The conceptual definition of conditional probability.
What is... The likelihood of one event occurring DEPENDS on the occurrence of some other event?
p(A┃B) = # of observations favoring A and B divided by # of observation favoring only B.
Define the concept of power.
Note: For this unit, as you did not cover it yet, you will only be expected to know the definition for exam 2. You will most likely calculate power next time.
What is...
The probability of correctly rejecting a false null hypothesis when you should.
Define the 3 components of the Central Limit Theorem.
What is...
1. As N approaches infinity, our standard error decreases in magnitude, and our standard deviation = standard error.
2. As N approaches infinity, our mean will = mu
3. As sample size increases, shape of the distribution will approach normality.
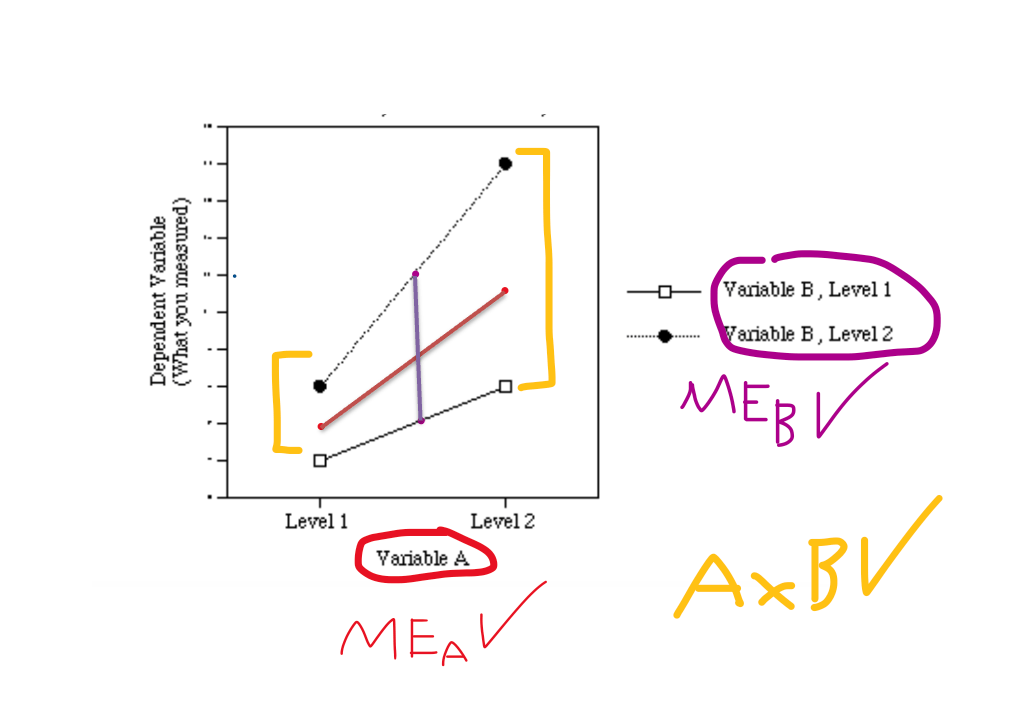
Define main effect (utilizing lecture definition).
A main effect is the differences in the level of one independent variable collapsed across, averaged across, or better yet, IGNORING a second independent variable.
In a psychology experiment, participants are asked to guess whether a card drawn from a deck is red or black. If a participant guesses for 10 cards, tell me the probability that they guess exactly 7 cards correctly.
Remember how to find mu, standard deviation, and to focus on the wording when it says "EXACTLY 7 cards." This will concern upper and lower real limits. You probably will NOT get a hint like this on the test, so try to remember the differences when you are asked "Exactly" "Greater" or "Less than."
TA helpful hint (maybe): When a question asks you the probability of getting more than a certain number, you include the lower real limit of that number. When a question asks you to find the probability of getting less than something, you include the upper real limit of that number.
Draw it out on the curve and it will make sense. For instance, if instead I were to ask you the probability of getting more than 7 guesses correctly, you would use 6.5 as the lower real limit. Once you calculate the Z-score, refer to the unit normal table, and shade in the area to the right (remember, the wording--MORE), this will include 7 in that. If you were to use the upper-real limit of 7.5, you would be mistaken as it would not include 7 in that boundary.
Hope that makes sense. Back to the question with asking you to calculate the probability of getting 7 guesses correct...
Mu =pn
SD = square root of npq.
X = 7.
What is...
The probability of guessing red or black is 0.5. There is a fifty-fifty chance of guessing here. The probability that they will guess correctly (p) is 0.5. The probability they will guess incorrectly is also 0.5 (q)
Number of trials (n) = 10.
p * n (or pn) = 5. This is our mu.
SD = square root of (0.5)(10)(0.5) = 1.5811388. Rounded = 1.58.
p(7) right by chance = find the upper and lower limits of z score.
