54. Which of the following neurotransmitters plays a key role in regulating the transition between sleep and wakefulness?
A. Choline
B. Serotonin
C. Histamine
D. Glutamate
E. Anandamide
C. Histamine
Histamine plays a crucial role in regulating the sleep-wake cycle by promoting wakefulness and inhibiting sleep.
It acts through H1 and H3 receptors. H1 agonists induce wakefulness and H3 agonists promote sleep.
Histamine neurons in the tuberomammillary nucleus (TMN) of the hypothalamus are active during wakefulness and inactive during sleep.
90. Psychiatry is consulted to evaluate a patient who has been hospitalized for two weeks. On interview, the patient displays bright affect and fast speech. The patient is slightly irritable, describing frustration with the two-hour wait and is upset with being treated by a trainee. The patient reports as being a high-level manager at a large technology company and expects the best care. The patient repeatedly changes the subject to focus on their own accomplishments. They report regular sleep patterns though and frequently up late to finish work and occasionally uses stimulants to facilitate this. What is the most likely diagnosis for this patient?
A. Bipolar disorder
B. Substance use disorder
C. Histrionic personality disorder
D. Borderline personality disorder
E. Narcissistic personality disorder
E. Narcissistic personality disorder
DSM Criteria of NPD
A) A pervasive pattern of grandiosity (in fantasy or behavior), need for admiration, and lack of empathy, beginning in early adulthood and present in a variety of contexts, as indicated by 5 (or more) of the following:
-A grandiose sense of self-importance (exaggerates achievements and talents, expects to be recognized as superior without commensurate achievements).
-Preoccupation with fantasies of unlimited success, power, brilliance, beauty, or ideal love.
-Believing that they are "special" and unique and can only be understood by, or should associate with, other special or high-status people (or institutions).
-Requiring excessive admiration.
-A sense of entitlement (unreasonable expectations of especially favorable treatment or automatic compliance with their expectations).
-Being exploitative (taking advantage of others to achieve their own ends).
-Lacking empathy (unwilling to recognize or identify with the feelings and needs of others).
-Often being envious of others or believing that others are envious of them.
-Showing arrogant, haughty behaviors or attitudes.
B. The enduring pattern is inflexible and pervasive across a broad range of personal and social situations.
C. The enduring pattern leads to clinically significant distress or impairment in social, occupational, or other important areas of functioning.
D. The pattern is stable and of long duration, and its onset can be traced back to adolescence or early adulthood.
E. The pattern is not better explained as a manifestation or consequence of another mental disorder (such as a mood disorder or psychotic disorder).
F. The pattern is not attributable to the physiological effects of a substance (e.g., a drug of abuse or medication) or another medical condition.
9. In the 1970's, evidence for the role of serotonin in depression and a desire to develop drugs with a better side effect profile than the tricyclics and monoamine oxidase inhibitors, led to the development of which of the following medications?
A. Buspirone
B. Bupropion
C. Fluoxetine
D. Lamotrigine
E. Clomipramine
C. Fluoxetine
In the late 1960s evidence began to emerge that serotonin played a significant role in MDD. As a result, the pharmaceutical company Eli Lilly began developing ligands that would selectively inhibit the reuptake of serotonin at serotonin transporters, and as a result would increase serotonin concentrations within the synaptic cleft to further stimulate postsynaptic serotonin receptors.
26. Which of the following attachment behaviors typically presents in the first month of life?
A. Separation distress
B. Anticipatory posturing to be picked up
C. Smiling preferentially to caregiver's voice
D. Imitation of caregiver's facial expressions
E. Babbling more with primary caregiver than stranger
C. Smiling preferentially to caregiver's voice
Other milestones at 1 month:
-Can focus on objects 8 to 12 inches away
-Prefer black-and-white patterns
-Respond to sounds, including their parents' voices.
-Start to recognize their own scent.
-Head can move side to side while laying pronated
38. In child custody disputes, who is a guardian ad litem?
A. A professional tasked with evaluating each parent's level of competence.
B. A mediator between parents who cannot agree on custody arrangements
C. An individual appointed by the court to represent the interests of the child.
D. A community member who has been screened and trained to care for children.
E. A clinician tasked with determining which parent is best able to care for the child.
E. A clinician tasked with determining which parent is best able to care for child
C. An individual appointed by the court to represent the interests of the child.
89. The Wisconsin Card Sorting Test is a measure to assess which of the following neuropsychological domains?
A. Memory
B. Attention
C. Language
D. Executive functioning
E. Intellectual functioning
D. Executive functioning
-Dorsolateral Prefrontal Cortex
Participants in the Wisconsin Card Sorting Test are presented with a set of cards and instructed to sort them into piles based on a specific rule. Participants are not told what the rule is and must figure it out. They are given feedback (correct or incorrect) after each sort, and the rules change during the test, requiring participants to adjust their strategy.
