What is "life expectancy"?
The average number of years that a person can expect to live.
What are the two main causes of population aging?
1. Decline in the fertility rate
2. increase in life expectancy
In what part of a city does most commercial and financial activity take place?
The central business district (CBD)
Cities which lack good public transport systems may face what type of problem?
Too much traffic in the streets can lead to accidents and delays
About what time did Spain change from being a country of emigrants to a country of immigration?
After the recession of 1973, and until the economic crisis of 2008.
Why has life expectancy risen across the globe?
Advances in medicine, nutrition, and hygiene.
In which regions of the world is population aging the fastest?
In developed countries, especially Japan and parts of Europe.
How many inhabitants must a city have to be considered a 'megacity'?
More than 10 million.
Why might large companies choose to be located in a city?
1. Transport networks
2. Availability of workers
3. Cities are centers of innovation
Which were some of the first cities in Spain to grow in the 19th and 20th centuries?
Bilbao, Barcelona and Madrid (also Valencia and Zaragoza)
When was the population explosion?
In the second half of the 20th century
Name at least 2 reasons why people migrate.
1. Economic: job opportunities and higher wages
2. Social: better services or to be near family
3. Political or religious: people flee persecution
4. Natural disasters: events force people to leave
In emerging and less developed countries, particularly in Asia and Africa.
What is it called when a city has a slightly higher temperature than the area around it?
An urban microclimate or a heat island
The national metropolises in Spain are Madrid and Barcelona. Name 2 other Regional metropolises.
Valencia, Bilbao, Zaragoza Seville, and Málaga.
Why is population growth so low in developed countries?
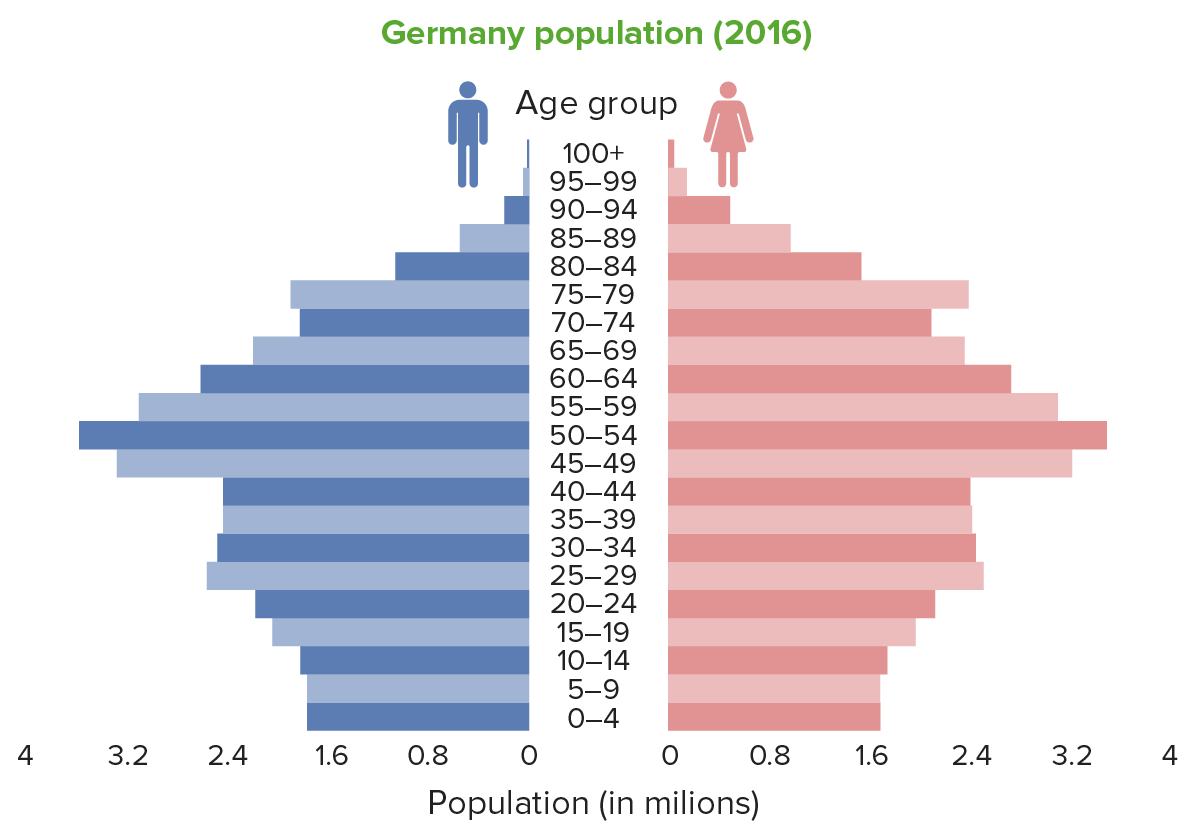 What population trend is shown in this pyramid?
What population trend is shown in this pyramid?
A contracting, declining, or aging population.
What is the required population density to be considered an urban or metropolitan area?
150 people per km2
What is it called when groups of people are separated into different areas according to their income?
Residential segregation
What industry has a helped speed the growth of cities along Spain's Mediterranean coast?
The tourism industry.
What is the fertility rate necessary for generational replacement?
2.1 children per woman.
What are some benefits to a country that its receiving many migrants?
1. Can prevent population aging/decline
2. Immigrants are often young people who can fill jobs
3. Many migrants have useful skills or knowledge and can contribute to economic growth
A slum of shanty town.
What features and/or institutions should a city have to be considered a global city?
1. Important financial institutions (such as NYSE)
2. National/International institutions (EU, UN, etc.)
3. Headquarters major multinational companies
4. Key information and communications industries (TV stations, newspapers, etc.)
What percent of Spain's population today is over age 64?
18%. This is a sign of population aging.