For URL: 7.5 - 5/1.58
URL: 2.5/1.58
URL: +1.58.
For LRL: 6.5 - 5/1.58
LRL: 1.5/1.58
LRL: +0.95.
Since these are on the same side as the mean, we subtract their respective column Ds to find the area.
Column D for 1.58 = .4429
Column D for 0.95 = .3289
Area: .4429 - .3289 = 0.114
0.114 * 100 = 11.4%.
Tell me the likelihood that someone with a Bachelor's degree is satisfied given that they are satisfied in a relationship.
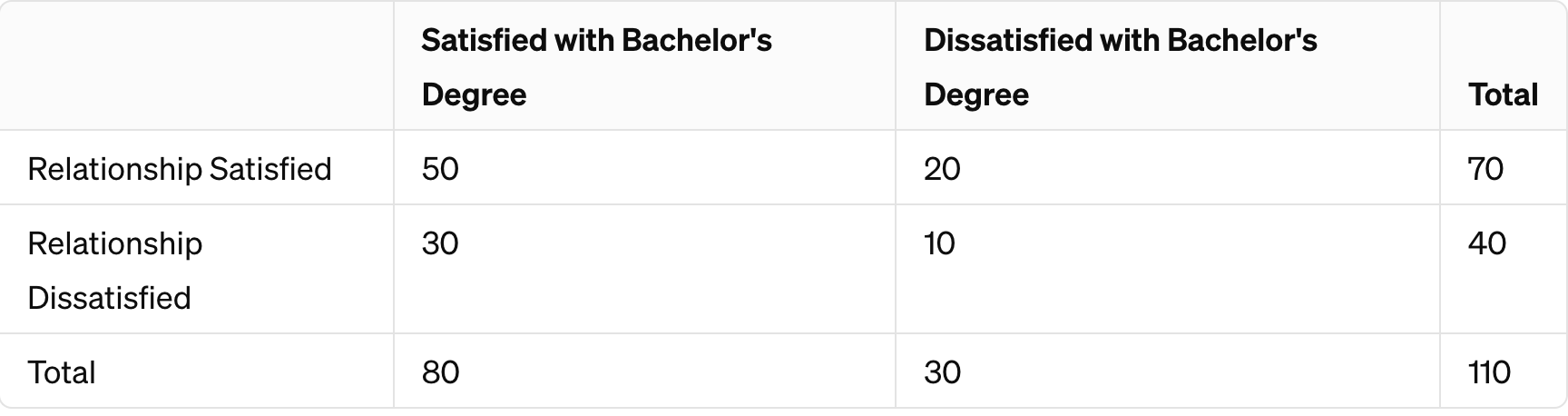
What is...
Satisfied with Bachelor's GIVEN satisfaction with Relationship = 50.
Satisfied with relationship only: 70.
p(A┃B) = 50/70 = 0.7142857
= 0.71% of those satisfied with Bachelor's degree given that they are also satisfied with relationship.
The assumptions for performing a Z-test.
What is...
1. Has a normal distribution.
2. The SD is unchanged (we know the population standard deviation as such).
3. Independent observations.
4. Randomized sample.
Define the Law of Large Numbers.
What is...
The Law of Large numbers specifies that the bigger N (sample size) we have, the more likely it is that the sample mean will be close to the population mean. The error between the sample mean and population, as such, decreases.
Define interaction (utilizing lecture definition).
What is...
An interaction is a difference across the levels of one independent variable that differs across the levels of the second independent variable.
You are playing a card game where there are 10 face-down cards, each with either a red or black face. You know that 60% of the cards are red, but you don't know which ones. Your task is to guess whether each card is red or black. After guessing, you will flip the card to check if you're correct.
You will earn points based on the number of correct guesses you make. You want to know the probability of getting more than 6 correct guesses out of 10.
First, determine if you will use the upper real limit of x, the lower real limit, or both, based on what the question is asking.
Second, determine p (probability of success) and q (probability of failure) from question.
Third, determine the number of trials.
This information should help you find the mean and standard deviation. Good luck.
What is...
First, I figured out that "getting more than X" would mean to refer to the lower real limit of 6. This is because we when we shade to the right on the distribution, 5.5 will include 6 in that boundary.
Second:
Number of trials = 10
P = 0.60
Q = 0.40
Use this information to find the population mean:
P * n = mu
0.60 * 10
= 6
Now, to find the standard deviation...
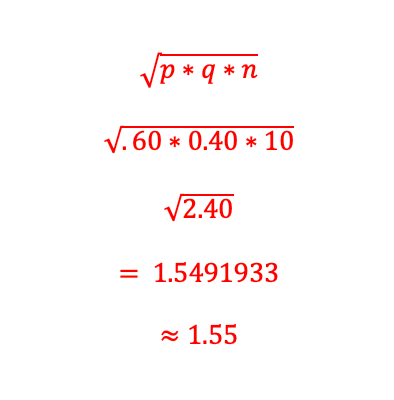
We know the values of X (use LRL of 6 which is 5.5), as well as the population mean (6) and the standard deviation (1.55), plug these bad boys into the Z-score formula below to locate the Z-score. This will also help determine which column we use for the unit normal table, and again, when seeing the words "more than," we are shading to the RIGHT.
