What is the correspondence problem?
These are used to test spatial acuity.
What are gratings or patterns?
Threading a needle, catching a ball, ...?
This is one feature which appears to be processed without attention (pre-attentively).
(we have seen a few examples!)
What is color? (or orientation, or luminance, or...)
This is the name usually given to the part of an image that we interpret as foreground.
What is figure?
One of the simplest forms of adaptation occurs in the retina, and is called this.
What is light or luminance adaptation?
(or color adaptation!)
This effect demonstrates what happens when your brain tries to anticipate the future position of a moving object (to compensate for delayed perception)
What is the flash-lag effect?
What is large?
Sidewalk chalk illusions usually rely on this cue for distance
What is linear perspective?
Finding the odd element out in this display is an example of this kind of search.
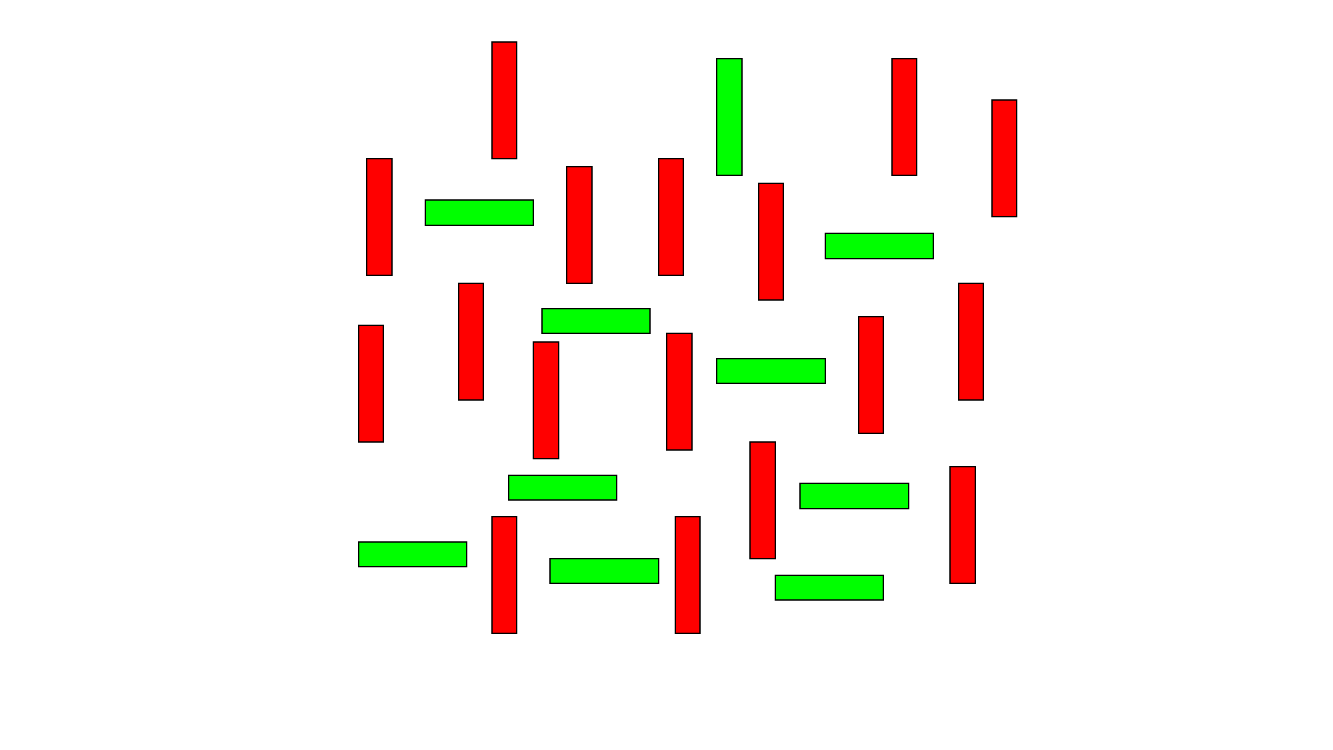
What is serial search (or conjunction search)?
