What is the indicated section of the map called?
Scale
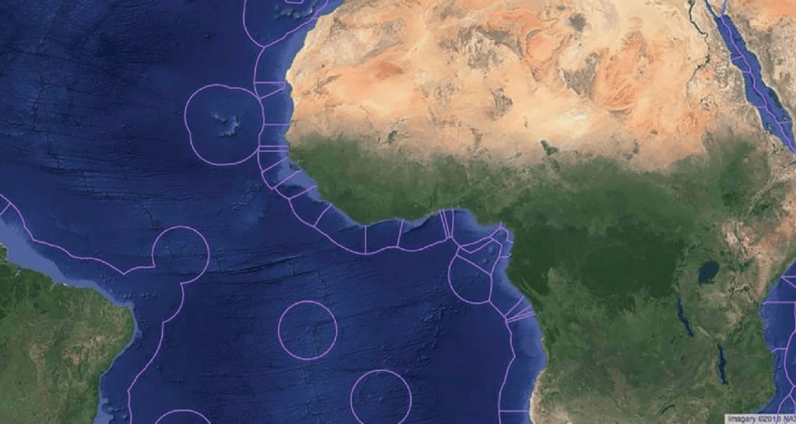 How are the EEZs (Exclusive Economic Zones) in this map an example of formal regions?
How are the EEZs (Exclusive Economic Zones) in this map an example of formal regions?
There are clearly defined boundaries for specific areas
What is the difference between emigration and immigration?
Emigration is the act of leaving your own country while immigration is when someone moves into a foreign country
A drought would lead to the scarcity of what natural resource?
Water
What are the four cardinal directions?
North, East, South, West
How is this map an example of a functional region?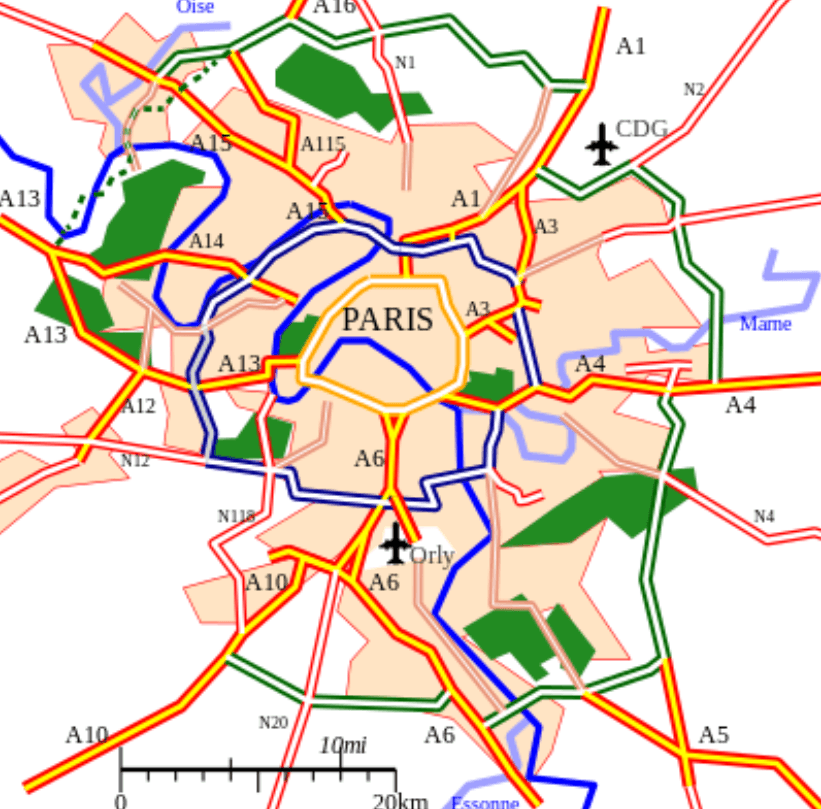
There is a central (nodal) point that is connected to/influences surrounding areas
What is an example of a pull factor?
Job opportunities, higher quality of education, etc.
How can new agricultural practices lead to the growth of population?
New processes can lead to a food surplus resulting in population growth
What is the purpose of a key in a map?
To identify symbols and markers on a map
What tells you this is a perceptual regions map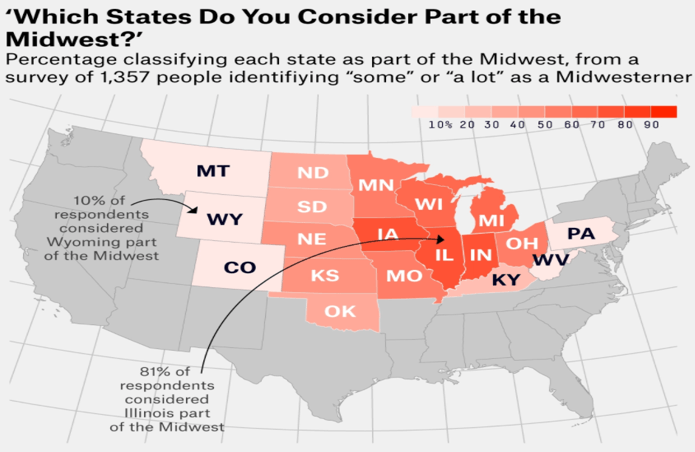
it is characterized by the beliefs, attitudes and perceptions people have about an area
What is an example of a push factor?
War, famine, corruption of government, etc.
What happens to a population when the birth rate is higher than the death rate?
Natural increase of total population
Is the Equator a line of latitude or longitude?
Latitude
What makes regions different from locations?
Locations are specific areas while regions do not have fixed boundaries
Based on the population pyramid, what can be said about the Total Fertility Rate of Kenya?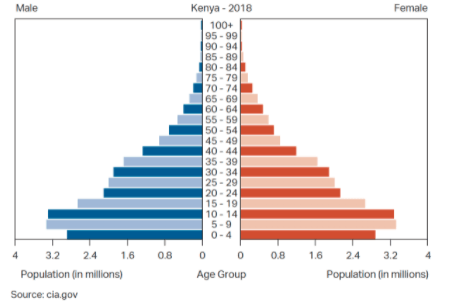
It is higher than average because children under 19 years old greatly out number groups of people older in age
What is a Food Surplus?
A time when humans had more food than they needed. This leads to population growth.