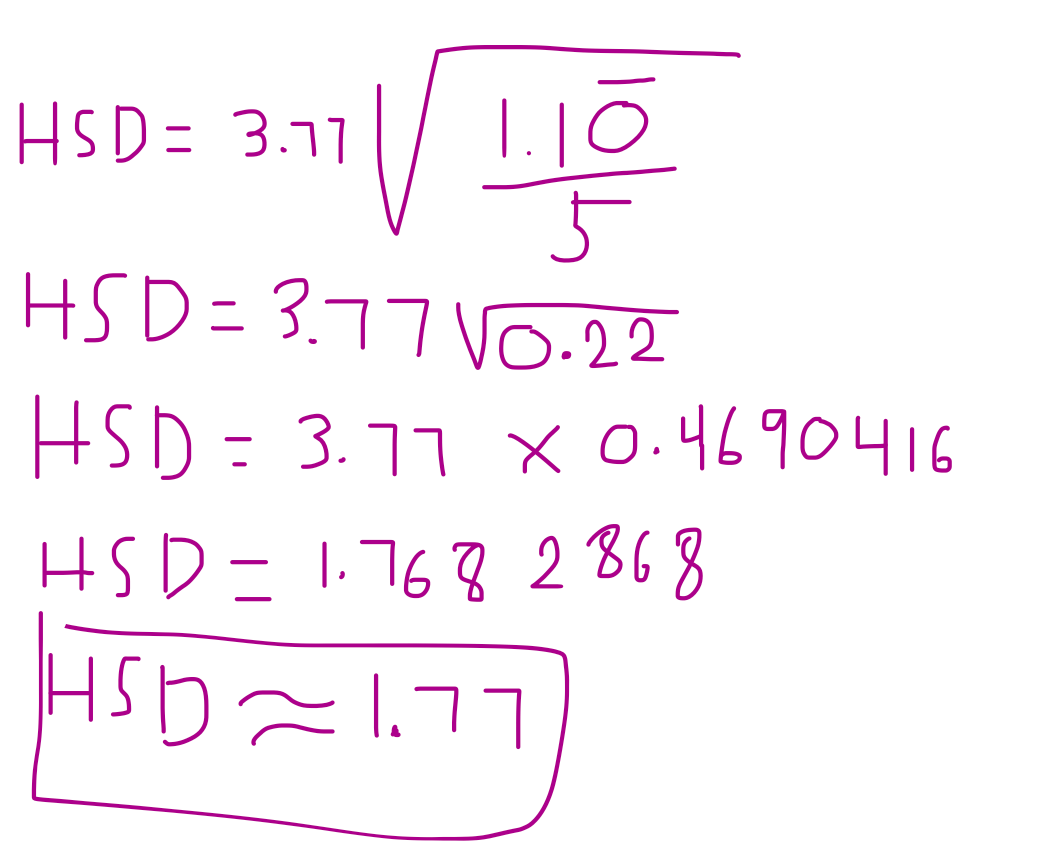Repeated Measures).
Conceptual content: The assumptions for a one-way between subjects ANOVA (hint: Exactly the same as the assumptions for an independent-samples t-test).
What is...
Homogeneity of variance, or just equal variances.
Population from which samples are drawn is normal.
Observations within each sample are independent.
Conceptual content: Decide if it is possible to calculate a negative F-value.
What is...
It is not. Something went wrong with your calculations, as variances can never be negative.
Conceptual: Define main effect (utilizing lecture definition).
What is...
A main effect is the impact of one independent variable collapsed across, averaged across, or better yet, IGNORING a second independent variable.
Conceptual: Define a post-hoc test.
What is...
Additional hypothesis tests that are done after an ANOVA to determine which mean differences are significant (or not).
Note that since ANOVA is dealing with 3+ groups/levels, doing an ANOVA alone is not telling us WHICH mean differences are significant. A significant F-ratio is only revealing that of the mean differences, there is AT LEAST ONE that exists. Post-hoc helps us to clarify which of those mean differences are actually significant.
Conceptual: The assumptions underlying a repeated measure ANOVA.
What is...
Data collected within each level of IV are independent of one another.
Population distribution is assumed to be normal.
Sphericity: The variance of the differences between each possible pair of groups is the same.
Conceptual content: Identify the conditions to perform a one-way between-subjects ANOVA.
What is...
The DV is quantitative and at the interval level.
The IV is qualitative or quantitative, but must be between-subjects.
IV has 3 or MORE levels.
Note that ANOVA can be performed when you have 2 levels, but it makes more sense to just perform an independent-samples t-test in that case, especially since it's going to be obvious which means you are comparing directly.
Conceptual: An F-value of 1.00 means...
What is...
It means you retain the null and that none of the mean differences are different from each other. If F-value is greater than 1.00, it is more likely you will reject the null as there is a larger mean difference.
Conceptual: Define interaction (utilizing lecture definition).
What is...
An interaction is a difference across the levels of one independent variable that differs across the levels of the second independent variable.
Conceptual: You only use a post-hoc test under two "conditions", tell me what those conditions are.
What is...
1. You rejected the null hypothesis (F-value is significant).
2. There are 3 or more treatment groups (defined as k).
Conceptual: The conditions to perform a repeated measures one-way ANOVA.
What is...
The DV is quantitative and on an interval level.
The IV is quantitative and qualitative but must be within-subjects.
IV has 3+ levels.
Computational: Fill in the values from the following, incomplete ANOVA source table: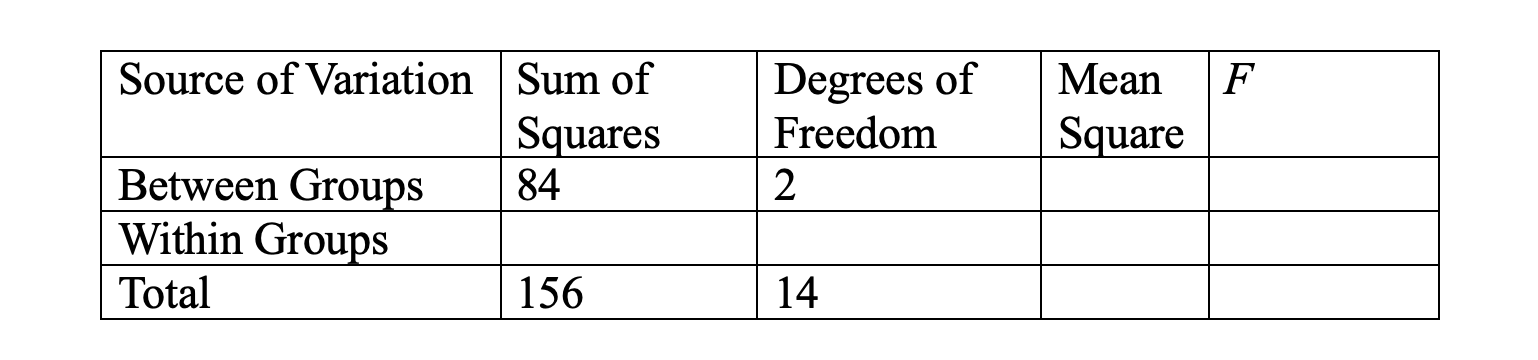
What is...