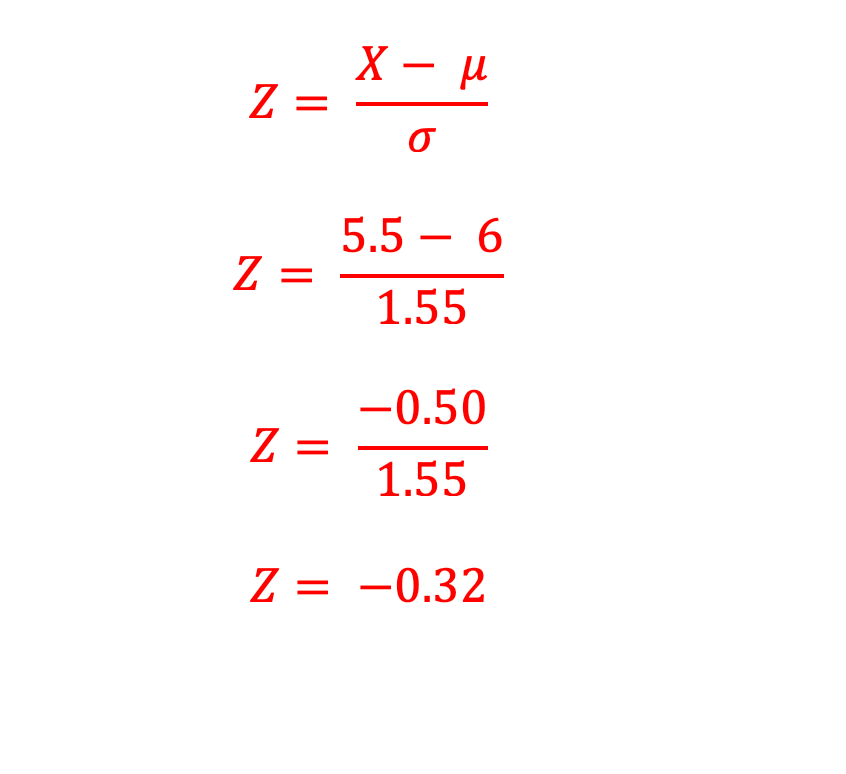
If you draw out a distribution curve, you would see that -0.32 is on the left side of the distribution. Shading to the right would mean you would refer to column B of the unit normal table, which is the body. The body is the larger portion--in case you needed a traumatic reminder from your time in 260 and calculating Z-scores.
Proportion of body corresponding to Z = 0.32 is 0.6255.
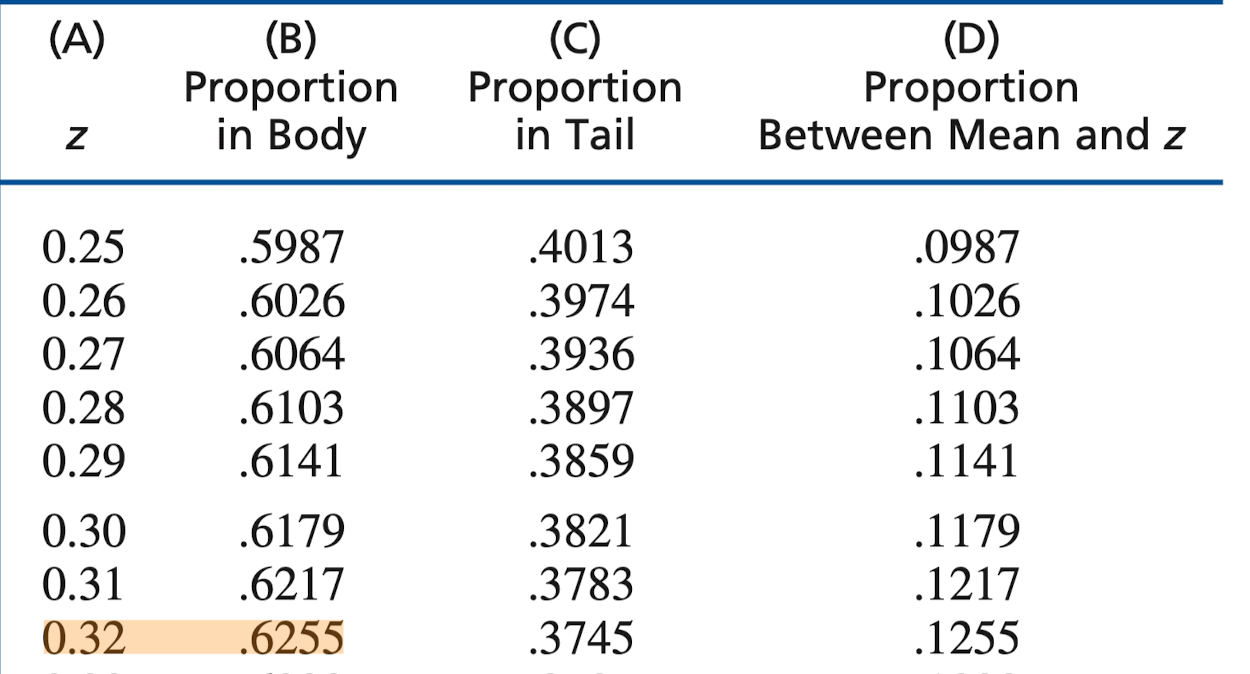
The probability of getting MORE than 6 guesses correct is 62.55%.
