∞ , f(x) -> ∞
As x -> ∞ , f(x) -> -∞
When a root happens more than once the exponent on the factor changes and this is called ____________
What is multiplicity
What is the equation of the asymptote of the function
f(x) = log (x -2) ?
x = 2
f(x) - 5 Represents this type of transformation
Vertical Shift 5 units down
The inverse of g(x)=(8-5x)/4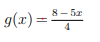
What is -(4x-8)/5
-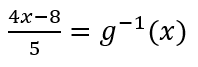
The end behavior of the function f(x) = log (x + 2)
As x -> -2, f(x) -> -∞
As x -> ∞ , f(x) -> ∞
What has to happen for a graph to turn around on the x-axis?
What is the multiplicity is even.
What is the equation of the asymptote of the function
f(x) = 2x + 3
y = 3
f(x + 3) Represents this type of transformation
Horizontal Shift 3 units Left
g(x) = 1/2(x-6)
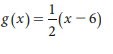
What is 2x+6
The end behavior of f(x) = -log (x - 4)
As x -> -∞ , f(x) -> ∞
As x -> 4 , f(x) -> -∞
What is the equation of the asymptote of the function
f(x) = 2x - 5 ?
y = -5
-f(x) and f(-x) Represents this type of transformation.
(Double points for specifying each!)
Reflections over the x - axis and y-axis (respectively)
f(x) =x2 +4
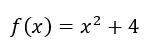
What is sq rt(x-4)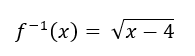
What is the end behavior of f(x) = 5x + 3
As x -> -∞ , f(x) -> 3
As x -> ∞ , f(x) -> ∞
What are the equations of the asymptotes of the function
f(x) = (2x)/(x-1)
(DOUBLE POINTS FOR GIVING BOTH!)
x = 1 AND y = 2