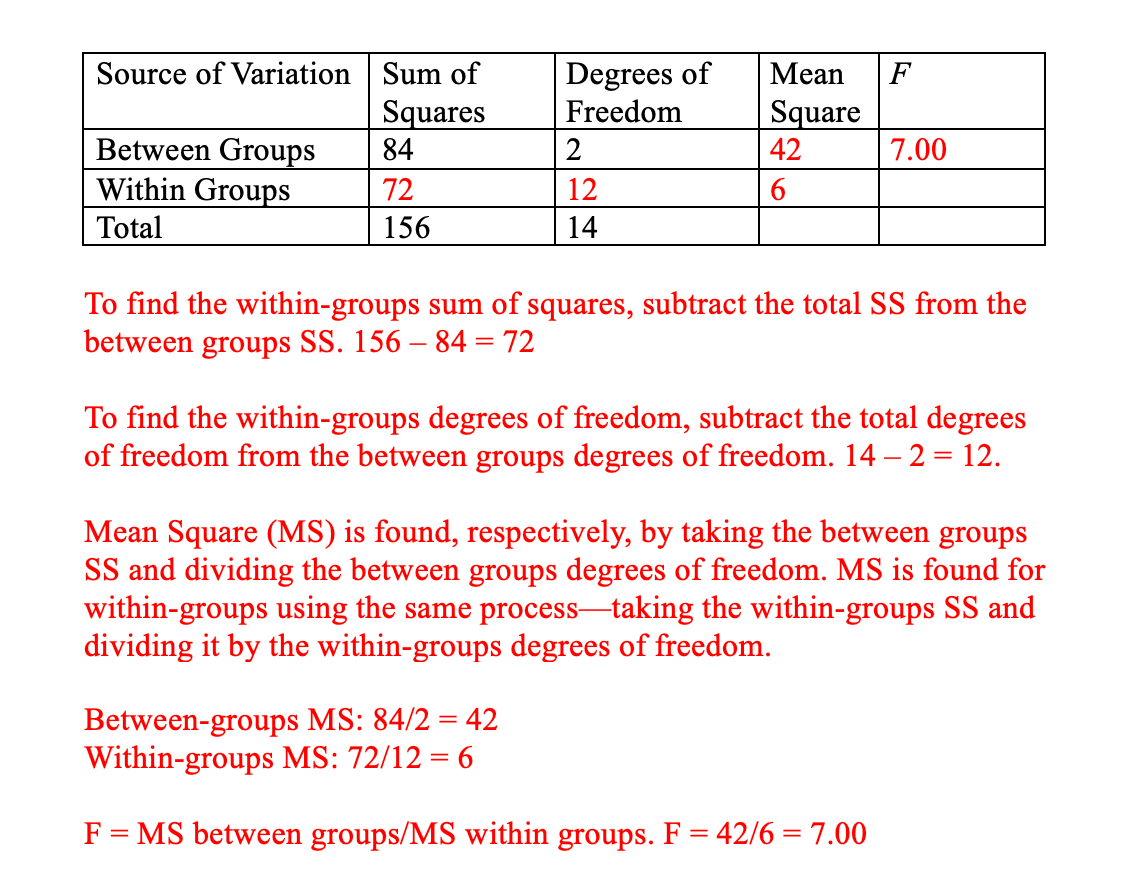
Additional tricks:
If F was missing, you would divide Between Groups MS by Within Groups MS.
If the Sum of Squares for Between Groups (84) was missing, you can multiply the Between Groups MS by the between groups degrees of freedom (2) to find it. Same goes for within groups if the SS was missing.
If the total SS was missing, you can add the between and within SS.
If one of the SS values was missing (either 84 or 72), just subtract the total from one of those values. Same goes for degrees of freedom.
If your degrees of freedom was missing for between groups, divide the between groups SS by the between MS to find it. Same goes for within groups.
Conceptual: Determine using the SPSS output below if the F-value is statistically significant.
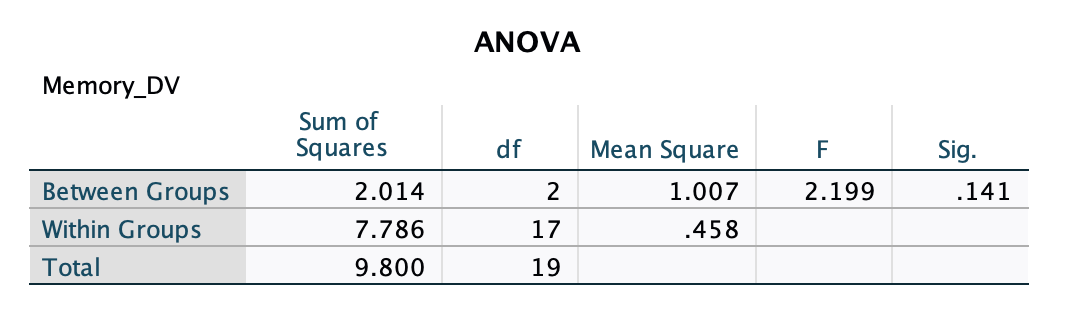
What is...
Using ONLY the SPSS output, you can find if statistically significant by referring to the "Sig." column where it says .141
As 0.141 is greater than our p-level of 0.05, this is a statistically non-significant F-value. We retain the null that the three mean differences are NOT different from each other.
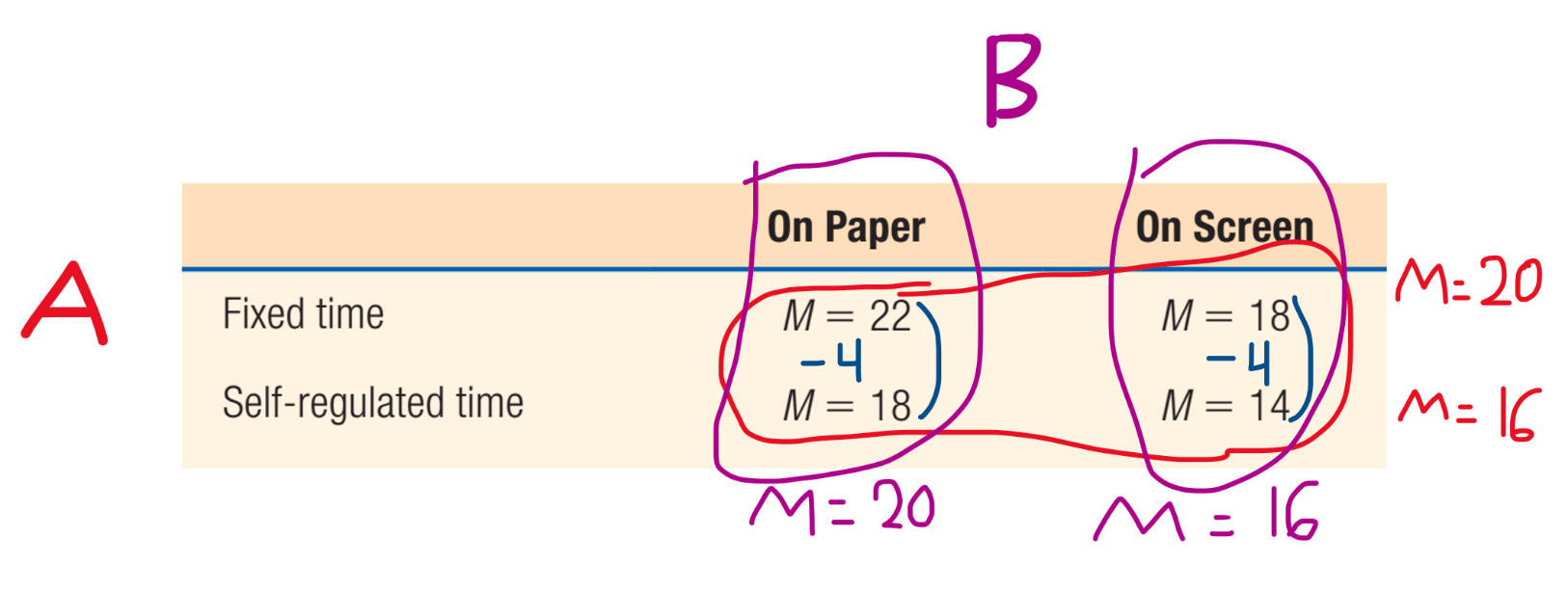
Computational: IDENTIFY IF...