Tell me the probability of someone being dissatisfied with a Bachelor's Degree AND their relationship.
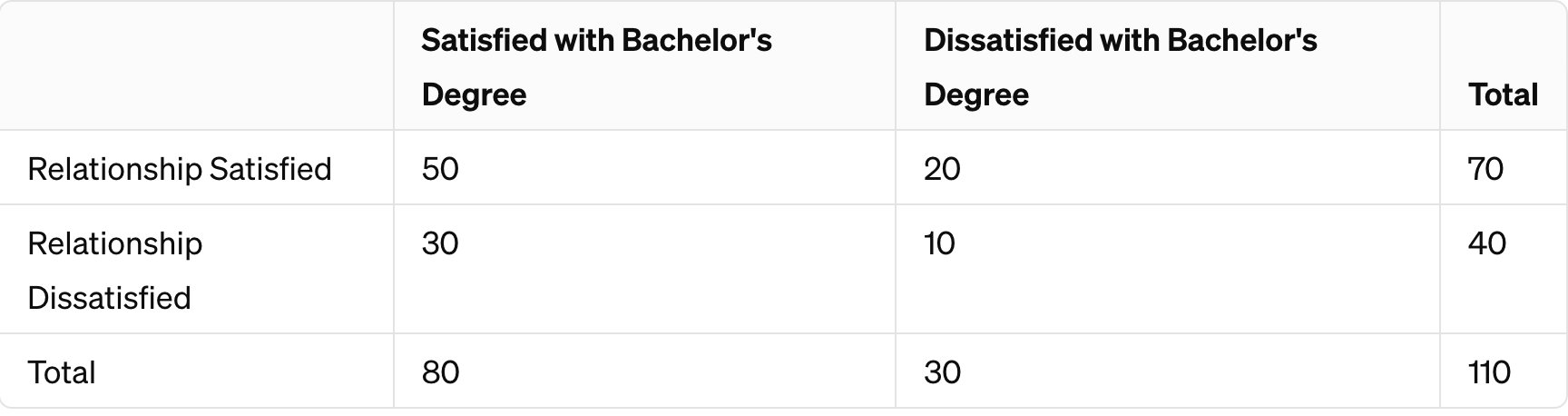
What is...
P(A and B): # of events favoring both A and B divided by total # of observations. This is joint probability--the AND probability.
P(A and B) = 10/110
= 0.0909091
= 0.09% of people are dissatisfied with their Bachelor's Degree AND their relationship.
Tell me some of the factors that influence a hypothesis test.
What is...
1. Mean difference. If the size of the sample mean and pop mean is large = more likely there is a real treatment effect.
2. Magnitude of standard error. Larger standard error = more likely result is due to error/chance.
3. Number of scores in the sample. The more scores we have, the more representative it is of the population and will likely yield a significant result.
Define the standard error of the mean.
What is...
The standard error is a measure of sampling error. It describes the discrepancy, by chance if the null is true, between the sample mean to the population mean.
Using the chart below, find the missing value that would make it so that there is no main effect for A. 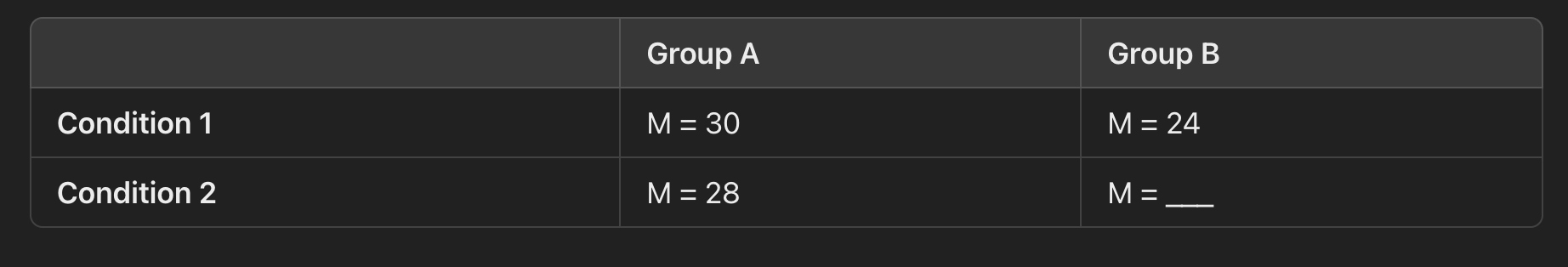
What is...
