The definition of natural selection.
Organisms with preferred traits (adaptations) will live longer and reproduce more than others, causing changes in the population over time.
The equation for HWE.
p2 + 2pq + q2 = 1
The 5 conditions that can disturb genetic equilibrium and cause evolution to occur.
Natural selection
Random mutations
Genetic drift
Gene flow
Sexual selection
The difference between convergent and divergent evolution.
1. Convergent: when unrelated species evolve similar characteristics because they live in similar environments.
2. Divergent: when many different species arise from one common ancestor.
The different levels of the classification of organisms (in the correct order).
Domain, kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, species.
The 3 patterns of biodiversity that Darwin noted while aboard the HMS Beagle.
Species vary globally.
Species vary locally.
Species vary over time.
We can use the principle to prove that populations are evolving!
In a population of rabbits, long ears are dominant to short ears. Of the total 355 rabbits in a population, 112 have short ears. Assuming HWE, what is the frequency of the homozygous dominant genotype?
Frequency of homozygous dominant = 0.193
The 2 types of genetic drift and the difference between them.
1. Bottleneck effect: a change in allele frequency following a dramatic reduction in the size of a population.
2. Founder effect: a loss in genetic diversity when a new population is founded by a very small group of colonizers.
The difference between taxonomy and phylogeny.
Taxonomy: science of naming, describing, and classifying organisms
Phylogeny: science of classifying organisms based on evolutionary relatedness
The 3 modes of natural selection.
1. Directional
2. Stabilizing
3. Disruptive
In a population of mice, 79% express the dominant trait. Assuming HWE, what is the percent of mice that have the heterozygous genotype?
50% are expected to be heterozygous.
In a population of crickets, green body color is dominant over yellow body color. Of the total 826 crickets in a population, 584 have a green body. Assuming HWE, what percent of the population should be heterozygous?
Percent of heterozygous = 50%
Provide an example of each of the three types of isolation (behavioral, geographical, and temporal).
[Answers can vary]
Which group of organisms is most closely related to primates?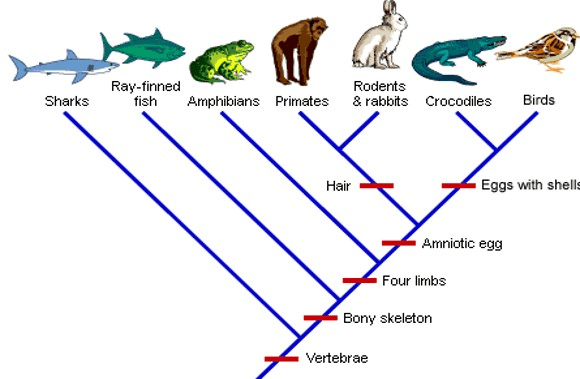
Rodents and rabbits
1. Struggle for existence
2. Variation and adaptation
3. Survival of the fittest
4. Descent with modification (natural selection)
In a population of birds, 587 exhibit the dominant trait of black feathers and 204 exhibit the recessive trait of white feathers. Assuming HWE, what are the genotypic frequencies for this population?
FF = 0.242
Ff = 0.500
ff = 0.258
In a population of 639 frogs, 412 are homozygous dominant, 134 are heterozygous, and 93 are homozygous recessive for a particular trait. If the population is in HWE, what would we expect the genotypic frequencies to be?
AA = p2 = 0.563
Aa = 2pq = 0.375
aa = q2 = 0.063
Explain the relationship between rough skinned newts and garter snakes, including the pattern of evolution they exhibit.
Coevolution. Newts are toxic, garter snakes are resistant to toxins. Newts are evolving to be more toxic but in return, garter snakes are evolving to resist more toxins.
Which group or organisms is most closely related to the Salamander? Explain your reasoning.
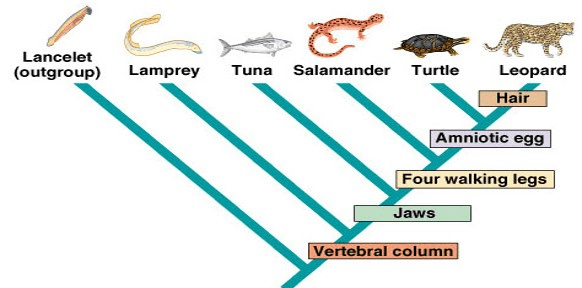
Tuna. Tuna and salamander share the most recent common ancestor.
Darwin's hypothesis about the evolution of finches on the Galapagos Islands.