There is a main effect for A (mode of presentation).
There is a main effect for B (time).
There is an interaction (AxB).

What is...
Main Effect for A? YES.
Explanation: Find the average for each row and if there is a difference between the means, there is a main effect for A. There is a 4 point difference between the first and second means.
Main Effect for B? YES.
Explanation: Find the average for each column and if there is a difference between the means, there is a main effect for B. If you look closely, you will see that it's using the same values as the ones we found with A. There is a 4 point difference here too. There is a main effect for B.
Interaction (AxB)? NO.
Explanation: Look inside the "boxes," it doesn't matter if you look at it vertically or horizontally (columns or rows), but be consistent and go in the same direction. The difference between 22 and 18 is the same difference as 18 and 14. The difference is 4, and because they are the same, there is no interaction here between the presentation modality and the time allotted.
Conceptual: Define experimentwise alpha.
What is...
When performing multiple t-tests, it defines the probability of a type I error from all of the hypothesis tests, which does accumulate the risk of type I.
Conceptual: Define SS Subjects.
What is...
The sum of Square Subjects measures the size of individual differences between each subject.
Computational:
A psychologist is interested in studying the impact of different lighting conditions on reading comprehension. Participants are randomly assigned to one of three groups, each experiencing a different lighting condition while reading a passage: bright light, dim light, and natural light. The psychologist hypothesizes that the lighting condition will significantly affect reading comprehension scores. Perform a one-way between-subjects ANOVA and show all work.
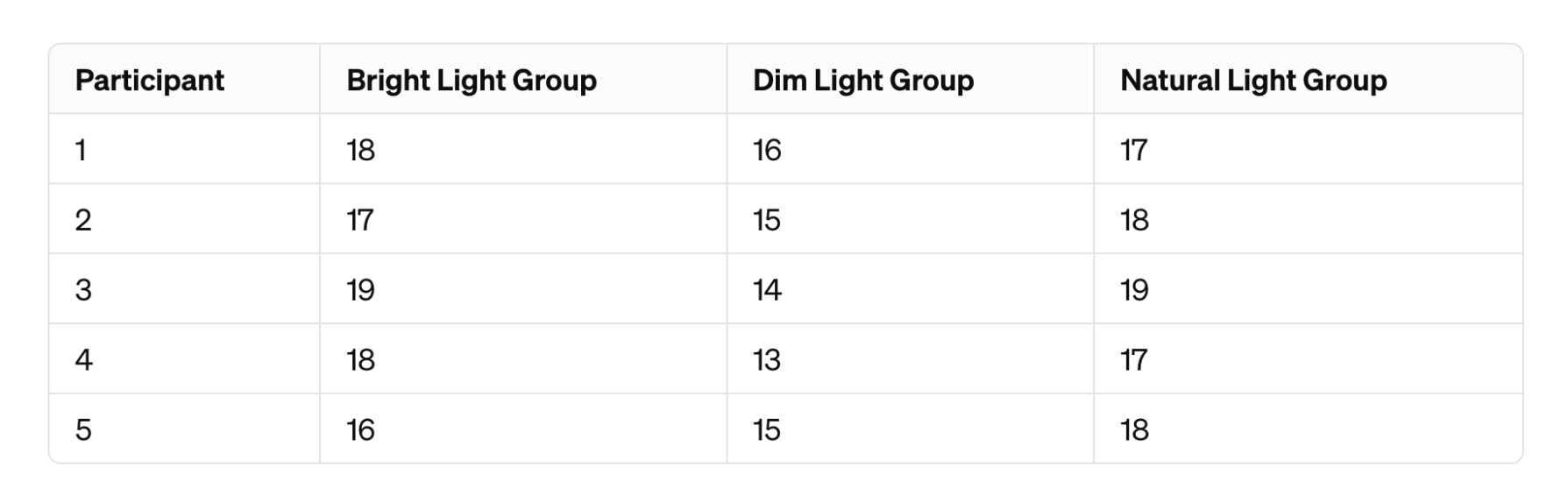
What is...