This is one cue that makes the white triangle here appear to be figural.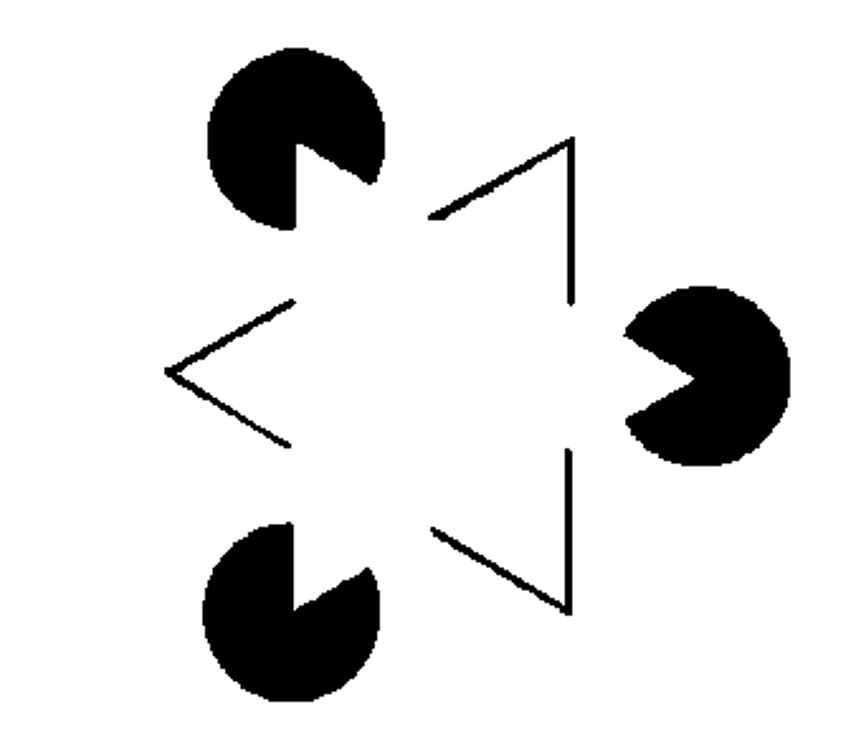
Over time, we tend to adapt to the faces we see most commonly around us, and this can result in difficulty distinguishing faces of other racial groups. This phenomenon is known as this.
What is the other race effect?
This domain of vision ALSO requires matching locations in images.
What is binocular depth perception?
These are two factors that limit the spatial acuity of our vision.
What are the optics of the eye and receptor density?
What is a texture gradient?
When detecting a briefly appearing object, valid cues tend to do this to reaction times.
What is make it faster?
This is the name for the movement in psychology that first emphasized that the whole can be greater than the sum of its parts.
What is Gestalt?
In the domain of color, adaptation can serve to eliminate perception of this, such that true colors can be percieved more readily
What is the color of the illuminant?
(or seasonal color)
(or the yellow color of your lens)This is the reason that we can't rely on the outputs of V1 cells to accurately detect the direction of motion of large patterns.
What is the aperture problem?
We are best at seeing spatial frequencies in this range.
What is medium (3-6 cycles per degree)?
This is the name for the motion cue for depth which was used to great effect in the Super Mario Brothers games in late 80s video games
What is parallax?
Most sleight of hand magic tricks rely on this phenomenon.
What is inattentional blindess?
This most often determines which of two ambiguous interpretations of a figure/ground relationship we will choose.
What is likelihood? (or probability of each interpretation)
Adaptation occurs at this level of the visual system
What is all levels?
This internal signal is one mechanism that the brain uses to distinguish self-motion from external motion.
What is an efference copy?
This animal has particularly high acuity vision.
what is a hawk?
This is the name for the imaginary curved line in space in front of you (at your fixation distance) at which objects can be successfully merged into a single percept.
What is the horopter?
(Also OK: Panum's fusion area)
This is the name commonly given to our ability to hear and understand one of two overlapping streams of sound.
What is the cocktail party phenomenon?
MC Escher drawings are often locally consistent but globally inconsistent; it often takes multiple fixations around a drawing to appreciate its full complexity (or absurdity). LONG ANSWER: Do you best to explain why it's difficult to comprehend MC Escher drawings in one glance!
[open answer!]
If an adaptation effect persists no matter which eye is open during adaptation and subsequent perception, then the neural locus of that kind of adaptation must be here.
What is in V1 (or in the cortex!)