87. A 21-year-old patient is brought to the emergency department after having an episode of nausea, sweating and hematemesis. The patient reports recently having severe headaches and numbness in the extremities. Computed tomography scan reveals generalized brain atrophy. Laboratory studies reveal evidence of renal tubular acidosis and a CPK of 3120 mcg/l. This presentation is consistent with chronic use of which of the following substances?
A. Phencyclidine
B. Amphetamines
C. Steroids
D. Cocaine
E. Inhalants
E. Inhalants
Acute effects: Respiratory depression, tachycardia, arrhythmia, peripheral neuropathy, confusion, dizziness, headache, seizures, or loss of consciousness, GI distress, aggression, AVH, agitation, loss of muscle coordination.
Chronic effects:
-Cardiac toxicity (myocardial edema, irreversible myocarditis, fibrosis, CHF).
-Respiratory damage (mainly from toluene abuse - panacinar emphysema, Goodpasture's syndrome.
-Renal toxicity (distal RTA, anion-gap acidosis, Fanconi's syndrome, renal calculi, hematuria, proteinuria, and renal failure).
-Bone marrow suppression --> leukopenia, anemia, thrombocytopenia, and hemolysis.
31. A 36-year-old is becoming increasingly more aggressive and has begun to develop writhing movements of the arms and legs. The patient's parent had similar symptoms before passing away at a young age. Which of the following would be the most effective in treating the abnormal movements?
A Levodopa
B. Primidone
C. Pramipexole
D. Levetiracetam
E. Tetrabenazine
E. Tetrabenazine
Tetrabenazine acts as a reversible high-affinity inhibitor of mono-amine uptake into granular vesicles of presynaptic neurons by binding selectively to VMAT-2, leading to depletion of the monoamines, particularly dopamine.
84. A therapist guides a patient with arachnophobia to visualize a spider crawling on their foot while engaging in diaphragmatic breathing. This technique is an example of:
A. extinction.
B. preparedness.
C. sensory preconditioning.
D. second-order conditioning.
E. systematic desensitization.
E. systematic desensitization
Systematic desensitization: reduces anxiety responses through gradual exposure to anxiety-provoking stimuli while using relaxation techniques to counteract the anxiety.
Extinction: based on the principle of classical conditioning. Involves decreasing a conditioned response (such as fear) by repeatedly presenting the conditioned stimulus (spider) without the unconditioned stimulus (being bitten) that originally triggered the response.
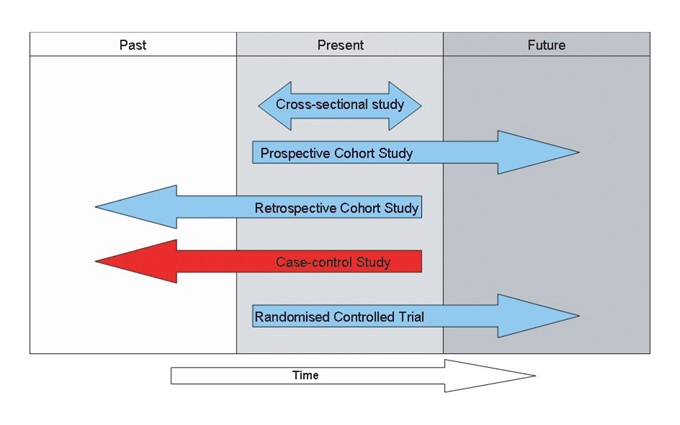
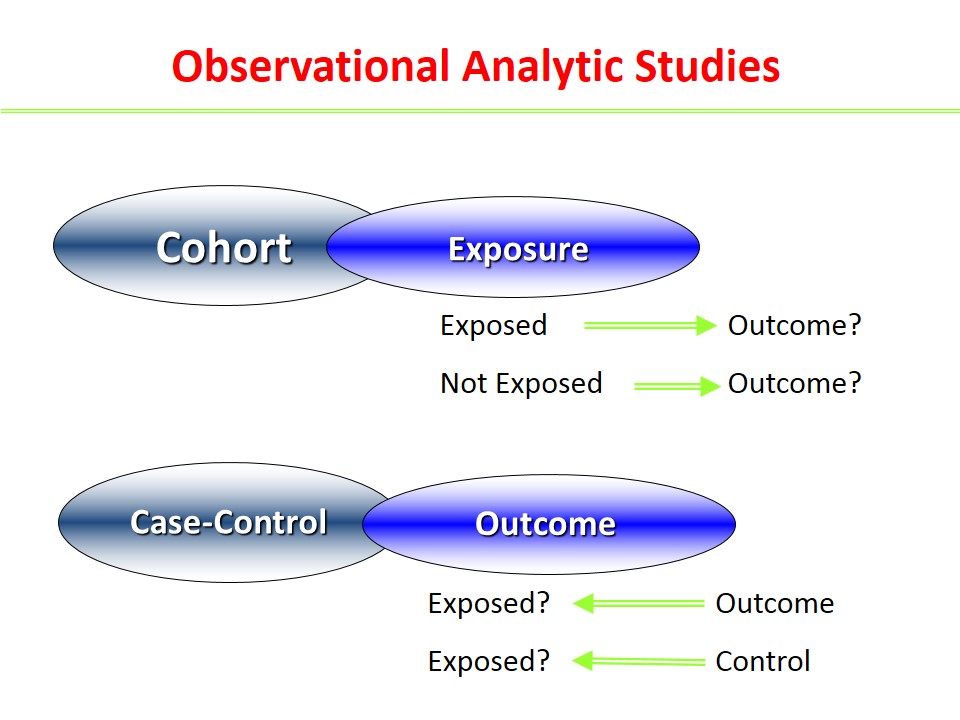
3. Medical record data was used to estimate the prevalence of diabetes among patients who started on an antipsychotic medication. Which of the following best describes this study design?