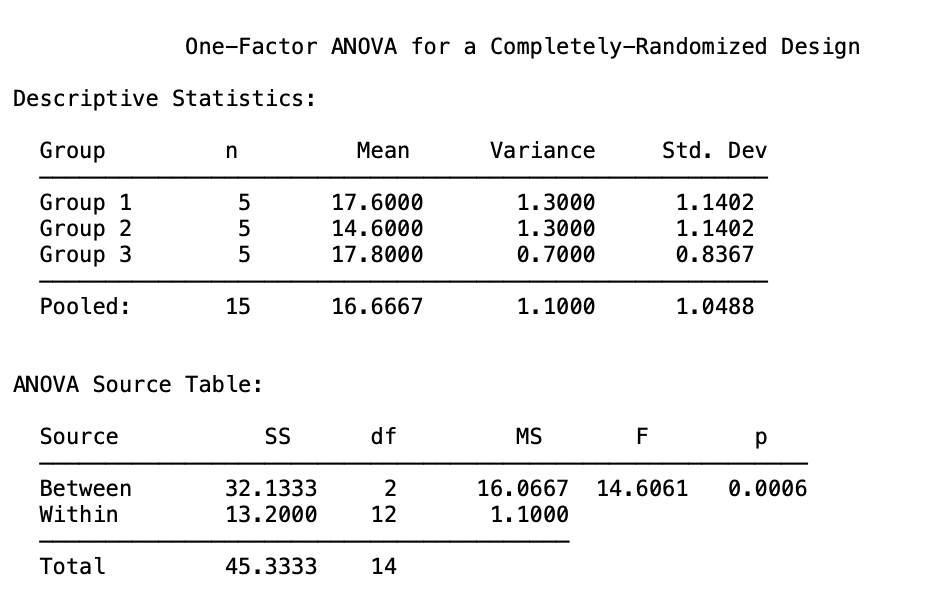
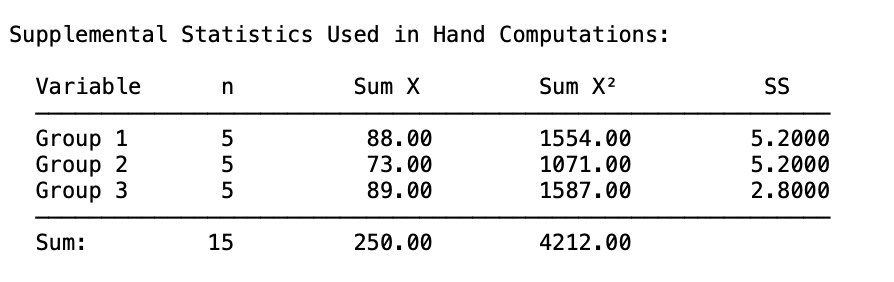
TA work by hand (sorry for the handwriting, but you would know already since you've seen it before, haven't you?):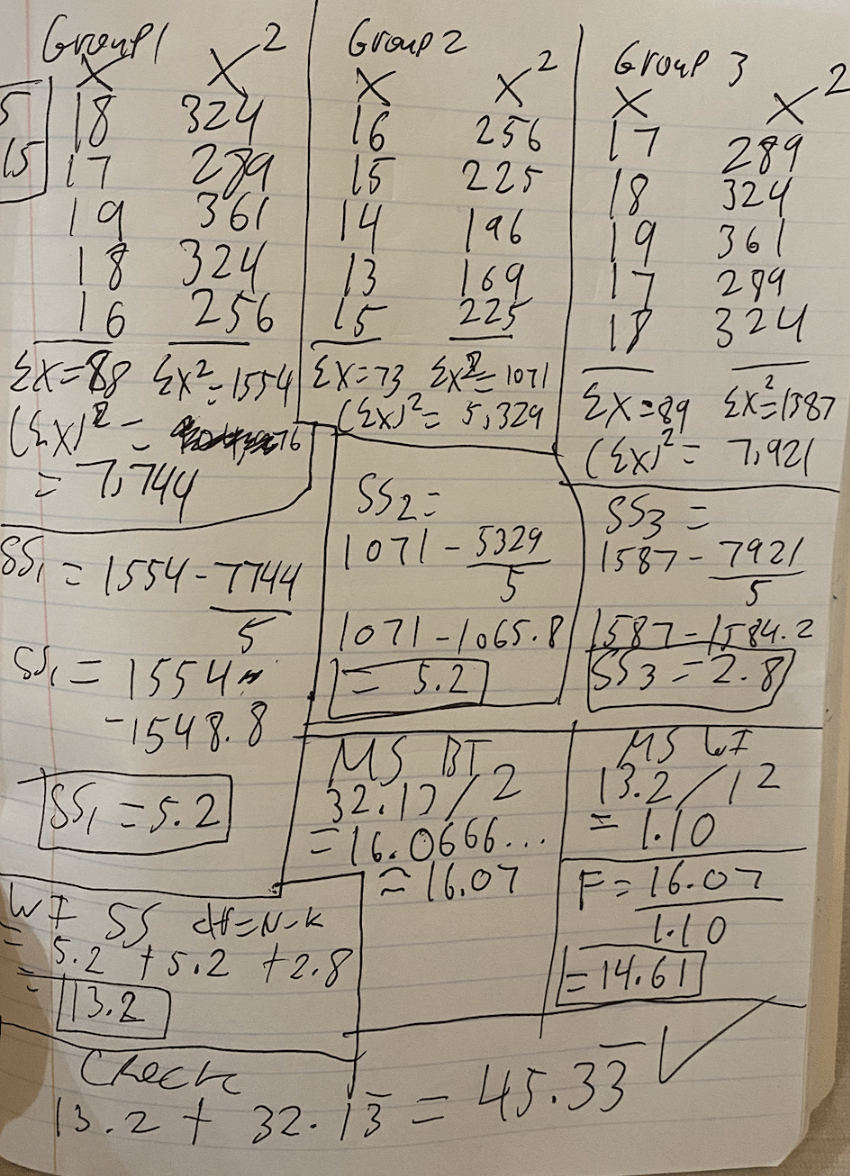
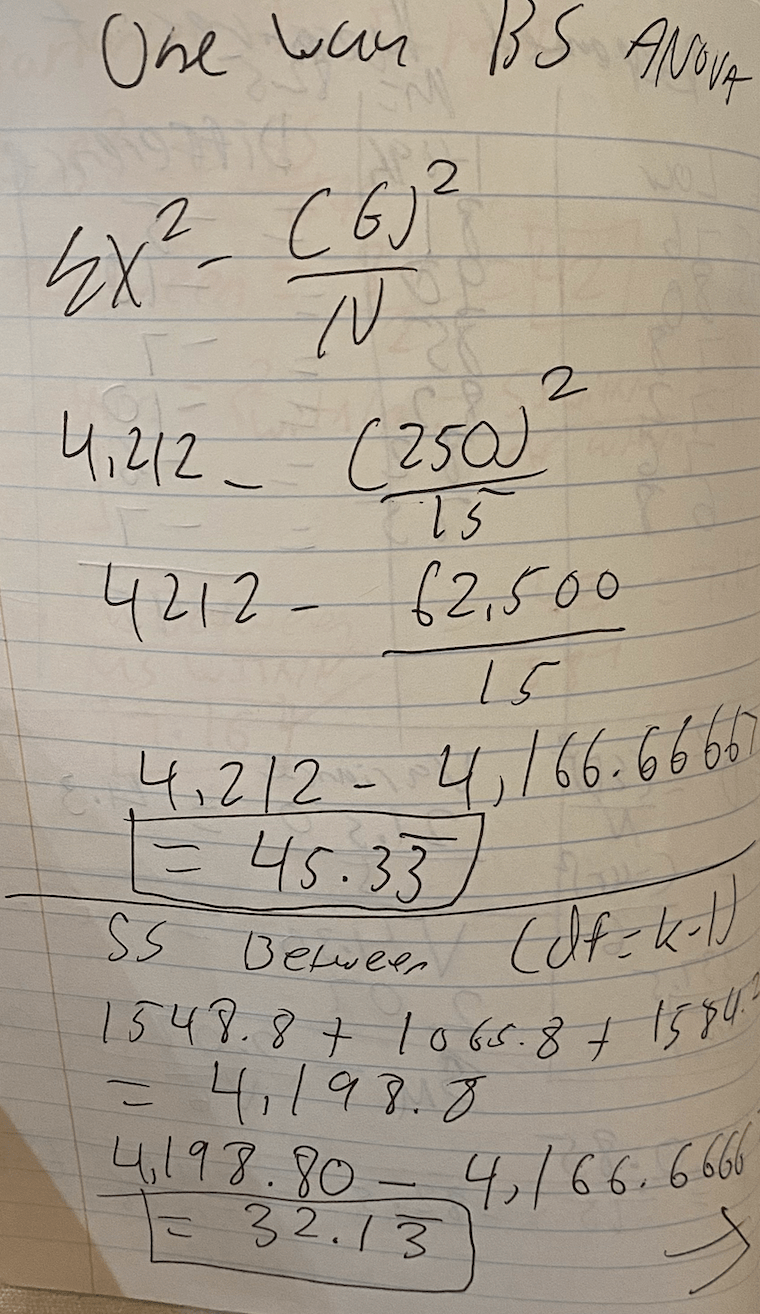
Conceptual:
Identify IF...