Missing value = 26
Tell me the probability that someone is satisfied in their relationship OR dissatisfied in their relationship.
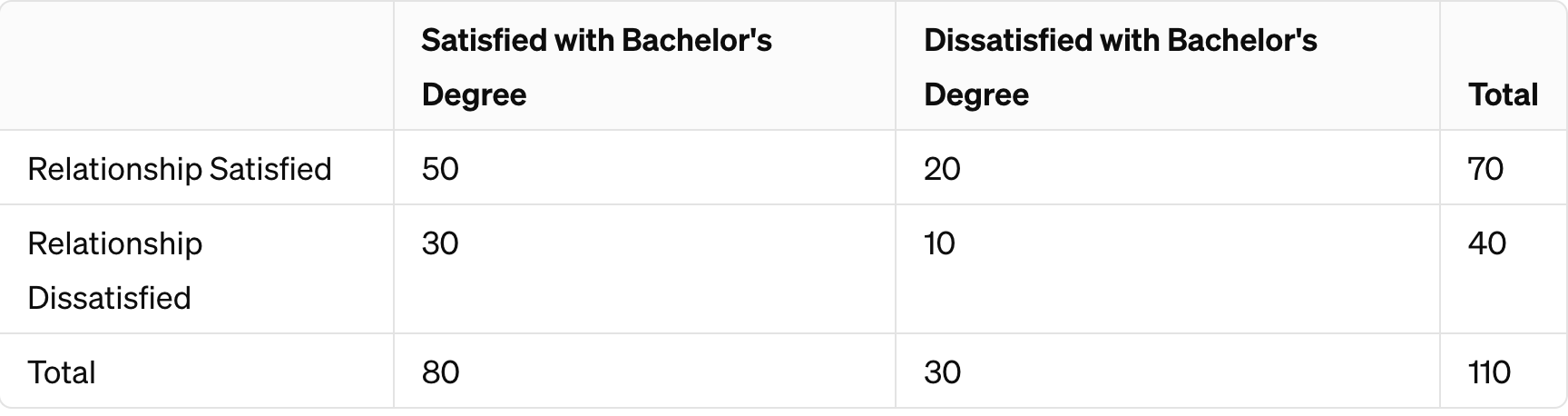
What is...
p(A or B) = p(A) + p(B)
p(A or B) = 70 + 40 = 110.
This is the "or" probability. Events are mutually exclusive. They do not happen at the same time.
Two definitions of an alpha level (Yes, there are two!).
What is...
1. It defines the probability of committing a type I error.
2. It defines the critical region of values unlikely to be out in the tails if the null was true.
Define a sampling distribution.
What is...
A sampling distribution is a distribution of statistics obtained by selecting all the possible samples of a specific size from a population.
It tells us the sample-to-sample variability we can expect by chance or sampling error.
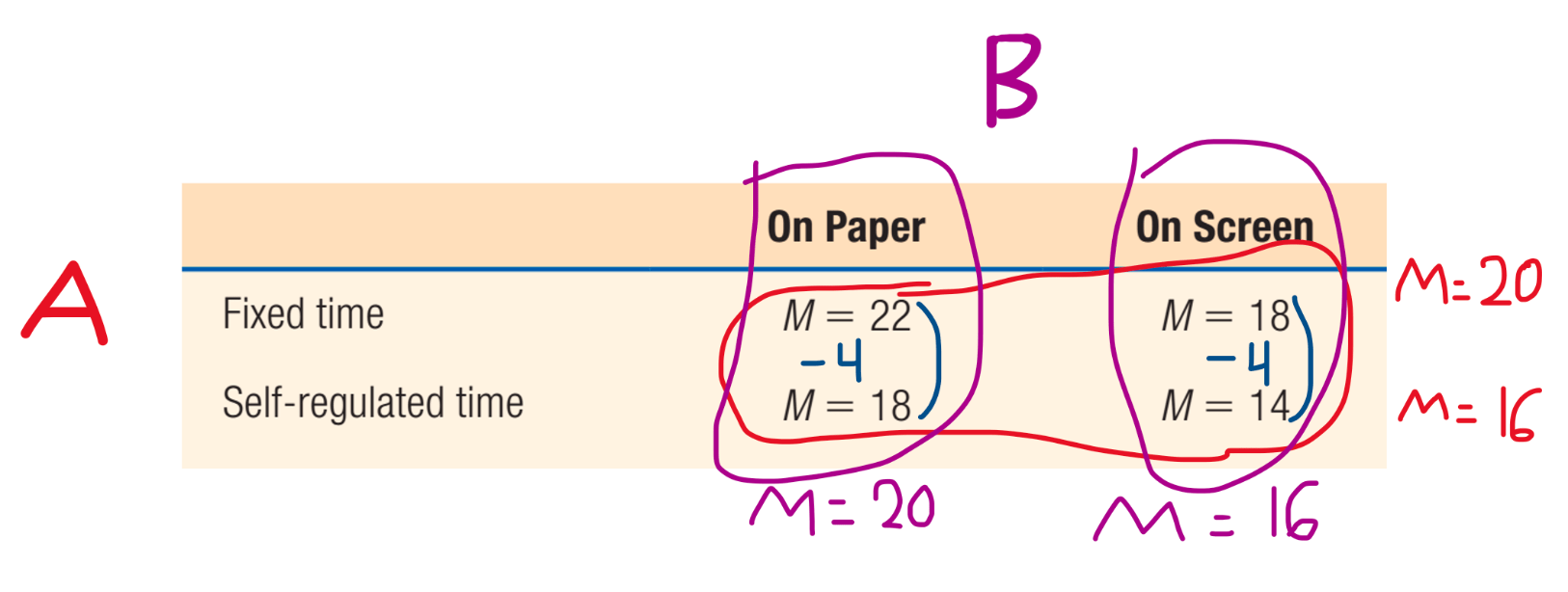
Identify IF...
There is a main effect for A (mode of presentation).
There is a main effect for B (time).
There is an interaction (AxB).

What is...
Main Effect for A? YES.
Explanation: Find the average for each row and if there is a difference between the means, there is a main effect for A. There is a 4 point difference between the first and second means.
Main Effect for B? YES.
Explanation: Find the average for each column and if there is a difference between the means, there is a main effect for B. If you look closely, you will see that it's using the same values as the ones we found with A. There is a 4 point difference here too. There is a main effect for B.
Interaction (AxB)? NO.