Founders arrive, geographic isolation, changes in gene pool, behavioral isolation, competition and continued evolution
A population of 167 butterflies consists of: 83 individuals who are homozygous dominant, 68 individuals who are heterozygous, and 16 individuals who are homozygous recessive for a particular trait. Is this population in HWE? If not, what mode of selection is being favored?
Yes, in equilibrium.
In a population of 1327 wildflowers, white flowers are dominant over red flowers. We know 899 flowers are homozygous white, 58 are heterozygous, and 370 are homozygous red. Is this population in HWE? If not, what mode of selection is being favored?
Not in equilibrium. Disruptive selection.
The 3 types of structures that the field of morphology has determined are evidence of evolution. Include the definition and an example of each.
1. Homologous structures: similar structures that suggest evidence of common ancestry (EX: bone structure of human arm, cat limb, whale fin, and bat wing)
2. Vestigial structures: structures of an organism that serves little or no function (EX: dewclaw, ostrich wings)
3. Analogous structures: similar structures that evolved independently in different organisms (EX: owl and dragonfly wings)
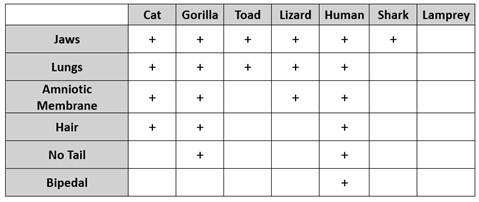
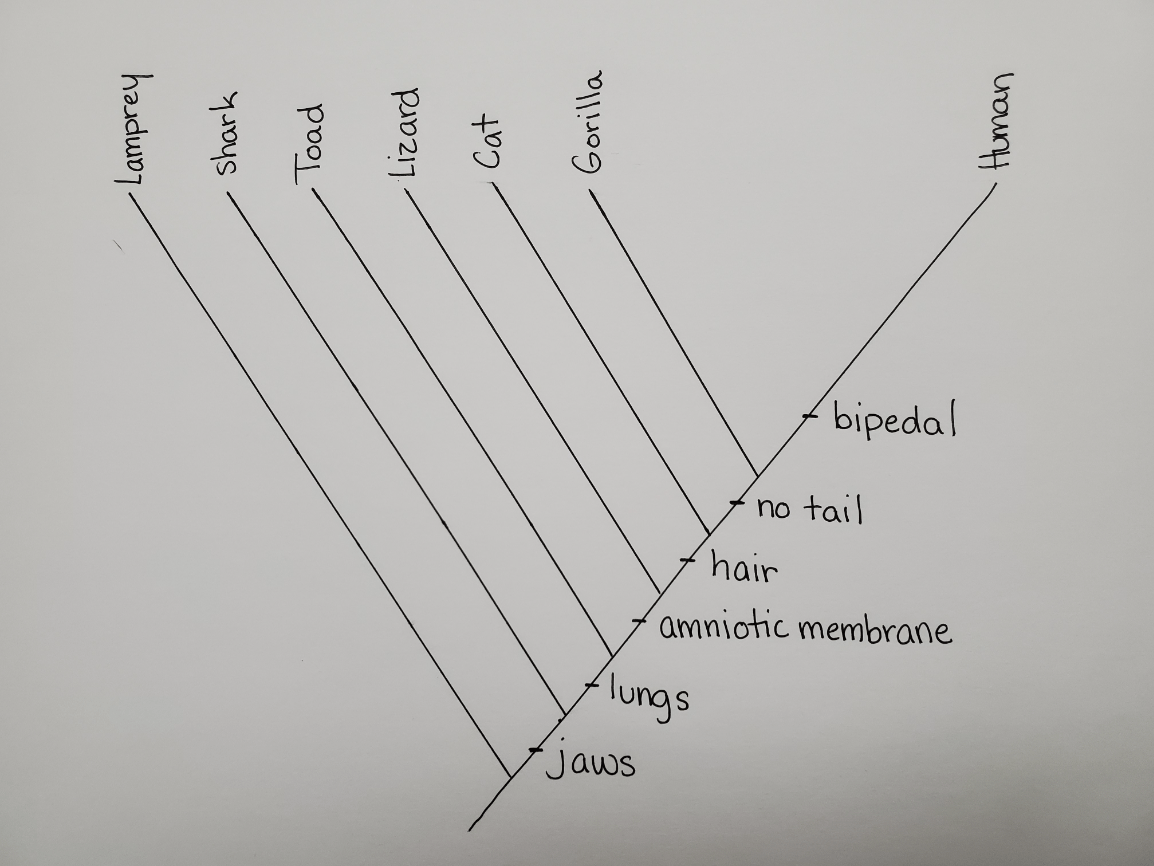
Create a phylogenetic tree using the information in the table below. Include the traits.