1. There is a main effect for A.
2. There is a main effect for B,
3. There is an interaction (AxB).
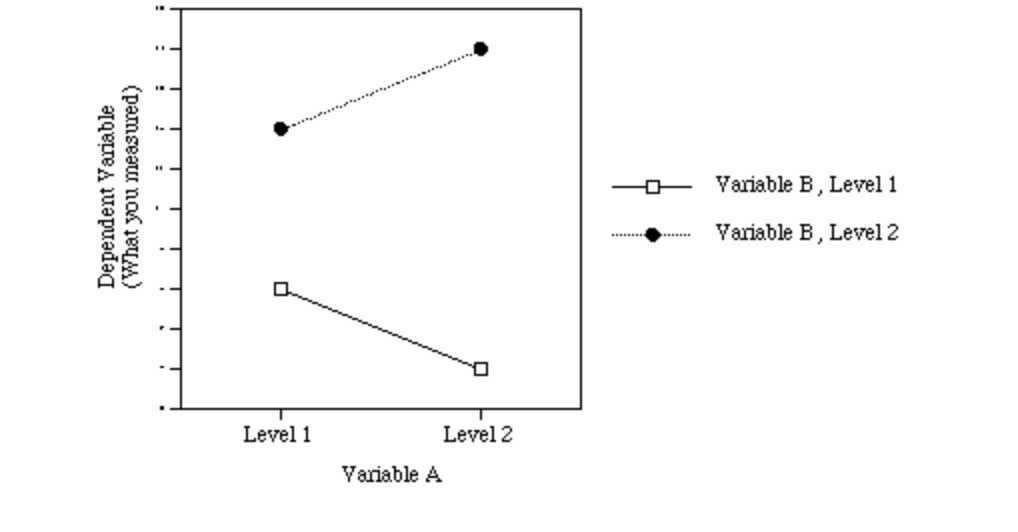
What is...
Main Effect for A? NO.
Main Effect for B? YES.
Interaction (AxB)? YES.
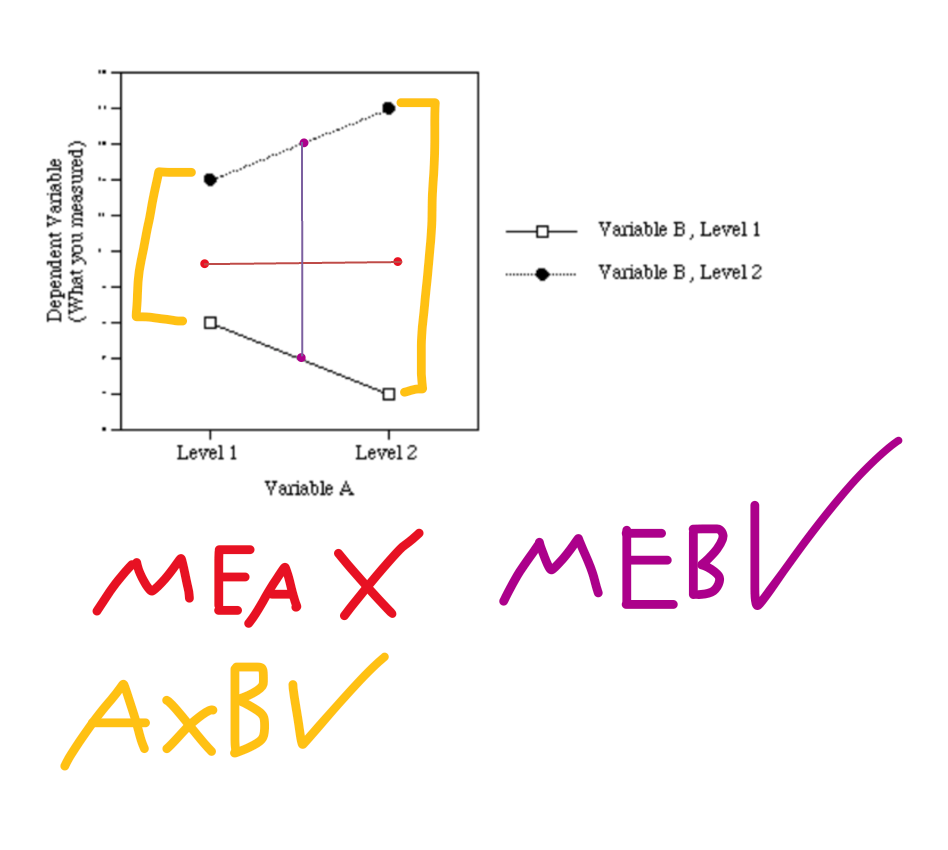
Computational: Calculate the risk of a Type I error if there were 7 means involved and you considered doing multiple t-test comparisons. Then, calculate the experimentwise error. Assume an alpha level of 0.05.

What is...
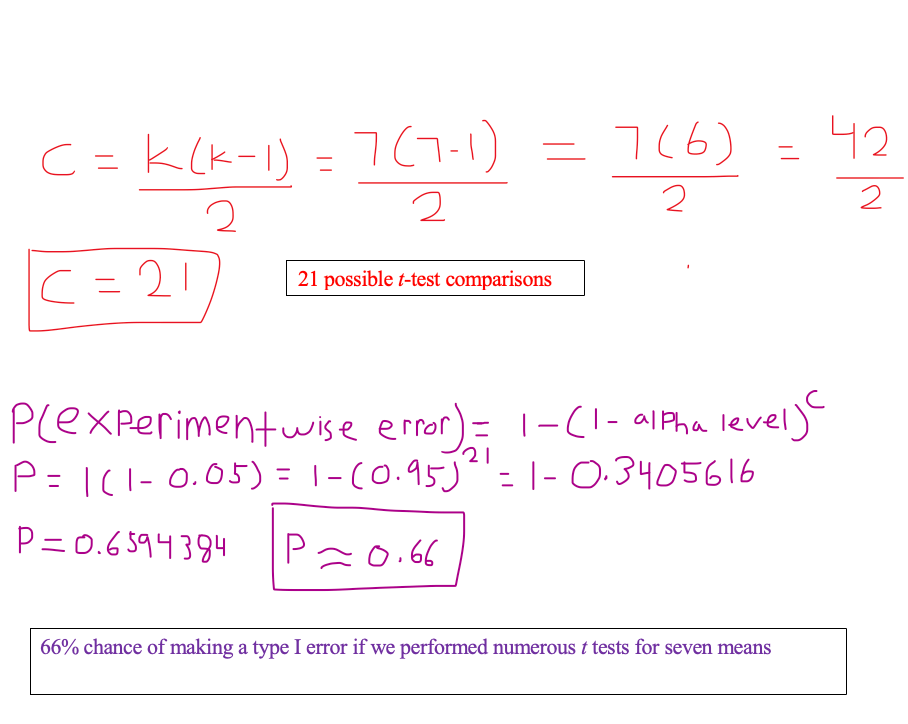
Conceptual: Define SS error.