Explanation: Look inside the "boxes," it doesn't matter if you look at it vertically or horizontally (columns or rows), but be consistent and go in the same direction. The difference between 22 and 18 is the same difference as 18 and 14. The difference is 4, and because they are the same, there is no interaction here between the presentation modality and the time allotted.
A beverage company claims that their new energy drink INCREASES concentration levels. To test this claim, a researcher conducts an experiment with 40 participants. The population mean concentration level consuming the drink was 60, with a standard deviation of 8. In the sample, the mean concentration level was 64. Assuming a significance level of 0.05, tell me if the researcher can conclude that the energy drink increases concentration levels.
What is...
Using one-tailed Z-test because we want to see an increase in concentration levels. This implies a directional hypothesis test (look out for those keywords). The CV in this case would be +1.65 when alpha level is at 0.05.
Our sample mean (M or x̄) = 64.
Our population mean (mu) = 60.
Population standard deviation = 8.
N = 40.
Standard error found by dividing the SD by the square root of N.
8/√40 = 8/6.3245553
= 1.2649111
= 1.26.
Z = M - mu divided by standard error.
Z = 64 - 60 /1.26
Z = 4/1.26
Z = 3.1746032
Z = +3.17
Since +3.17 is beyond the critical value needed for rejection (+1.65), we can conclude that there is a treatment effect. From the sample mean (64) to the population mean (60), there is evidence that the new energy drink increases concentration levels.
Define a distribution of sample means.
What is... the distribution of sample means over repeated sampling from a population?
Identify IF...
