Expand the expression: 2(x + 3)
2x + 6
Simplify the following expression:
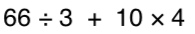
Solve
x + 7 = 15
x = 8
x + 4 > 9
x + 4 > 9 → x > 5
Factorise
6x + 9
3(2x + 3)
Simplify the following expression:
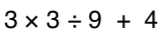
3x - 5 = 10
3x = 15 → x = 5
y - 5 > 10
y > 15
Expand and simplify
3(x + 4) - 2(x - 1)
= 3x + 12 - 2x + 2
= x + 14
3 + 42 * (3 + 2)
What is 95?
- Solve and check using substitution: 2x + 4 = 10
2x + 4 = 10
2x = 6 → x = 3
Check: 2(3) + 4 = 10 ✔
What does x > 5 represent?
x > 5 means x is any number greater than 5, not including 5.
Factorise
4x² - 8x
= 4x(x - 2)
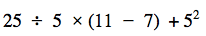
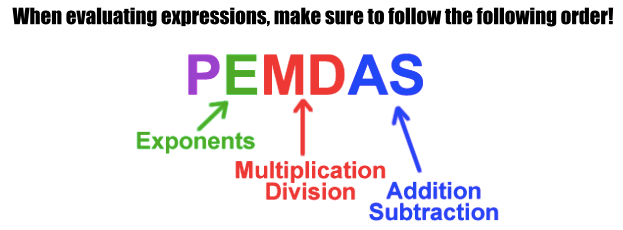 What is 45?
What is 45?
- Error Check: 4x - 2 = 10 ⇒ x = 2. Is this correct? Explain.
4x - 2 = 10 ⇒ x = 2
Check: 4(2) - 2 = 6 ≠ 10 → ❌
Correct solution:
4x = 12 → x = 3
Solve -3x > 6.
-3x > 6
Divide by -3 (flip inequality):
x < -2
Why factorising is inverse of expanding:?
Expanding multiplies out brackets to simplify an expression; factorising reverses that by finding common factors and writing the expression as a product.
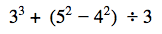
 What is 30?
What is 30?
BONUS
3 − 2(n − 4) > −1
n < 6