What is...
SS error substracts out the individual differences (from SS Subjects), and we can see the variance left over that is not accounted for by treatment effects and individual differences.
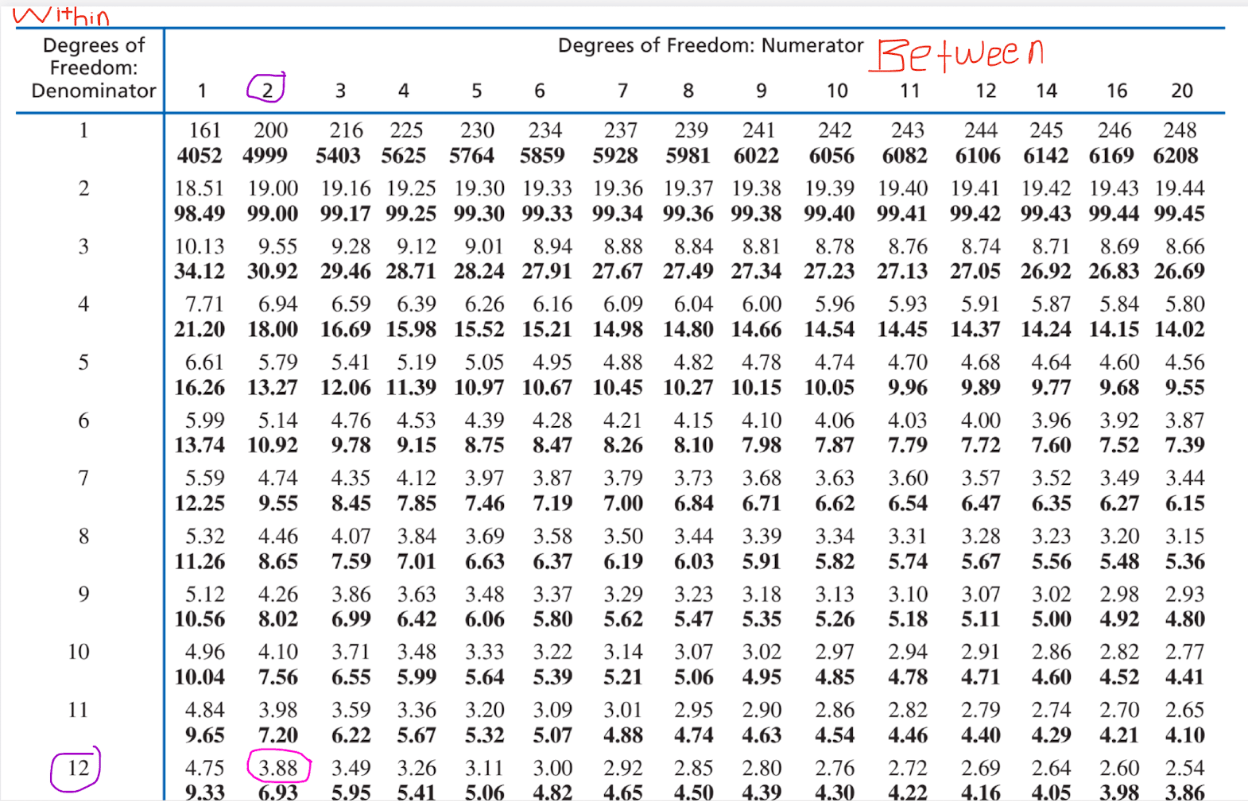
Computational/Conceptual: Using the F-value (14.61) from the last question, reference the F distribution from G&W appendix b, page 597, and determine if it is significant. If so, compute r2 and omega2.
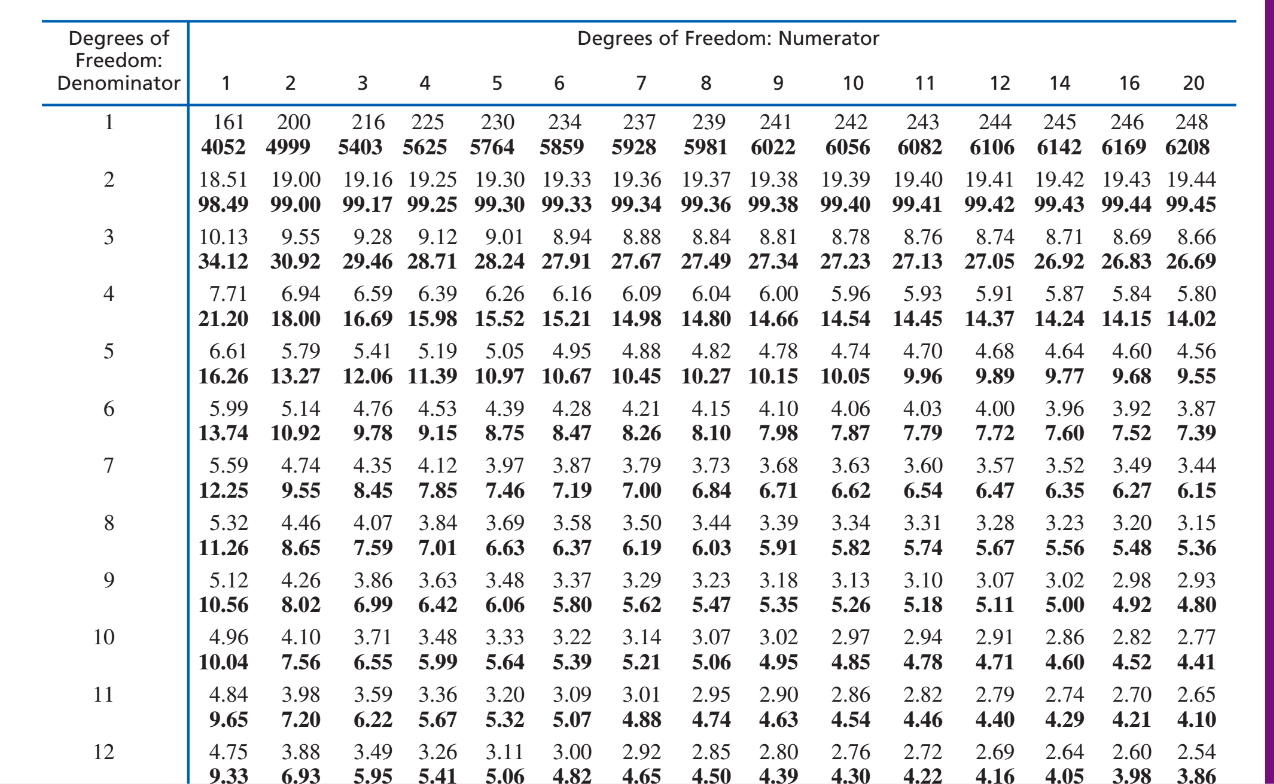
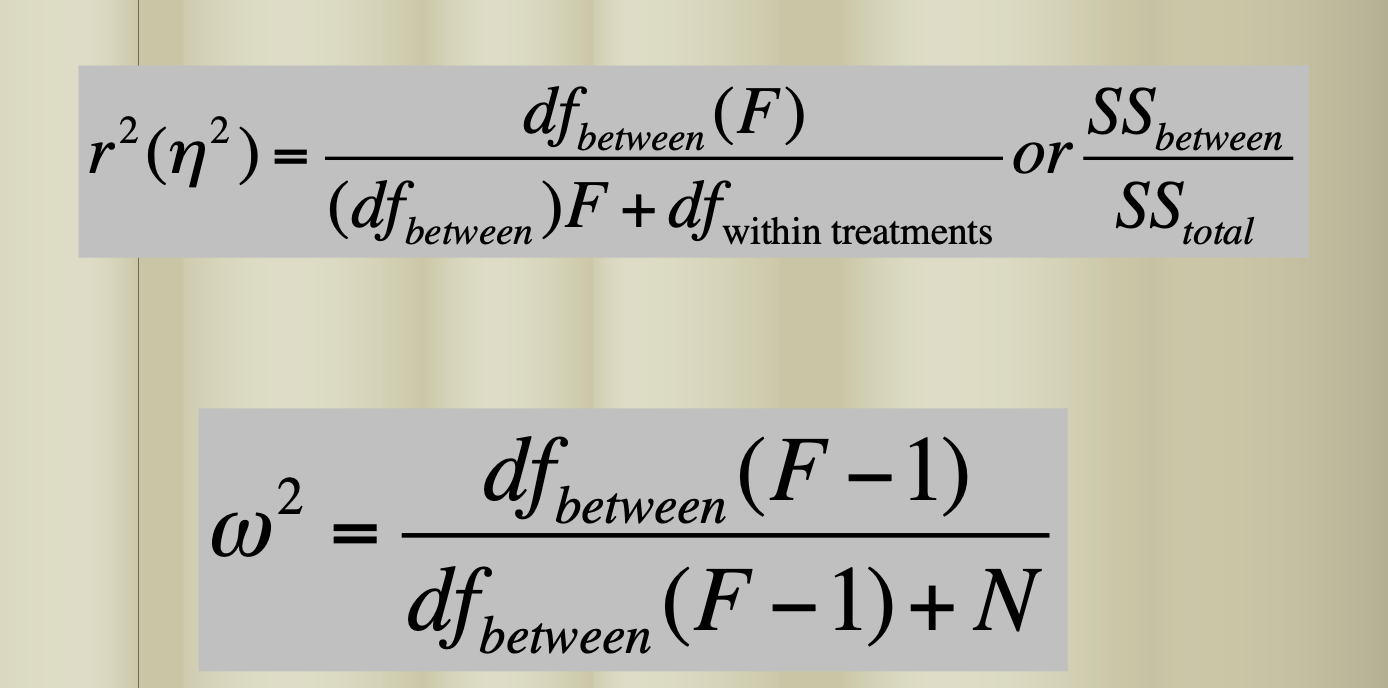
