Factors that cause a population to stop growing or decrease in size
Limiting Factors
Limiting factors can be abiotic or biotic.
True or False
TRUE
The number of births per 1,000 individuals for a given time period.
Birth Rate
The parts of the land, sea and atmosphere in which organisms are able to live.
Biosphere
a relationship in which two different organisms live in close association with each other.
Symbiosis
The largest population that an area can support.
Carrying Capacity
Give an example of a density independent factor.
What is any natural disaster or weather event.
BUSTED!
The team who chose this question loses 200 points!
All the different populations that live together in a particular area.
Community
relationship where both organisms benefit.
Mutualism
The number of individuals in an area of a specific size
Population Density
Give an example of density dependent factor.
Competition, loss of resources, spread of disease, etc.
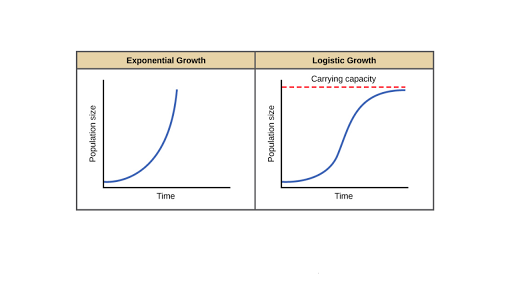
Which graph best illustrates healthy growth of a population in a given area?
Logistic Growth
A living thing
Organism
Double Jeopardy
If you get this correct you receive double the points!
Name the three types of Symbiotic relationships and the difference between them .
Mutualism= both benefit
Commensalism= one benefits and other is unaffected.
Parasitism= one benefits and the other is harmed.
The number of deaths per 1,000 individuals for a given time period.
DOUBLE Jeopardy!
If you get this question correct, your team gets double the points!
What is the difference between density-dependent factors and density-independent factors?
Density-dependent: limiting factors that influence a population's birth and death rates when the population becomes too dense. (Starvation, lack of resources, spread of disease, predator/prey, competition, etc.)
Density-Independent: limiting factors that influence a population’s birth or death rates, regardless of the population density. (Temperature, natural disasters, level of oxygen in the atmosphere, etc.)
Give one example as to why an animal might Emigrate from a habitat.
Lack of resources
Too much competition
Disease
ETC..
All the members of one species living in the same area.
Population
Some shrimp and crab live and capture food from within the tentacles of giant anemones.
Commensalism
Moving into a population
Immigration
Why are limiting factors important in ecology?
They keep the ecosystem balanced.
In terms of populations in an ecosystem, what does ZPG stand for?
The community of organisms interact with each other and their environment.
Ecosystem
The siboglinid tube worm, found at deep-sea hydrothermal vents and cold seeps, has no digestive tract. It relies on symbiotic bacteria that live in the tube worm’s tissues. The bacteria oxidize hydrogen sulfide or methane for the worm.
mutualism