Are Monosaccharides, Disaccharides, and Polysaccharides examples of structural or non-structural carbohydrates?
Non-structural Carbohydrates
What is the basic structure of a lipid?
triglyceride
What is the principle photosynthetic organ?
leaf
What organelle is major in energy metabolism?
Mitochondria
Where do ruminates break down carbohydrates?
rumen microbes
What are four vitamins are fat soluble?
A, D, E, K
What part of the plant supports and connects organs with roots, and has little photosynthetic activity?
Stem
What is responsible for converting energy from sunlight?
chloroplasts
Why do mammals have to utilize microbes in the digestion of forages?
Mammals do not produce cellulase
What are 3 things that modified lipids and plants help?
-capture light (cartotenoids)
-regulate physiological processes
-form the basic structure of the cell wall
What is the primary growing point at the stem apex (tip)?
Apical Bud
What binds cells together?
pectin
What are the two types of bonds between monosaccharides?
𝛂-1, 4 glycosidic linkages
𝛃-1, 4 glycosidic linkages
Which fatty acid is inflammatory and which is anti-inflammatory?
Inflammatory -> Omega-6
Anti-inflammatory -> Omega-3
Which organ opens and closes to allow respiration?
Stomates
Microscopic channels between cells & through cell walls to transport large molecules such as proteins, RNA, and nutrients is called what?
Plasmodesmata
What is the cycle called when chlorophyll molecules in chloroplasts of green plants take in CO2 and H20?
what is the Calvin cycle
Name at least 2 functions of lipids.
-store energy
-provide thermal insulation
-repel water on the outer surface
-insulation around nerves
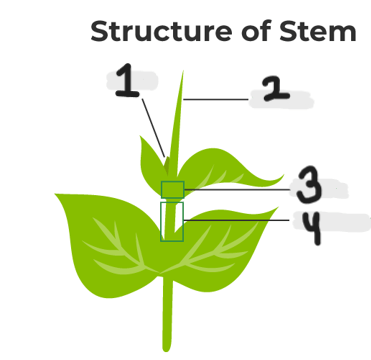
1. Bud
2. Stem
3. Node
4. Internode
What is the difference between the contents of the primary and secondary cell walls?
Primary Cell Wall- cellulose & hemicellulose
Secondary Cell Wall- cellulose & hemicellulose & lignin