What is...
Critical F value is located at (2, 12) and it is 3.88.
Since our computed F-value is beyond the critical value needed for rejection we can compute r2 and omega2
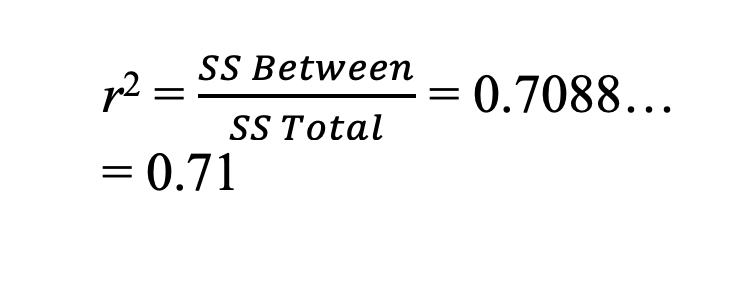
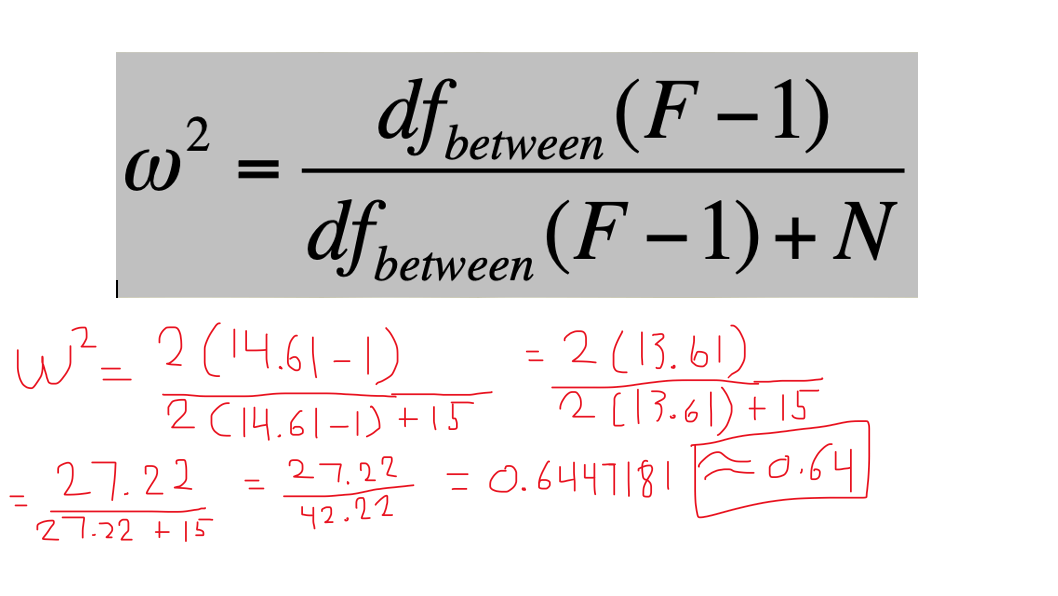
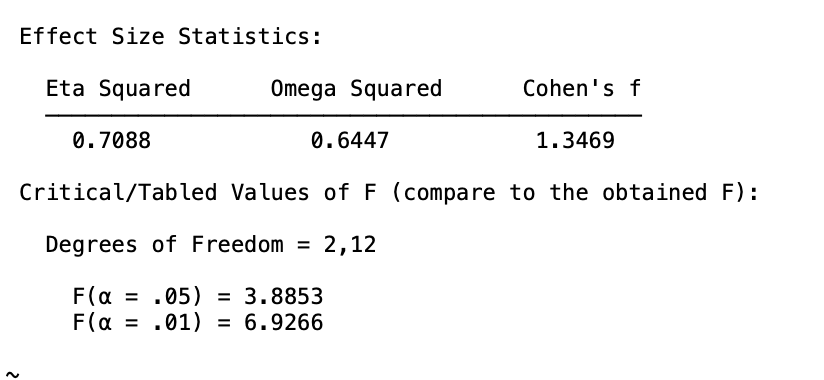
Conceptual: Identify IF...
1. There is a main effect for A.
2. There is a main effect for B,
3. There is an interaction (AxB).
What is...
Main Effect for A? YES.
Main Effect for B? YES.
Interaction (AxB)? YES.