A. Cohort study
B. Meta-analysis
C. Systematic review
D. Cost-benefit analysis
E. Randomized controlled trial
A. Cohort study
79. Post-mortem brain samples have noted which of the following differences in the prefrontal cortex of individuals with schizophrenia as compared to controls?
A. Reduced neuronal density
B. Reduced number of neurons
C. Increased gray matter volume
D. Reduced dendritic spine density
E. Increased pyramidal somal cell volumes
D. Reduced dendritic spine density
Reduced dendritic spine density: schizophrenia, Alzheimer’s, stress, and sleep deprivation
Reduced neuronal density: aging, schizophrenia, suicide, MDD, neurocysticercosis
Reduced number of neurons: synaptic pruning, atrophy, TBI/physical damage, Alzheimer’s
Increased pyramidal somal cell volumes: brain development where neurons are actively growing and expanding
95. Which of the following hormones is secreted by small intestinal endocrine cells soon after meal onset and returns to basal levels between meals?
A. Leptin
B. Ghrelin
C. Cholecystokinin
D. Peptide Tyrosine
E. Glucagon-like Peptide-1
C. Cholecystokinin
-Peptide hormone produced mainly by duodenum.
-Triggers gallbladder to contract and release bile into the small intestine to emulsify and digest fats.
-Stimulates pancreas to release digestive enzymes (e.g., amylase, lipase, and proteases) to break down carbohydrates, fats, and proteins.
-Slows down the emptying of stomach contents into the small intestine, allowing more time for digestion, especially of fats.
-Signals satiety
-Activates somatostatin → inhibits gastric acid secretion in stomach gastric acid.
13. Which antidepressant has demonstrated efficacy in the treatment of akathisia?
A. Bupropion
B. Fluoxetine
C. Mirtazapine
D.Venlafaxine
E. Desipramine
C. Mirtazapine
Akathisia is linked to imbalances in neurotransmitters like dopamine (usually low) and serotonin in the brain.
Mirtazapine is a 5-HT2A, 2C, and 3 antagonist. It also indirectly increases dopamine release by blocking alpha-2 adrenergic receptors.
78. Which of the following forms of psychotherapy is most likely to describe a therapeutic goal as "improving ego functioning and self-esteem"?
A. Family therapy
B. Exposure therapy
C. Supportive psychotherapy
D. Dialectical behavior therapy
E. Interpersonal psychotherapy
C. Supportive psychotherapy
Supportive psychotherapy: alleviate symptoms, improve self-esteem, restore relation to reality, regulate impulses and negative thinking, and reinforce the ability to cope with life stressors and challenges.
Dialectical behavior therapy: to strike a balance between validation (acceptance) of who you are and your challenges and the benefits of change.
Interpersonal Psychotherapy: to improve a person's interpersonal relationships and social functioning to help relieve symptoms and reduce distress.
Family therapy: improve communication, solve family problems, understand and handle special family situations, and create a better functioning home environment.
Exposure therapy: to help people overcome fears and anxieties by breaking the pattern of fear and avoidance.
12. Which of the following types of research studies is most likely to result in external validity?
A. Efficacy trials
B. Case-control study
C. Effectiveness trials
D. Cross-sectional study
E. Randomized controlled trials
C. Effectiveness trials

76. The test used to probe for cytochrome P450 polymorphisms uses which technology to identify genetic variants?
A. Karyotype analysis
B. In situ hybridization
C. Mass spectroscopy
D. Immunohistochemistry
E. Polymerase chain reaction
E. Polymerase chain reaction
PCR, or Polymerase Chain Reaction, can be used to identify CYP450 gene polymorphisms by amplifying specific DNA regions containing the polymorphism and then analyzing the amplified products.
