If Troy’s behavior is viewed as active and self-determining, he would be perceived as demonstrating the __________ model of behavior.
(A) _______________ research deals with objectively measurable data, while (B)________________ research focusses on nonnumerical data, suc as subjective experiences, feelings, or beliefs.
(A) QUANTITATIVE
(B) QUALITATIVE
During the embryonic stage, babies are most vulnerable to this RANGE OF HARMFUL ENVIRONMENTAL SUBSTANCES which can pass through the placenta and may potentially cause birth defects.
What are TERATOGENS?
In aging adulthood, (A)________ _________ increases as (B)__________ __________ decreases.
What are (A) CRYSTALLIZED INTELLIGENCE and (B) FLUID INTELLIGENCE?
Research indicates that this PARENTING STYLE that blends respect for a child's individuality with an effort to instill social values through high levels of expectation and responsiveness (identified by Baumrind) is associated with positive outcomes such as higher levels of independence, self-sufficiency, social acceptance, and academic success.
What is AUTHORITATIVE PARENTING?
The primary DOMAINS of development we have studied in this course.
What are physical, cognitive and psychosocial development?
This theoretical perspective asserts that qualitative changes in thought occur between infancy and adolescence and that children are active initiators of development.
What is PIAGET'S COGNITIVE STAGE THEORY?
The chief advantage of experimental methods over case studies, ethnographic studies, or correlational studies is that they are ___________________.
What is BETTER ABLE TO DETERMINE CAUSE AND EFFECT?
(Also: highly controlled and can be repeated by another investigator.)
If Laurie has a trait, but neither of her parents exhibits this inherited trait, the trait must be __________ .
RECESSIVE
When 16 month-old Annie begins searching for an object that is partially hidden, she is demonstrating some concept of _________ ____________.
According to Parten, this type of play occurs when a child plays independently but among other children (beside but not with other children).
What is PARALLEL PLAY?
The scientific study of processes of change and stability throughout the human life span.
What is human development?
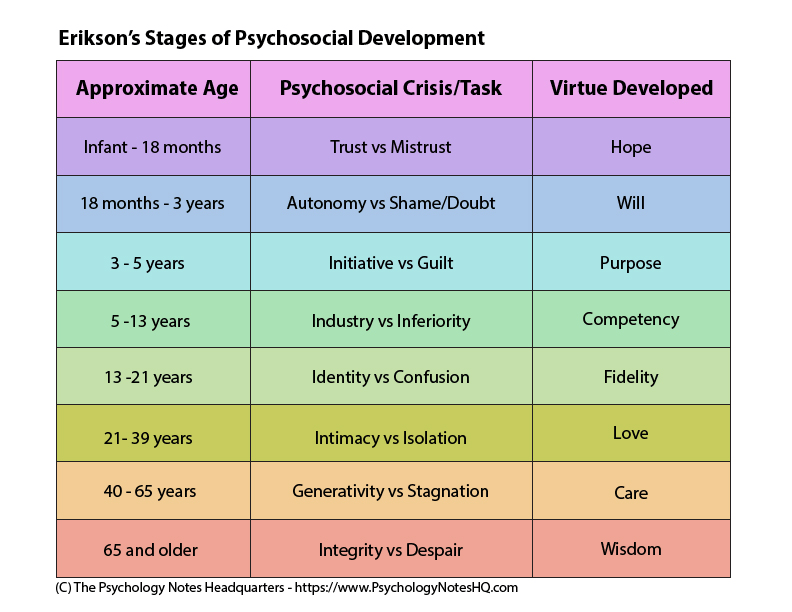
This psychoanalytic theory asserts that personality is influenced by society and develops through a series of crises.
What is ERIKSON'S PSYCHOSOCIAL THEORY?
In an experiment, Professor Daley manipulates the (A)__________ variable and then looks for an effect of that manipulation by measuring the (B)___________ variable.
