The study of production, distribution and exchange of goods and services in an economic system.
What is economics?
The mathematical formula that shows the relationship between disposable income, consumption and savings.
Y = C + S
Where the factors of production are bought and sold.
What are factor markets?
Derived from the demand for the goods and services that labour is used to produce.
What is meant by the term ‘derived demand for labour’?
Provides funds from people with a surplus to those with a shortage of funds and want to borrow.
What is the role of financial markets in the Australian economy?
Goods or services that are beneficial to society but may be produced in insufficient quantities because the private sector lacks incentive to supply.
What are merit goods?
What is Australia's inflation target?
2-3%
The scarce things used to produce goods and services to satisfy needs and wants.
What is meant by the term 'factors of production'?
An increase in average costs due to factors outside the firm’s direct control.
What is meant by 'external diseconomies of scale'?
What is meant by the term ‘derived demand’?
The demand for productive resources (e.g. labour) is derived from the demand for the final goods and services.
Individuals who have been unemployed for more than 52 weeks
What is meant by ‘underemployment’?
A firm that holds the funds or individuals or firms as deposits, and then loans these funds to other firms or individuals.
What is a financial intermediary?
Consumption of the good by one individual does not reduce the quantity of the good available for other consumers.
What is meant by the term ‘non-rival’?
What is the unemployment rate in Australia in Aug 2025?
4.2%
Deals with the economy as a whole and how government policies and other factors impact the economy.
What is macroeconomics?
When consumers go into debt because consumption exceeds income.
What is meant by the term 'dissavings'?
The sum of individual demands for a good or service.
What is market demand?
Individuals that are applying for jobs or have registered with a job agency or Centrelink as a jobseeker.
What is meant by the term 'unemployed'?
Where financial assets that are based on the value of other financial assets are bought and sold.
What is a derivatives market?
People who benefit from a good or service without having to pay for its production or maintenance.
What are ‘free-riders’?
What is the cash rate target in Australia?
3.60%
The theory that consumer preferences determine the production of goods and services.
What is consumer sovereignty?
The business structures that have unlimited liability.
Sole trader and partnership.
Determine the impact on demand if consumers expect that the price of new shoes will increase in the future because of a new government tax.
Increase in demand (will purchase now before the price increases).
Refers to benefits employees receive in addition to their ordinary payments, such as sick leave, holiday leave, superannuation and fringe benefits.
What is meant by ‘non-wage outcomes’?
Requires a buyer to purchase and a seller to set the asset, on a specific date.
What is a futures contract?
Responsible for delivering government services and developing infrastructure such as roads.
What are the main responsibilities of the state government?
What is the lowest level of unemployment that can be achieved without increasing inflation? (i.e. the NAIRU)
4-5%
Distinguish between the four main stages of the business cycle.
Downswing: Expenditure, output, income and employment start to decrease
Recession: It is usually measured as two consecutive quarters of negative economic growth (fall in GDP).
Upswing: Expenditure, income and employment increase.
Boom: Expenditure, output etc have reached the maximum. Can lead to shortage of resources and inflation.
Two sources of economies of scale.
Lower input costs
Advances in technology
Specialisation
Division of labour
The responsiveness of the quantity demanded to a change in the price of a good or service.
What is meant by the ‘price elasticity of demand’?
Caused by a mismatch between the skills of employees and the job vacancies offered by employers.
What is the cause of structural unemployment?
Reducing the cash rate in order to stimulate aggregate demand and increase consumption, employment and economic growth.
What is meant by expansionary monetary policy? (easing stance)
Refers to the parts of the economy that are owned or controlled by the government.
What is meant by the ‘public sector’?
How much was the cash rate changed in April 2025
0.00%
Shows the various combinations of two alternative products that can be produced, given technology and a fixed quantity of resources, when all resources are used to their full capacity.
What is a production possibility frontier?
What will be the impact on demand if there is a change in the price of a substitute good?
Price increase of substitute = increased demand
Inverse is true.
Identify one of the main factors that influence the price elasticity of demand for goods and services.
Necessities/luxuries
Substitutes
Proportion of income spent on the good
Length of time since a price change
A macroeconomic factor that determines the demand for labour.
Level of economic activity
Productivity of labour
Cost of labour
Government policies
The rate of interest charged by financial institutions on deposits.
What is a borrowing rate?
Involves achieving a budget deficit by increasing government spending and/or reducing taxation.
What is expansionary fiscal policy?
What is the inflation rate in Australia in August 2025
2.1%
Name the factor income return for each factor of production.
Land – rent
Labour – wages
Capital – interest
Enterprise - profit
Calculate the APS and MPS if:
Savings = $600, APC = 0.7 and MPC = 0.6
APS = 0.3 and MPS = 0.4
Compare and contrast a monopoly and an oligopoly.
Both have high barriers to entry.
Both are price setters (monopoly to a greater degree than an oligopoly).
A monopoly involves a single firm that has no close substitutes e.g. Australia Post.
An oligopoly involves a few large firms (3-8). They sell a slightly differentiated product e.g. banks.
Individuals who have been discouraged from seeking work or due to family responsibilities, short-term illness or study.
What is meant by ‘hidden unemployment’?
The difference between the nominal interest rate and inflationary expectations.
What is the real interest rate?
(Real interest rate = Nominal Interest Rate – Inflationary Expectations)
Refers to the person or group who ultimately pays the tax.
What is meant by the ‘incidence’ of a tax?
What was wage growth in Australia by June 2025
3.4%
At which point is full employment of resources experienced, and at which point are resources underutilised?
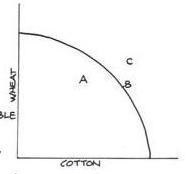
B - full employment
A - underutilised
Outline the main components of the consumption function.
C = C0 + cY
C = total consumption
C0 = autonomous consumption (what you will spend regardless of how much you earn)
c = MPC (△C/△Y).
Explain an issue associated with the use of a price support scheme.
Price support scheme = price floor.
Floor established above equilibrium = excess supply.
This will need to be stockpiled/stored for sale at a later date to remove the surplus from the market.
The performance of the labour market in terms of wage and employment levels and how efficiently labour is allocated in the economy.
What is meant by ‘labour market outcomes’?
The buying and selling of commonwealth government securities to maintain the cash rate.
What is meant by liquidity management? (open market operations)
To avoid a reduction in consumer sovereignty, consumer choice and output which can lead to a decline in consumer welfare.
Why do governments attempt to control monopoly power?
Name all the cash rate changes that occurred in 2024?
No changes.