1. There is a main effect for A.
2. There is a main effect for B,
3. There is an interaction (AxB).
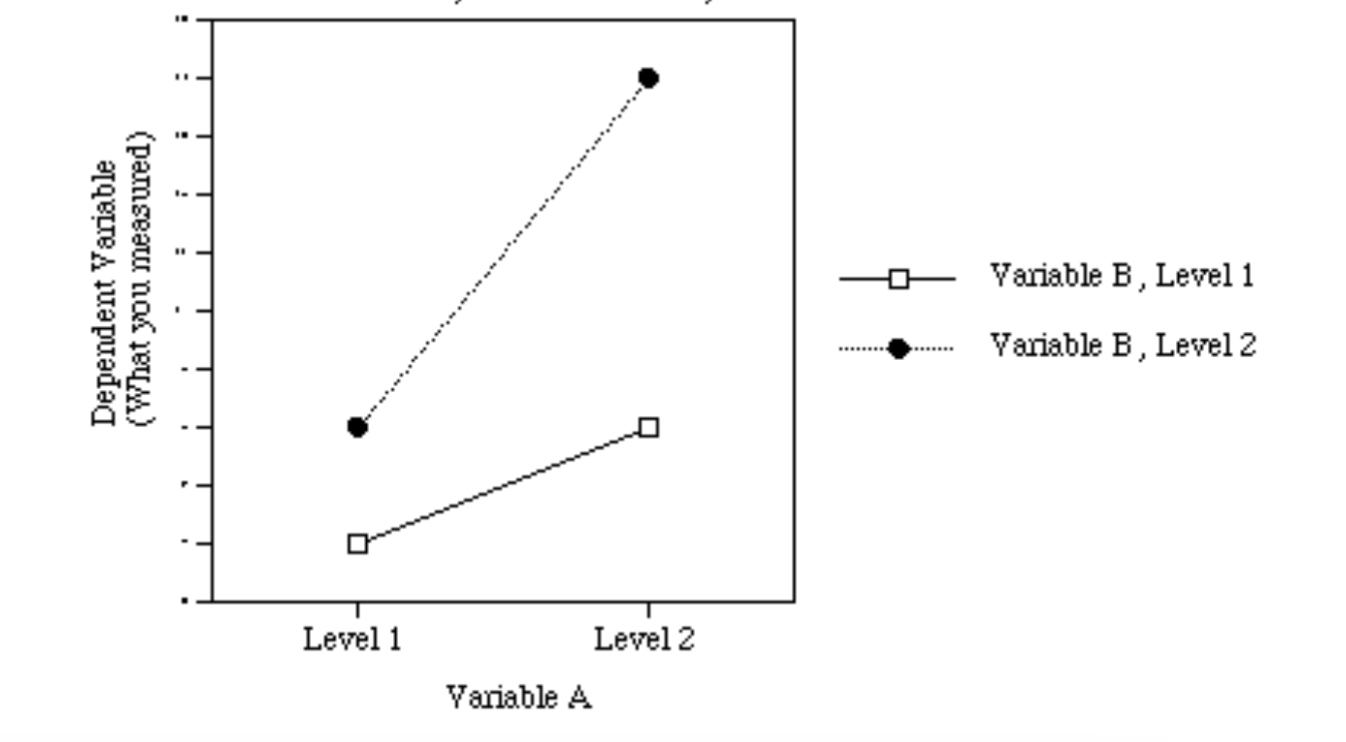
What is...
Main effect for A? YES.
Main effect for B? YES.
Interaction (AxB)? YES.
Tell me one benefit and one disadvantage of having a conservative, small alpha level (such as .01).
What is...
It reduces the likelihood of committing a type 1 error. We are saying in this case that we are okay with making a type 1 error one percent of the time. However, on the flipside, a disadvantage would be that it extends the critical value needed for rejection further out into the tails, and as such, it makes it harder to reach significance.
An image might be helpful to demonstrate:
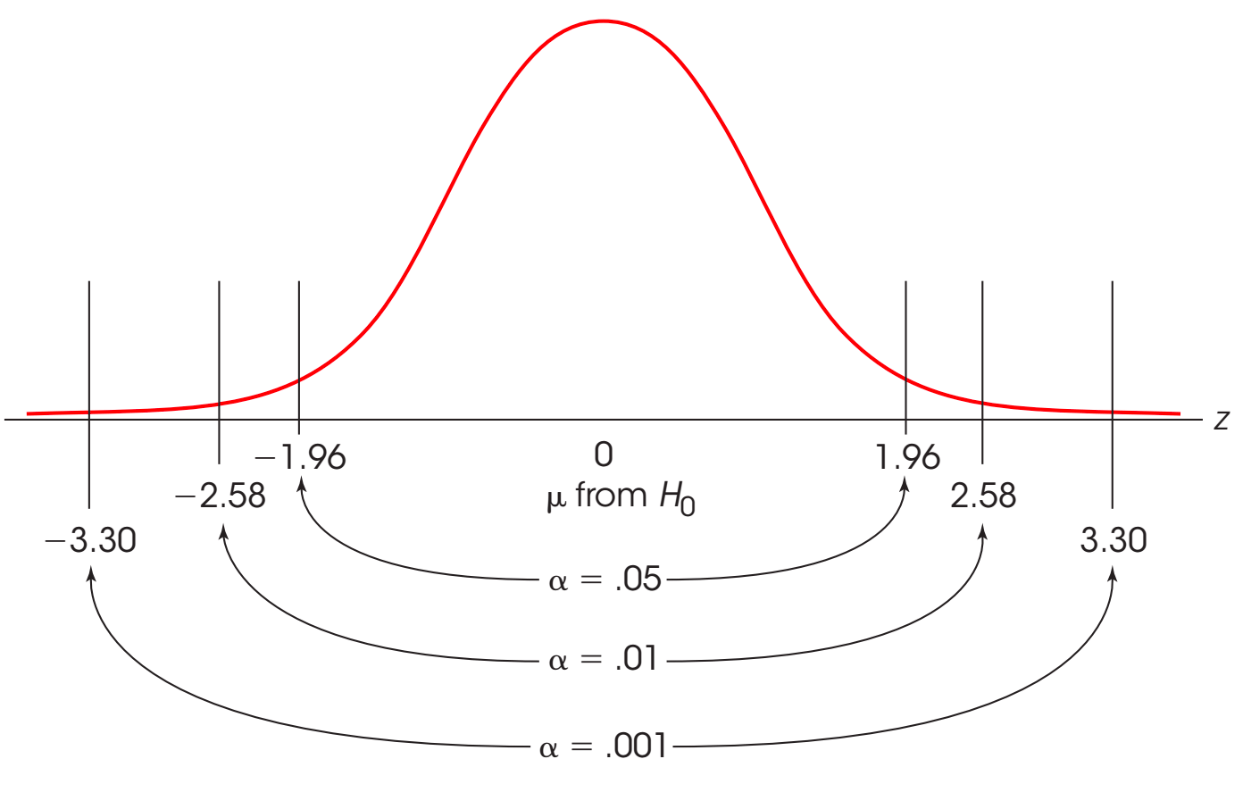
We see when the alpha level is at .01 and two tailed, the critical value needed for rejection becomes +/- 2.58 making it harder to reach than when it was at .05 and +/- 1.96.
