What are the three main particles that make up an atom?
What are protons, neutrons, and electrons?
Define an isotope.
What are atoms of the same element with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons?
Which force keeps us on Earth and makes objects fall at 9.8 m/s²?
What is gravity?
What does the Aufbau Principle say about how electrons fill orbitals?
What is electrons fill the lowest-energy orbitals first?
Write the electron configuration for hydrogen (H, atomic number 1).
What is 1s¹?
How old is Glendale High School
124 years old
Which particle decides the identity of an element (like its “name tag”)?
What is a proton?
What makes a sodium atom become Na⁺?
What is losing one electron?
Which fundamental force holds electrons around the nucleus?
What is the electromagnetic force?
How many electrons can fit in each orbital?
S:2
P:6
D: 10
F:14
Write the electron configuration for oxygen (O, atomic number 8).
What is 1s² 2s² 2p⁴?
A butcher has a size 13 foot and is 6 feet tall, what does he weigh?
meat
An atom has 8 protons and 8 neutrons. What is its mass number?
What is 16?
DOUBLE JEOPARDY!!!!
Which isotope of carbon is used in radioactive dating, and how does it differ from carbon-12?
What is carbon-14, which has 2 more neutrons than carbon-12?
Which nuclear force allows neutrons to turn into protons, causing radioactive decay?
What is the weak nuclear force?
What is this a picture of?
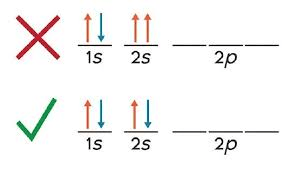
Pauli Exclusion Principle
Write the electron configuration for calcium (Ca, atomic number 20) in noble gas shorthand.
What is [Ar] 4s²?
"Have it your way” is the memorable slogan of what fast food restaurant?
Burger King
If an element has a neutral charge, the number of protons equals?
What is, the number of electrons
Write the ion for oxygen when it gains 2 electrons.
A: What is O²⁻?
Why is the strong nuclear force necessary inside the nucleus?
What is because it overcomes proton–proton repulsion and holds the nucleus together
What is this a picture of?
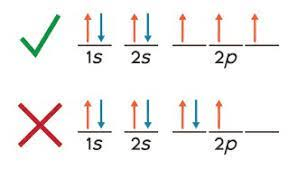
Hund's Rule
Write the electron configuration for iron (Fe, atomic number 26). Long hand only.
What is 1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s² 3p⁶ 4s² 3d⁶
What university did Mr. Chan go to?
CSUN
Compare the relative masses of protons, neutrons, and electrons. What is the mass of each subatomic particle with units?
Protons ≈ 1 amu, Neutrons ≈ 1 amu, Electrons ≈ 1/1836 amu → mass is concentrated in nucleus
What are cations? And what are Anions?
Cations are positively charged ions Anions are negatively charged ions
Rank from 1-4 the strongest forces to the weakest forces, with 1 being the strongest forces.
💥 Strong Nuclear Force
⚡ Electromagnetic Force
☢️ Weak Nuclear Force
🌍 Gravitational Force
DOUBLE JEOPARDY!!!!!!
How did Mr. Chan explain this picture in terms of going to school?
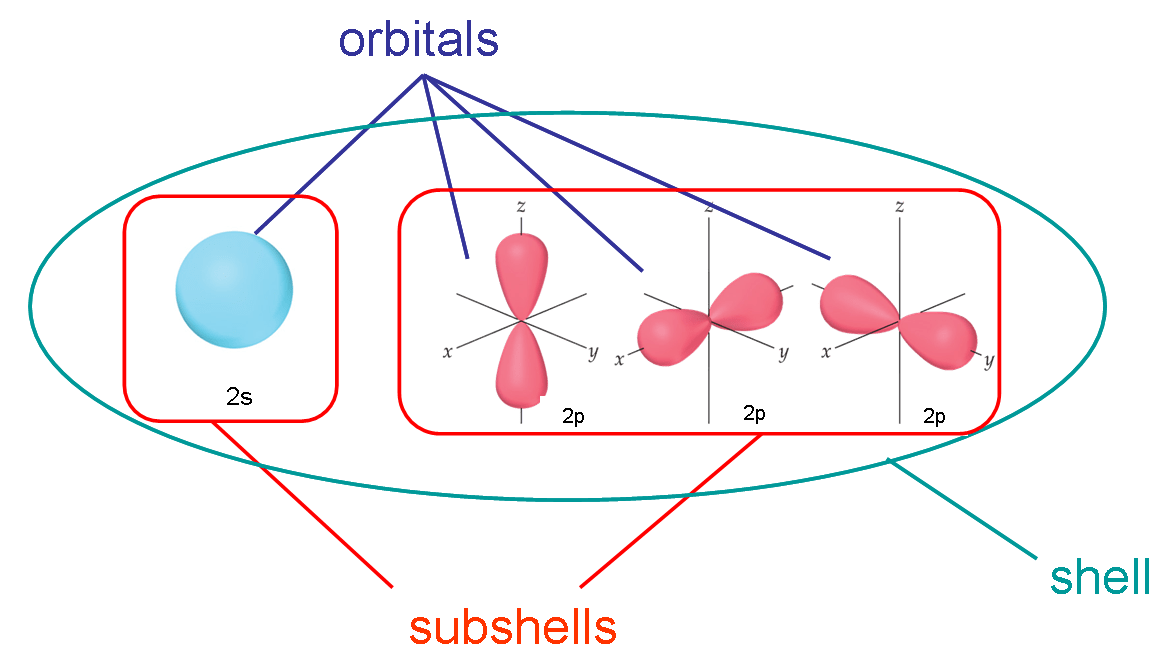
Think of a shell as a floor in a building, subshells as different types of rooms on that floor and an orbital as a specific room within that type.
Write the electron configuration for Tin (Sn, atomic number 50). Long hand only.
1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s² 3p⁶ 4s² 3d¹⁰ 4p⁶ 5s² 4d¹⁰ 5p²
DOUBLE JEOPARDY!!!!
According to Instacart, what the most disliked food in America?
Anchovies