The location this molecules is found in eukaryotic cells.

Nucleus
Identify the DNA structure that holds the instructions to build a protein.
Gene OR Nitrogen Bases
Identify the following:
1. Where transcription occurs.
2. The result of transcription.
1. Nucleus
2. mRNA
Do all mutations result in a change in the protein?
No - some mutations are "silent"
Identify what binds to the promotor of an operon to start transcription.
RNA polymerase
Identify the complementary second strand of DNA.
T A G C A T C G G
A T C G T A G C C
Proteins are polymers made up of what monomer?
Amino Acids
Identify the following:
1. The site of translation
2. The result of translation
1. Ribosome (rRNA)
2. Protein
Between point mutations and frameshift mutations, name the THREE types of mutations.
Substitution, Insertion, & Deletion
Identify the molecule that is produced that is responsible for a trait being expressed. Examples include eye color or the ability to "glow"
Protein
The TWO polymers that are made up of the following monomer.
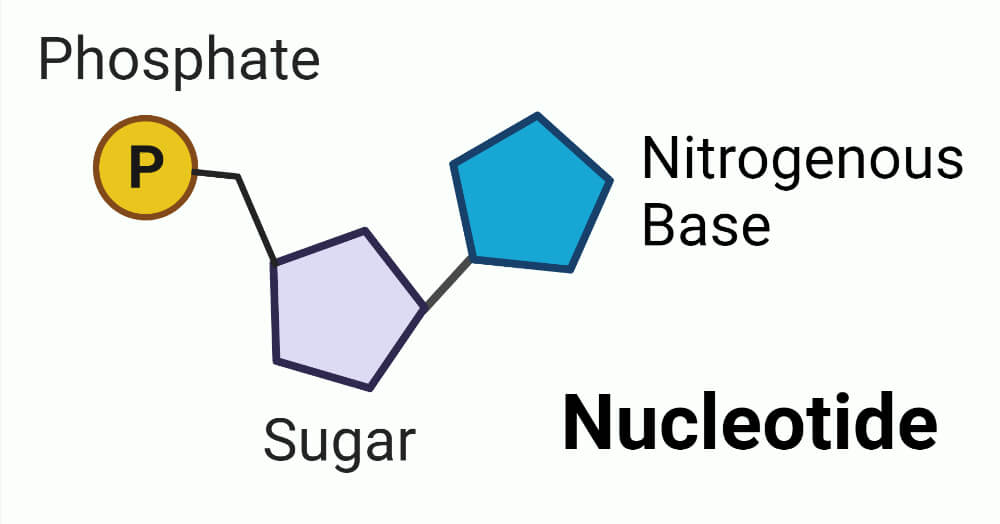
DNA and RNA
How many amino acids are coded for by 15 nitrogen bases?
15 / 3 = 5
5 codons = 5 amino acids
Transcribe the following
C A T T G C A G A
G U A A C G U C U
Describe the change mutations can cause to a protein and how it influences the outcome.
Amino acid sequence is altered and cause the protein to fold into a different shape, impacting the function of the protein.
Answer the following:
1. If a gene is expressed, does that mean the gene is turned on or off?
2. What is the end result of gene expression?
1. Turned on
2. A protein is being made and therefore the trait can be seen
1. Identify the SPECIFIC names of each type of RNA. 2. In detail, describe each of the functions of RNA.
Messenger RNA - carries the DNA message from the nucleus
Ribosomal RNA - creates the ribosome where translation takes place
Transfer RNA - carries the amino acid and links to the mRNA to build the chain
Identify TWO differences between mRNA & tRNA.
mRNA carries the genetic message and tRNA molecules carry amino acids.
mRNA has codons while tRNA has anticodons.
Identify the amino acid sequence for the following mRNA sequence.