27. Prenatal infection with which of the following has the most evidence for the risk of developing schizophrenia?
A. Rubella
B. Borna Disease
C. Epstein-Barr
D. Influenza
E. Respiratory Syncytial Virus
D. Influenza
Studies have shown a 7-fold increase in schizophrenia risk when maternal flu exposure occurs during the first trimester, though the overall risk remains relatively small.
52. A patient presents to the emergency room for sudden onset of weakness while traveling, as well as profuse sweating and shortness of breath with restlessness and mild confusion. Examination reveals twitching of the muscles and pupils are constricted but reactive. This condition is caused by toxicity of what substance?
A. Salicylates
B. Carbon monoxide
C. Diphenhydramine
D. Organophosphates
E. Synthetic cathinones
D. Organophosphates
1. According to Margaret Mahler's developmental theory of psychology, which of the following indicates a successful resolution of the process of separation-individuation in a toddler?
A. Trust
B. Intimacy
C. Object constancy
D. Normal symbiosis
E. Secondary individuation
C. Object constancy
25. A celebrity radio psychiatrist tells the listening audience that medications like alprazolam are often prescribed for insomnia. A radio listener obtains alprazolam 1 mg tablets from a friend. The listener takes four tablets, falls, and sustains a sprained wrist and a concussion. The listener is now suing the psychiatrist for malpractice. Which of the following is the most likely outcome of this case?
A. Psychiatrist will win because the patient was not sufficiently injured.
B. Patient will win because the concussion can have long-term effects.
C. Patient will win because the psychiatrist deviated from the standard of care.
D. Patient will win because the higher dose he took directly mediated the injury.
E. Psychiatrist will win because a doctor-patient relationship was not established.
E. Psychiatrist will win because a doctor-patient relationship was not established.
Normally, the doctor-patient relationship is formed when the patient seeks medical treatment and the doctor agrees to provide the treatment.
Doctors are under no legal obligation to undertake the medical care of a patient. Thus, doctors only have a duty of care to those they agree to treat.
17. Lesions to the orbitofrontal-subcortical circuit produce which of the following behaviors?
A. Placidity and apathy
B. Diminished libido
C. Disinhibition, impulsivity, and tactlessness
D. Hypergraphia, circumstantiality, and hypersexuality
E. Hyperreligiosity
C. Disinhibition, impulsivity, and tactlessness
The orbitofrontal-subcortical circuit is a brain network that plays a role in regulating complex behaviors, including decision-making, reward processing, and emotional control.

49. A patient undergoes a multiple sleep latency test (MSLT) and is diagnosed with narcolepsy. What finding on the MSLT would confirm the diagnosis?
A. Increased sleep latency
B. Decreased REM latency
C. Decreased total REM sleep
D. Increased total NREM sleep
E. Decreased sleep efficiency
B. Decreased REM latency
In individuals with narcolepsy, rapid eye movement (REM) sleep latency is significantly shortened. They enter REM sleep much earlier than normal, often within 15 minutes of falling asleep.
Shortened REM latency is a common finding in various psychiatric conditions, including depression, schizophrenia, and bipolar disorder.
SSRIs can increase REM latency.
122. What is the action of pramipexole in the treatment of restless legs syndrome?
A. 5HT2A agonist
B. a2-adrenergic agonist
C. D3 agonist
D. M1 agonist
E. MAO-B inhibitor
C. D3 agonist
In RLS, there may be insufficient dopamine or impaired dopamine signaling, leading to the urge to move.
Medications that increase dopamine activity (dopamine agonists) are sometimes used to treat RLS.
60. A 33-year-old woman reports feeling sad and experiencing symptoms of mild depression following the birth of her child four months ago. She reports distress about difficulty in making the change from working professional to mother. What psychotherapy was designed to address such changes?
A. Interpersonal therapy
B. Psychodynamic therapy
C. Dialectical behavior therapy
D. Cognitive behavioral therapy
E. Motivational enhancement therapy
A. Interpersonal therapy
Interpersonal Psychotherapy: improve a person's interpersonal relationships and social functioning to help relieve symptoms and reduce distress.
109. Which of the following statistical methods is most appropriate to control for multiple comparisons?
A. Bias correction
B. Bayesian inference
C. Bonferroni correction
D. Random forest classification
E. Support vector machine algorithm
C. Bonferroni correction
The Bonferroni correction is a statistical method used to adjust for multiple comparisons when conducting many statistical tests simultaneously. It helps control the risk of a Type I error, or false positive, by lowering the significance level (alpha) for each individual test.