The property(ies) responsible for surface tension

Cohesion.
Water's ability to stick to itself allows it to create a smooth and somewhat durable surface (at least for small insects and paper clips).
Which is less dense, solid ice or liquid water?
solid water (a.k.a ice) is less dense then water and it floats
will NaCl will dissolve in water?
It WILL!
NaCl (table salt) will dissolve in water because it is an ionic compound.
A substance with a pH of 4.5
An acid
This property explains how the sand at the beach can feel hot, while the water at the same beach remains cool
High specific heat capacity
Ribosome
The property(ies) demonstrated by pouring water down the string.
Both.
Adhesion as the water stuck to the string.
Cohesion as the water stuck to itself.
Which is less dense?
Hot water or cold water?
Hot water.
For some strange reason, hot water is less dense than cold water.
Will an acid will have a pH above 7?
It Won't!
Acids will have a pH below 7.
What is the pH of pure water?
7
This property allows aquatic life to survive the winter.
Lower density of ice (solid water floats)
Name that bond.
Sharing of valence electrons between two atoms.
Covalent bond
The property(ies) responsible for capillary action

Both.
Adhesion- as the water sticks to the sides of the tube
Cohesion- each water molecule sticks to itself and pulls molecules below up the tube.
Which is less dense?
Ice or Hot water
Ice.
Solid water is still less dense than liquid water, even if the water is hot.
Will polar molecules will dissolve in water.
They Will!
Water can dissolve other polar molecules.
A solution that has more OH- ions than H+
A Base
The property that keeps plants hydrated.
Capillary action due to adhesive and cohesive properties.
Unequal sharing of valence electrons between atoms.
Polar covalent bond.
What property(ies) are exhibited here.

Cohesion
Water sticking to itself allows for water to "pile" up and create a bead.
Which is less dense?
Water vapor (water in it's gas state) or Ice?
Water vapor.
Even though Solid water (ice) is less dense than liquid water. Water vapor is the least dense (most spread out) state that water can take.
Will pure water have an even number of hydrogen ions and hydroxide ions?
It will and it does!
pure water has a neutral pH because there is a balance of charge due to equal proportions of hydroxide (OH-) and hydrogen (H+) ions.
On the pH scale, where can you find the strong acids and the strong bases?
The ends.
Strong Acids are at 0
Stong Bases are at 14
The property that helps cool the body.
High specific heat.
Sweat on the skin can absorb a lot of heat before it evaporates altogether. This means that more heat can be pulled away from the body to help keep it at a constant temperature (i.e. homeostasis).
The gateway into or out of a cell
(found in both prokaryote and eukaryotes)
Cell membrane
The bonds that form between water molecules allow for their cohesive properties.
Hydrogen bonds.
Though fairly weak, the bonds formed between the slightly positive hydrogens and the slightly negative oxygens are what allow water molecules to "stick" to each other.
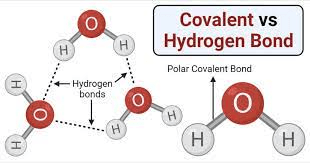
Which is less dense?
Pure water or saltwater?
Pure water.
Saltwater has salt dissolved into it, meaning there are more total atoms in any given volume of water (the way to calculate density is mass/vol. The dissolved salt adds more mass and thus makes the water denser)
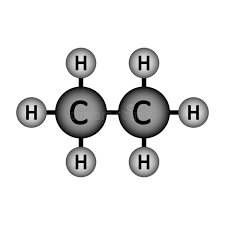
Will Ethane (pictured below) dissolve in water?
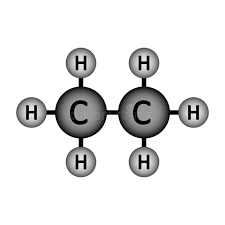
Won't!
Ethane is a non-polar molecule (because it is symmetrical). Non-polar molecules do not dissolve in water.
40x
each pH increment is 10x the concentration of ions (OH- or H+ depending).
This property of water is not unique to water itself but is the property that is ultimately responsible for adhesion, cohesion, and the ability to dissolve certain substances and even pH.
Polarity
The uneven distribution of charge within the water molecule is the driving force behind most of the unique properties of water.
List the sequence of events (and the organelles involved) in the formation and transportation of proteins.
DNA is copied into RNA inside the nucleus leaves the nucleus and enters the Endoplasimc reticulum. It attaches to a ribosome that then makes the protein. The protein is "packaged" in a vesicle in the Golgi body before it is sent out to where ever it is needed inside or outside the cell.