What is (A) INDEPENDENT VARIABLE and
(B) DEPENDENT VARIABLE
Physiological signs of sexual maturation observed in puberty such as breast and muscle development, voice changes, and growth of pubic and facial hair.
The second level of Kohberg's theory of moral reasoning, typically reached after age 10, in which standards of authority figures are internalized and people are concerned about being "good," pleasing others, and maintaining the social order.
What is CONVENTIONAL MORALITY (or morality of conventional role conformity)?
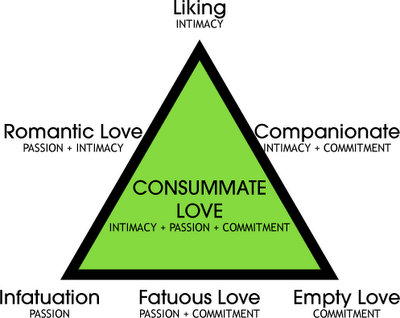
According to STERNBERG'S TRIANGULAR THEORY OF LOVE, there are three elements of love that together contribute to what he terms Consumate or Complete Love.
What are INTIMACY, PASSION, and COMMITMENT?
John is 15 years old his friends peer pressure him into repeatedly skipping school. As a result, John's grades at school suffer, and he eventually fails several classes. This is an example of an interaction between these two domains of development.
What are COGNITIVE and SOCIAL (psychosocial)?
This contextual theory asserts that development occurs through interaction between a developing person and five surrounding, interlocking contextual systems of influences, from microsystem to chronosystem.
What is BRONFRENBRENNER'S BIOECOLOGICAL THEORY?
Dr. Metzger has found in his research that when one variable increases, the other decreases.
What is a NEGATIVE (or inverse) CORRELATION between two variables?
A mechanism triggered by the environment that affects gene expression by turning genes on or off and determines functions of body cells without affecting the structure of the cell's DNA.
What is EPIGENISIS?
SENSORIMOTOR, PREPOPERATIONAL, OPERATIONAL, and CONCRETE.
What are PIAGET'S STAGES OF COGNITIVE DEVELOPMENT?
According to Costa and McCrae's FIVE FACTORS OF PERSONALITY model, personality development continues throughout the lifespan with the most change occurring between adolescence and age 30. However, these two traits tend to continue to increase with age.
What are AGREEABLENESS and CONTIENTIOUSNESS?
Share a NORMATIVE HISTORY-GRADED INFLUENCE that has shaped the behavior and attitudes of your HISTORICAL GENERATION.
???
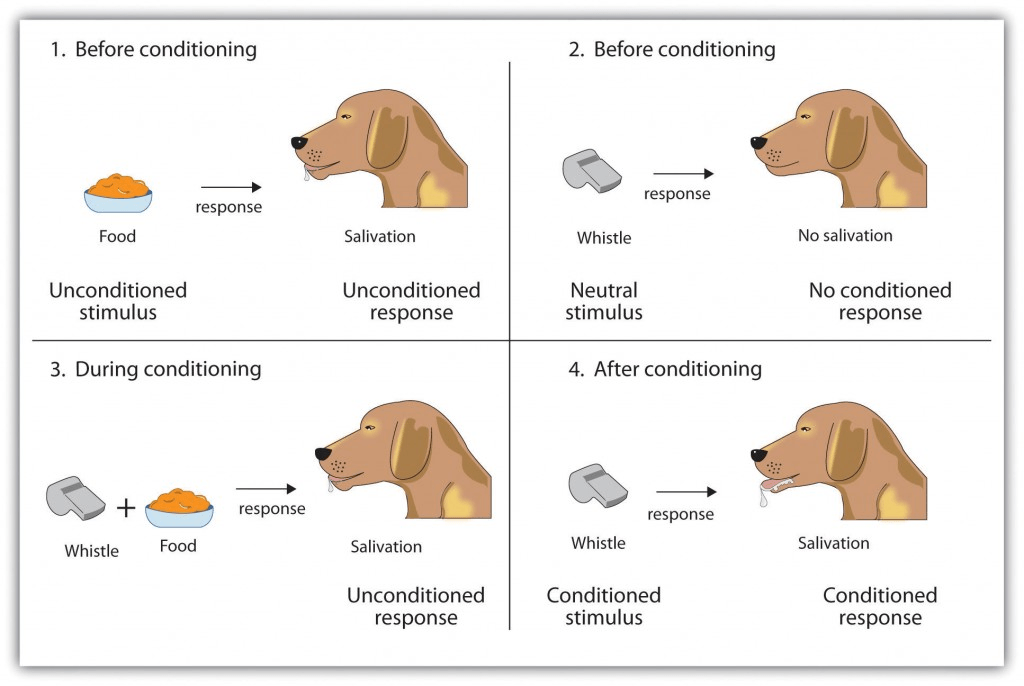
You have five minutes. In your group, draw/diagram the process of classical conditioning, then recreate your drawing/diagram on the board to explain the principle to the class.
