What is the formula for gravitational potential energy?
PE=mgh, where mm is mass, gg is gravity, and hh is height
What is the difference between transverse and longitudinal waves?
Transverse waves oscillate perpendicular to wave direction; longitudinal waves oscillate parallel.
What determines the pitch of a sound? How is this different from loudness?
Frequency determines pitch; higher frequency means higher pitch. Amplitude determines loudness.
What is the unit of electrical resistance?
Ohm (Ω)
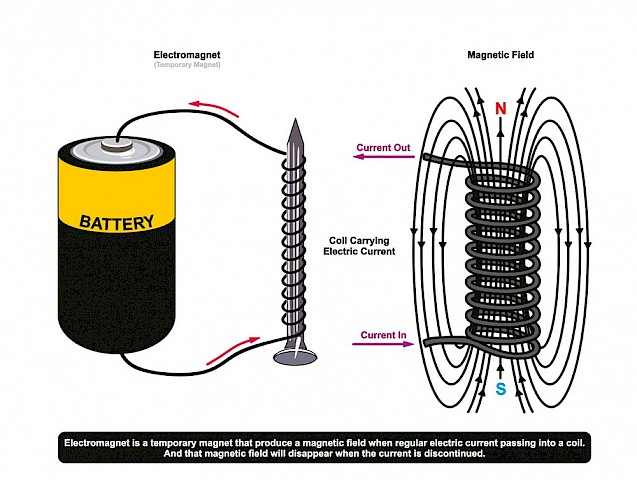
What is a magnetic field?
A region around a magnet where magnetic forces are exerted.
Explain how energy is conserved in a roller coaster
Throughout the ride, potential energy at the top of hills converts to kinetic energy as it descends, with total mechanical energy conserved minus losses due to friction.
Define and contrast wavelength and frequency.
Wavelength refers to the distance between two consecutive points on a wave that are in the same phase (like crest to crest), while frequency represents the number of complete wave cycles that pass a fixed point in a given unit of time
What is the Doppler effect?
The change in frequency or wavelength of a wave in relation to an observer moving relative to the wave source
How is electric power calculated?
Electric power is calculated as P=IV, where P is power, I is current, and V is voltage.
What causes a material to become magnetized?
To store and release electrical energy in a circuit.
Describe the energy transformations when a ball is thrown up into the air.
Kinetic energy is converted into potential energy as the ball rises and returns to kinetic as it falls back down.
What is amplitude in a wave?
Amplitude is the maximum displacement from the rest position.
Explain how sound waves differ from electromagnetic waves
Sound waves are mechanical and require a medium; electromagnetic waves do not.
Explain the role of a fuse/circuit breaker in an electrical circuit.
To automatically stop the flow of electricity if the current is too high/circuit is overloaded.
How does a generator use magnetism to produce electricity?
A generator converts mechanical energy into electrical energy by rotating a coil of wire within a magnetic field.
What is the energy transformation in a wind turbine?
Kinetic energy of the wind is converted into mechanical energy, then into electrical energy.
Define constructive and destructive interference
Constructive interference occurs when waves combine to increase amplitude; destructive reduces amplitude.

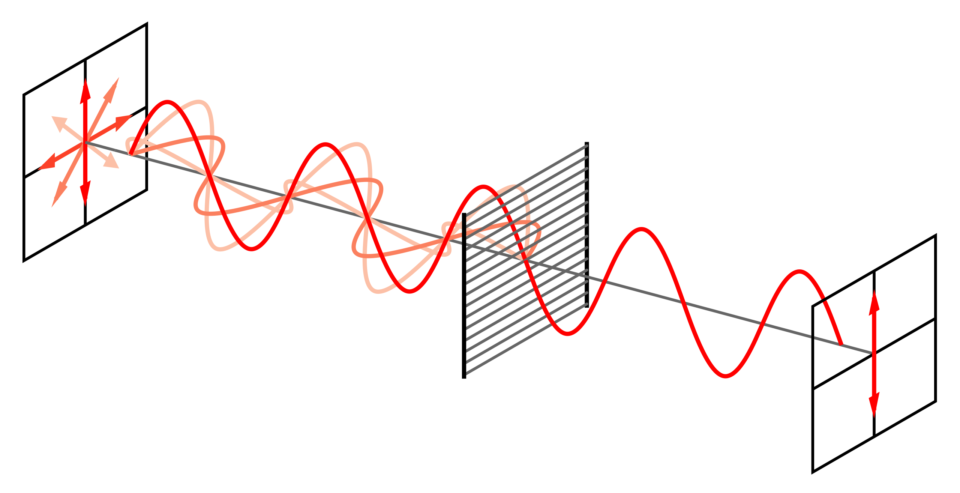
How do polarized sunglasses work?
They filter light waves to reduce glare by blocking certain light orientations.
Explain the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance.
Ohm's Law: V=IR, where V is voltage, I is current, and R is resistance.
Describe the differences between permanent magnets and temporary magnets.
Permanent magnets retain their magnetism, while temporary magnets lose their magnetism when the external magnetic field is removed.
A 10 kg object is lifted to a height of 5 meters. Calculate the gravitational potential energy of the object. Assume the acceleration due to gravity is 9.8 m/s29.8m/s2.
The gravitational potential energy is 490 Joules.
- Potential energy (PE) is given by the formula: PE=mgh
- PE = 10 kg × 9.8 m/s2 × 5 m = 490 J
A wave has a frequency of 50 Hz and a wavelength of 2 meters. Calculate the speed of the wave.
The speed of the wave is 100 meters per second.
- Wave speed (v) is calculated as: v=fλ
- v = 50 Hz × 2 m = 100 m/s
Describe how diffraction affects the behavior of light waves when they pass through a narrow opening.
Diffraction causes light waves to spread out as they pass through a narrow opening, potentially leading to interference patterns.
How do series and parallel circuits differ?
Series circuits have one path for current; parallel circuits have multiple paths.
What is the purpose of a solenoid?
A solenoid is a coil of wire that generates a magnetic field when current flows through it, often used in electromagnets.