This perspective of Psychology focuses on unconscious desires and childhood experiences.
Psychoanalytic perspective
This domain of psychology focuses on studying the mind, and its relationship to our actions and experiences.
Cognitive Domain/Cognitive psychology
If you want to work as a college professor in psychology, you will most likely get this type of degree.
PhD
A type of evidence that is objective and tangible.
Empirical Evidence
Type of research in which scientists passively observe and measure phenomena.(hint: does NOT equal causation)
Correlational research
The part of a research article that gives a concise summary of the work and findings.
Abstract
The belief that people get the outcome they deserve (good things happen to good people, and bad things happen to bad people).
Just-world hypothesis
When a witness does not help a victim/person struggling, increases as there are more people in the area
Bystander effect
Seeking out information that is consistent with a belief and ignoring information that challenges it.
Confirmation bias
Edward Titchener was a student of this man, whose ideas he built on in order to develop Structuralism.
Wilhelm Wundt
This domain of psychology focuses on things such as learning and behaviorism across the lifespan.
Developmental domain/ Developmental psychology
If you become a researcher, you will make observations, develop hypotheses, test conduct experiments, and draw conclusions from the results, which are all step in this method of research.
Scientific method
The second stage of the scientific method. A testable prediction that is logically concluded from a theory.
Hypothesis
This group within the experimental set-up is not exposed to any experimental manipulation.
A larger collection of individuals that we would like to generalize our results to.
Population
Valuing goals/achievements as higher when more effort is put in.
Justification of effort
Decreased individual work in a group setting.
Social loafing
the ___-___ is the group that people identify with vs the ___-___, which is the group people view as fundamentally different.
in-group vs out-group?
In the structural model of personality, Sigmund Freud thought that personality consisted of these 3 parts.
Id, Ego, and Superego
An individual's consistent patterns of thought and behavior.
Personality
If you want to have a career providing psychological treatment, rather than conducting research, you may want to pursue this type of doctoral degree.
PsyD (Doctorate of Psychology)
A term used to refer to the ability of an experiment to be repeated by another researcher.
Verifiability
A unaccounted for variable that causes the systematic movement of the variables of interest.
Confounding variable
The standard cutoff for the p-value.
<.05
An attitude one may not express outwardly but believes.
Implicit attitude
Improved performance when an audience is watching.
Social facilitation
The phenomena where an individual holds an exception of themselves, and behaves in a way that makes it come true.
Self-fulfilling prophecy
Under the Humanistic view, which emphasized the potential for good in humans, Carl Rogers developed this kind of therapy.
Client-centered therapy
Clinical psychologists refer to this when they are diagnosing their clients or patients.
DSM-V (Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders)
Human Resources, Marketing, and Sales are some of the top occupations that hire individuals with this level of degree in Psychology.
Bachelors of Arts (BA)
If deception occurs in a study on human participants, a ______ after the conclusion of the study is required.
de-briefing
Occurs when people's expectations influences their experience in a situation. A common example is feeling effects with sugar pills.
Placebo effect
Use of a probability-based method to select a subset of individuals for the sample from the population.
The _____ Attitude change approach hypothesizes that the biggest influences on persuasiveness are the source, the content, and the characteristics of the audience.
Assessing the risk and reward to helping in any given situation.
Cost-benefit analysis
Aggression that is motivated by a goal, with no intent to harm.
Instrumental aggression
As a result of the ___ revolution, the focus on strictly observable behaviors shifted to other types of Psychology.
Cognitive revolution
This model suggests that health/illness is determined by an interaction of three factors.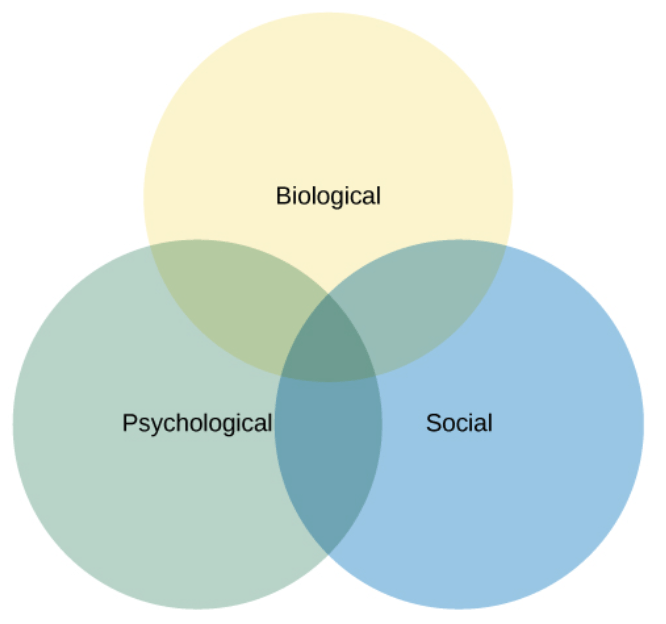
Biopsychosocial model
Of all the types of psychologists mentioned in your textbook, this type is one the most likely to appear in a courtroom.
Forensic Psychologist
A clear and easy to follow ______ section of a research paper is vital for other researchers to repeat the experiment.
Methods section
All your variables must have a ___ ___, which is clear and concise and determines how you will measure your variable. Also allows different researchers to replicate your study.
Operational definition
The expected amount of random variation in a statistic, often defined for 95% confidence level.
Margin of error
The route of persuasion that is indirect and utilizes cues and association.
Peripheral Route
The predisposition to help people who have helped us.
Reciprocal altruism
Which theory proposes that when we are prevented from achieving a goal, humans become aggressive?
Frustration aggression theory