List the 3 characteristics of the distribution of sample means.
What is...
1. Most sample means will have means close to mu.
2. The distribution of sample means should approximate a normal distribution.
3. Sample means from larger samples should be closer to the population mean (Law of Large Numbers).
Identify in the histogram below IF...
1. There is a main effect for A.
2. There is a main effect for B.
3. There is an interaction (AxB)
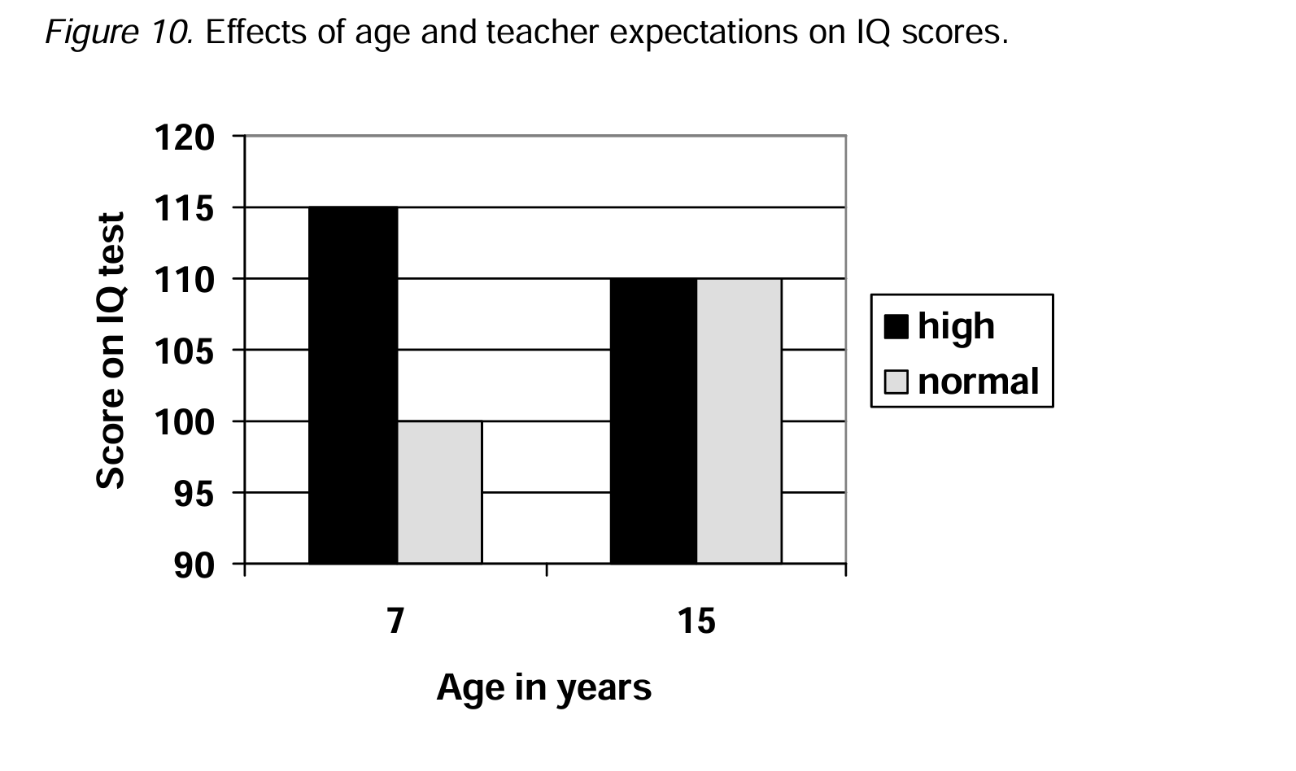
What is...
ME A? YES.
ME B? YES.
AxB? YES.