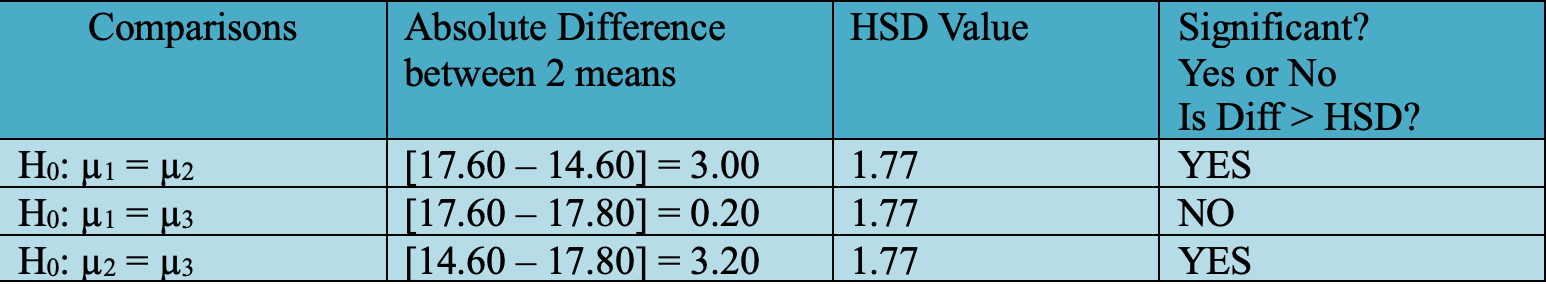
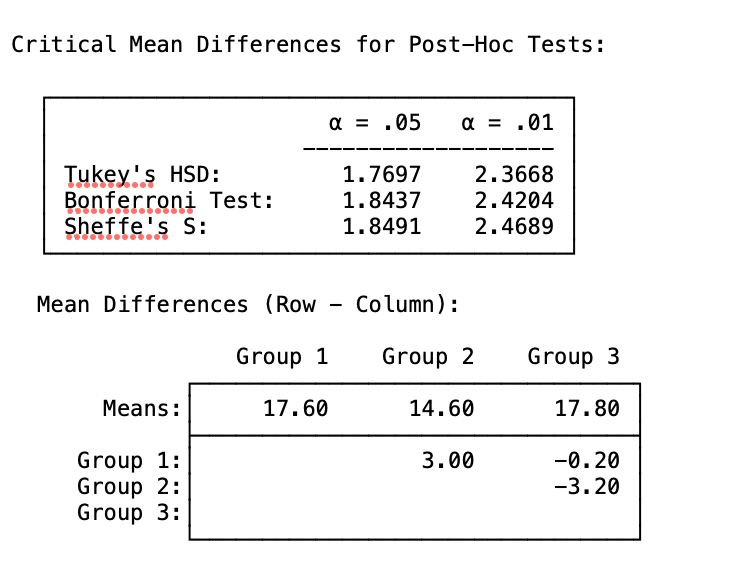
Computational: Compute Tukey's HSD from the values given below. Then, compare the mean differences and determine which ones are significant. Assume an alpha level of 0.05. Formula provided.
"To locate the appropriate value of q, you must know the number of treatments in the overall experiment (k), the degrees of freedom for MSwithin treatments (the error term in the F-ratio), and you must select an alpha level..." - Our Holy Saviors, G&W pg. 417.
USE the Studentized Range Statistic (q) to find the q value to compute Tukey's HSD. The table is located on page 600, appendix B. Table B.5.
Good luck, soldiers.
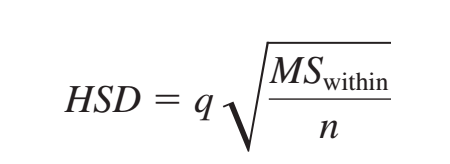

What is...
Q is found first by locating (k). K = number of treatments. If you were just given the source table, you would know that the between-groups degrees of freedom is found by k - 1. 3 - 1 = 2. Therefore, our # of treatments is 3.
Second, the error term is found by the MS within degrees of freedom, which is 12. When you intersect (3, 12), you will find a q value of 3.77
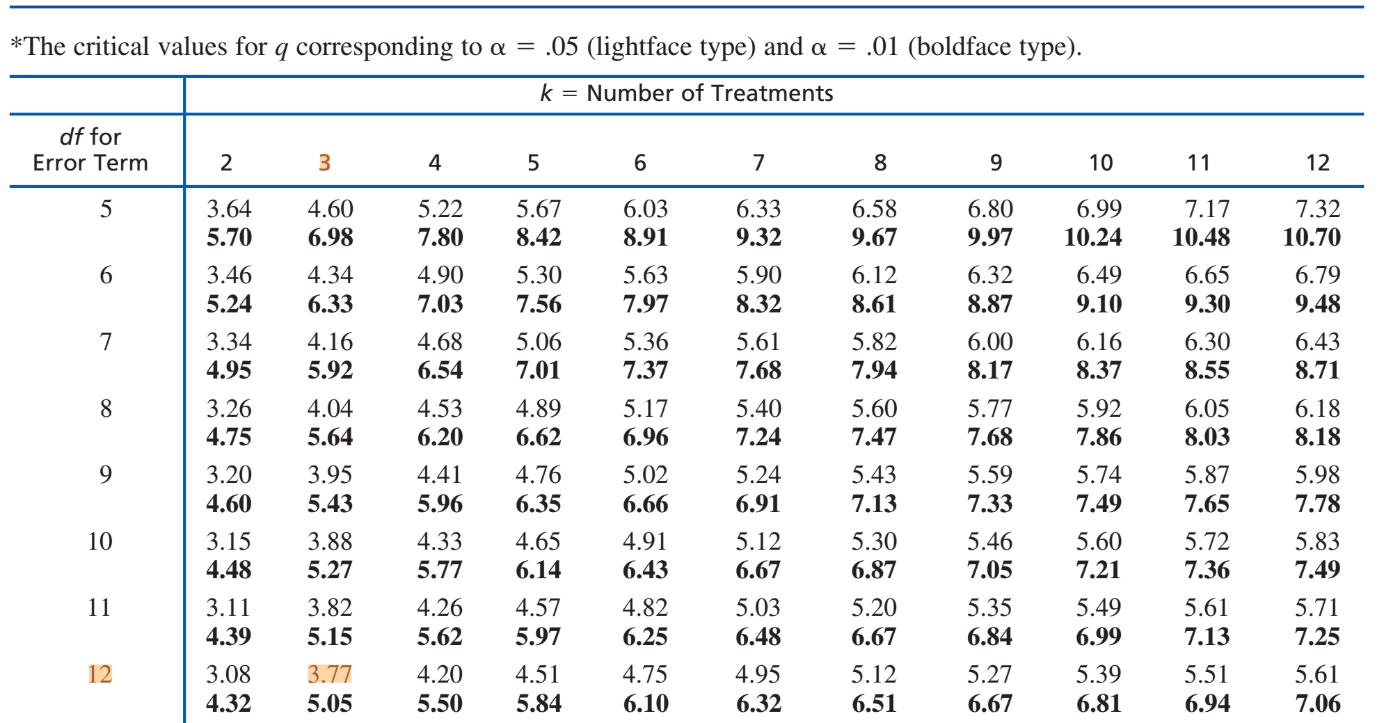
Now you can plug in the values in the Tukey's HSD formula.