What is the color of the stars with the lowest surface temperature?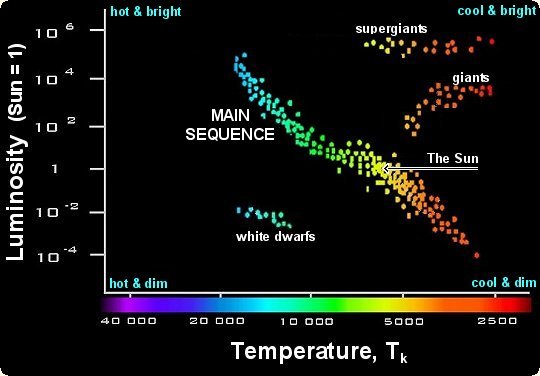 ?
?
Red
What determines how long a star will remain on the main sequence?
Mass or amount of Hydrogen
What is a supernova?
When a high mass red supergiant gravity collapses in upon itself.
What elements would be found in a class B star? 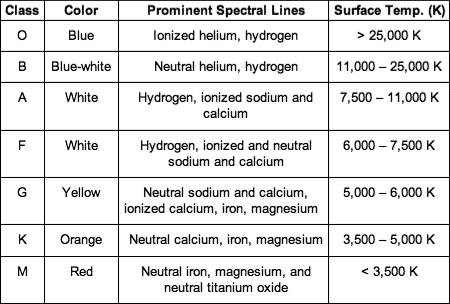
natural helium and hydrogen
A hot ball of glowing gases
A star
Where on the HR Diagram do you find the brightest stars? 
Top of the diagram
What is the luminosity of the sun?
1
A relatively small, dense star at the end of its life cycle, which generates little energy creating a faint white light.
What stage is this star in?
White Dwarf
Pollux is what type of star? 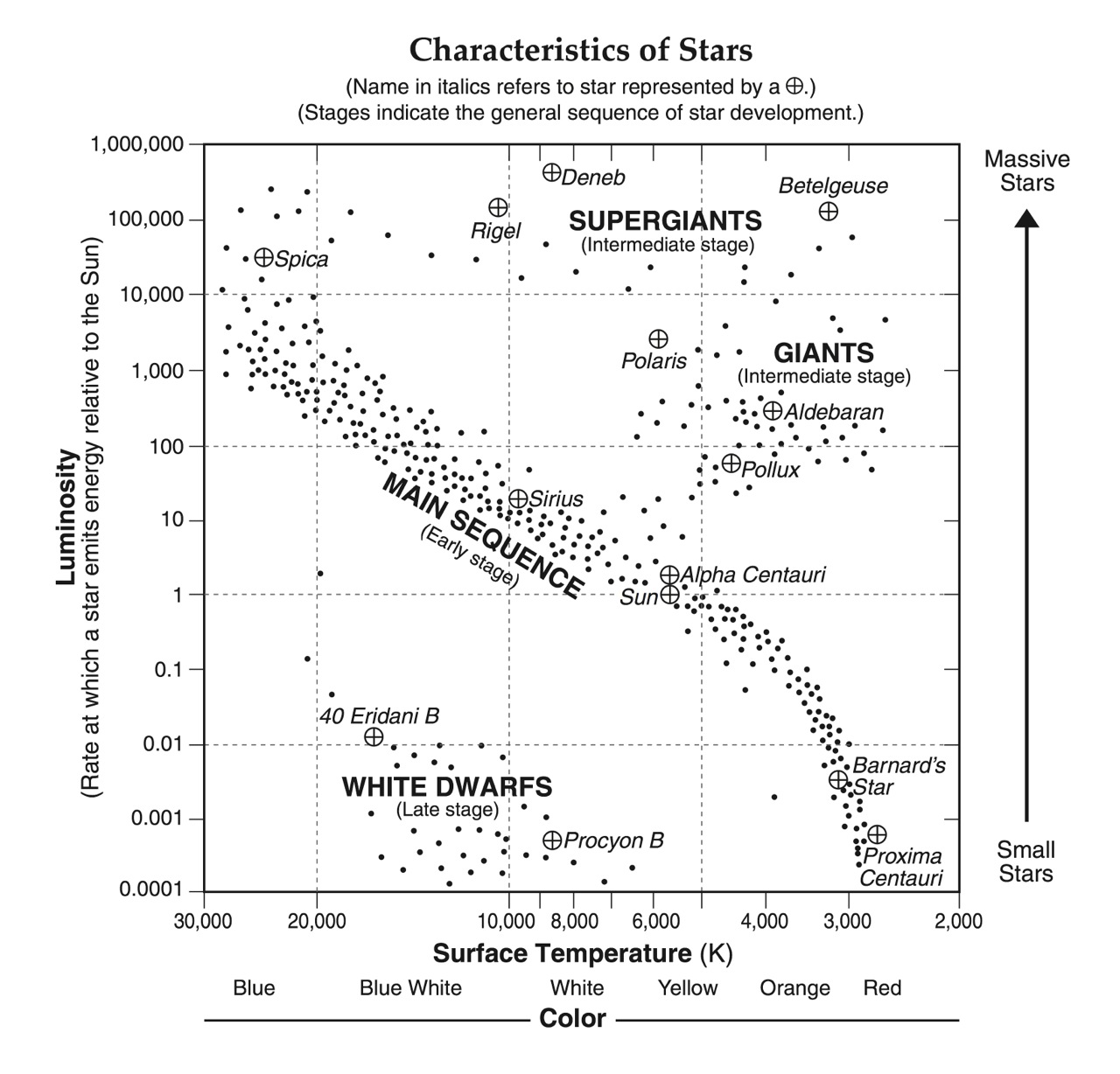
Giant
The closest star to Earth
The sun
What is the surface temperature of the sun?

About 6,000 K
What fuels stars?
Hydrogen fusion aka proton-proton fusion
What is a black hole?
A black hole is a place in space where gravity pulls so much that even light can not get out.
Which class of star in the life cycle of the star is the most dense?
neutron star
A group of stars that form a pattern
A constellation
Which type of stars have a high temperature and low luminosity? 
White Dwarfs
Why does the sun appear to be the brightest star?
The sun is the closest star to earth and so it seems brighter than distant stars
A very large star of high luminosity and low surface temperature. These stars are thought to be in a late stage of evolution when no hydrogen remains in the core to fuel nuclear fusion.
What stage in the life cycle does this describe?
Red Giant
What it the horizontal band on the HR diagram where most stars spend their life?
Main sequence
How bright the star is based on its distance from the Earth
Apparent Magnitude
The least amount of the stars on the HR Diagram are classified as what type of stars?
White Dwarfs
What color are the hottest stars?
Blue
The process begins when a nebula starts to shrink, then divides into smaller swirling clumps. Each clump becomes ball shaped and it continues to shrink the material in it as it gets hotter and hotter. When the temperature reaches 18 million degrees Fahrenheit, a massive explain called nuclear fusion occurs.
The above process is describing what?
A birth of a star
Where are stars created?
Nebulas
How bright the star truly is based on the amount of light it emits
Absolute Brightness