AUG CCU AUG GGU UUA ACU UAA
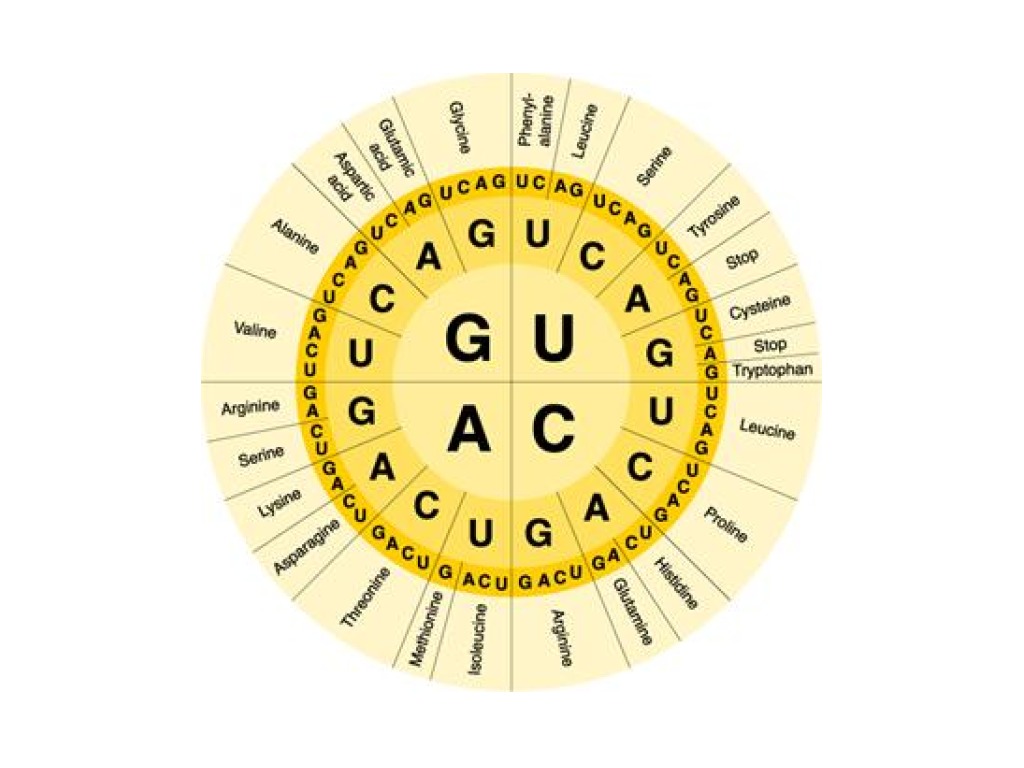
met – pro – met – gly – leu – thr – stop
An original sequence has 359 bases, when mutated it has 357 bases.
Identify the type of mutation that created this sequence and explain your decision.
It is a deletion mutation because the mutated sequence has LESS bases than the original, therefore nitrogen bases were removed.
In an operon system of bacteria, for the targeted protein to be created describe what must happen to turn the gene on.
The inducer must bind to the repressor, to lift the repressor off of the operator and turn the gene on.
Identify 3 differences between DNA and RNA.
DNA RNA
- A-T G-C A-U G-C
-nucleus only nucleus and cytoplasm
-double strand single strand
-deoxyribose ribose
1. Describe what is happening in this cellular process.
2. Identify each of the following labels in your description.
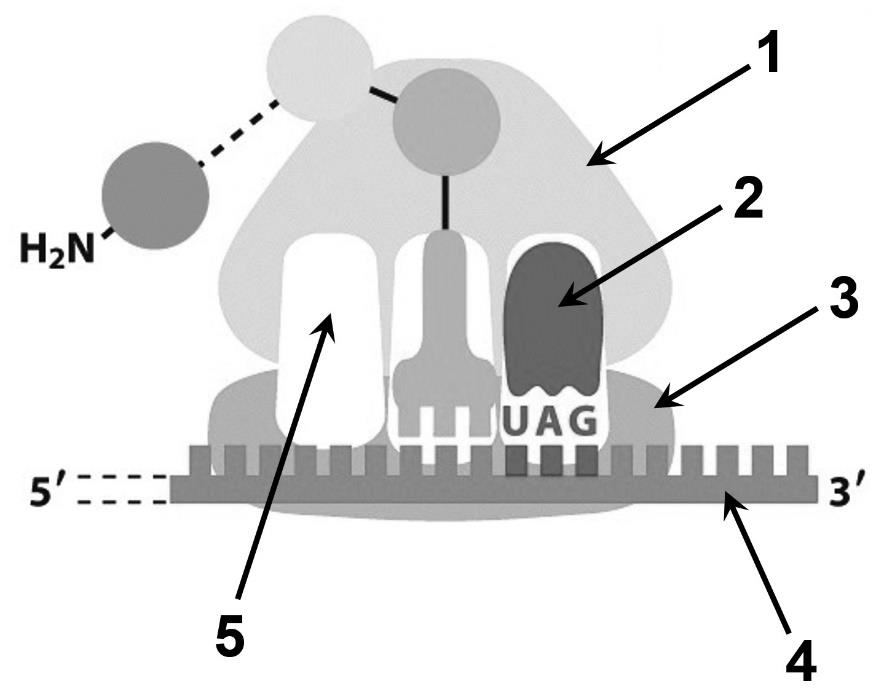
The process of translation - mRNA (4) traveled into the cytoplasm to the site of a ribosome, make up of a large subunit (1) and small subunit (3). As the mRNA is read, the tRNA (5) anticodons match the the mRNA codons to deliver amino acids. This continues until a stop codon (2) is reached and the protein is finalized.
Reverse transcription is a process that some viruses utilize. Using your understanding of transcription, identify the starting and resulting molecules of this process.
RNA to DNA
Explain why the addition or deletion of TWO nitrogen bases is more impactful to the DNA reading frame in comparison to the addition or deletion of THREE nitrogen bases.
Codons are read in a triplet sequence.
When you add or delete two bases, you end up shifting bases out of the intended reading frame, resulting in a frameshift mutation.
Why do cells regulate the expression of its genes.
To conserve energy and resources or because it doesn't need that particular protein at that time.