This type of research design can show age-related change or continuity but is time-consuming, expensive, and has a high risk of attrition.
What is a LONGITUDINAL STUDY?
In normal brain development, the loss of gray matter results from (A)_____________, while the increase in white matter is associated with (B) _____________.
What are
(A) SYNAPTIC PRUNING and
(B) MYELINATION.
This approach uses brain scans to determine which brain structures are associated with cognitive function and to chart developmental changes which indicate that neurological maturation is a major factor in cognitive development.
What is COGNITIVE NEUROSCIENCE?
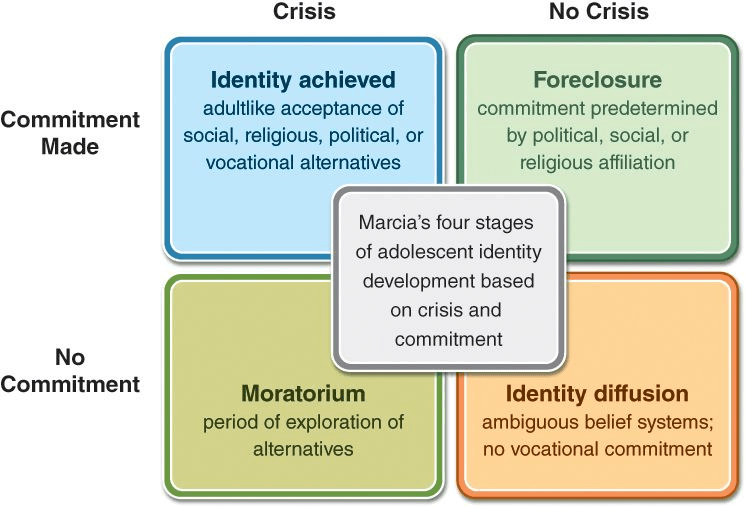
Draw a diagram illustrating MARCIA'S THEORY OF IDENTITY STATUS.
A critical period is known as a period of time when an organism is most likely to be influenced by a specific event. However, because many aspects of development have been found to show ____________, many researchers have replaced the term "critical period" with "sensitive period."
What is PLASTICITY?
Name three important theorists who are proponents of the LEARNING perspective of human development.
Who are:
(Behaviorism) PAVLOV, WATSON - classical conditioning; SKINNER - operant conditioning
(Social Cognitive Learning Theory) BANDURA
(5 minutes)
List five examples of SENSCENCE.
List at least five influences on school achievement in middle childhood.
(p. 283-284)
self-efficacy beliefs, gender, parenting practices, socioeconomic status, peer acceptance, educational methods, class size, educational innovations, media use.
Appropriately identify four of ERIKSON'S STAGES OF PSYCHOSOCIAL DEVELOPMENT, including the approximate age of development and the virtue developed through successful resolution of the crises.
Name five influences on development.
What are...
heredity? environment? maturation?
contexts of development (family; SES; neighborhood; culture, race, and ethnicity; historical context)?
normative and non-normative influences (age-graded or history graded)?
Timing of influences (critical or sensitive periods)?