This structure in the limbic system contributes to the encoding of strong visual memories, often formed during trauma or elation.
What is the the amygdala?
This is the first of the three-part of the Atkinson-Shiffrin model.
What is sensory memory?
Alan Baddeley renamed short-term memory to this more accurate representation of the effort employed when using it.
What is working memory?
By studying just before sleep, you could minimize this concept that could otherwise affect how accurately you encode information.
What is interference?
This is one of the ways memories can be affected before later retrievals.
What is reconsolidation?
Infantile amnesia is caused by the fact that this part of the brain is incompletely-developed at birth.
What is the hippocampus?
These are three ways that could lead to forgetting or not knowing something.
-Encoding failure
-Storage failure
-Retrieval failure
These are three ways to help with memorization.
-hierarchies
-mnemonics
-chunking
The effect of asking leading questions to influence perception of memories reflects this type of interference.
What is priming?
Source misattribution, the misinformation effect, and inflated imagination can all lead to these types of inaccurate memories.
What are false memories?
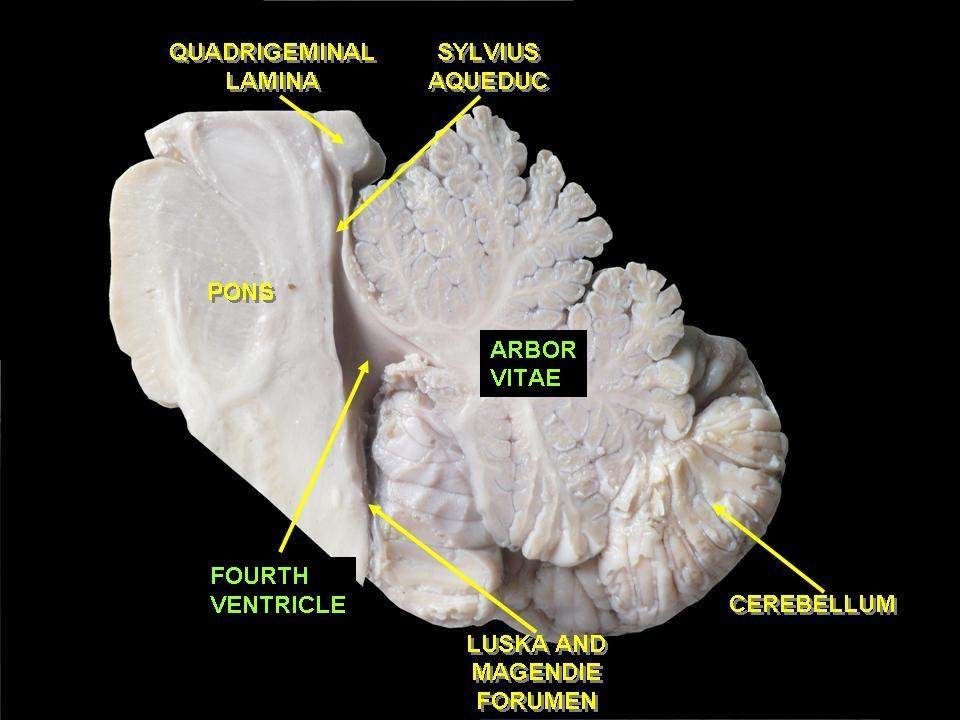
The image shown here, the cerebellum, is where these types of unconscious memories are stored.
What are implicit memories?
This selective directing of your senses toward sensory information is one of the first parts necessary for encoding.
What is attention?
The encoding specificity principle explains how these can help us recall information related to people or places.
What are retrieval cues?
The phenomenon that describes how humans tend to remember the firs and last items they were exposed to is described under this effect.
What is the serial position effect?
This type of amnesia works forward, affecting the short-term ability to form new memories.
What is anterograde amnesia?
After brief, rapid stimulation of a neuron, its firing potential increases, creating new synapses in this process.
What is long-term potentiation (LTP).
It's easier to store information when the brain undergoes extensive consolidation during this regular human habit.
What is sleep?
It declines rapidly first and then levels.
If you learned certain information in a good mood and then tried to recall it again later, it would be easier to retrieve this information in the same good mood and environment thanks to this concept.
What is state-dependent memory (specifically mood-congruency)?
These are the two types of interferences that can affect how you store or process memory.
-Prograde interference
-Retrograde interference
This brain structure is involved in implicit, procedural memories that store skills like playing piano.
What are the basal ganglia?
Explicit memories are either semantic, factual general knowledge, or this type of visual information.
Beneath this overreaching organizer, there are three major sub-processes of working memory that include the phonological loop, the episodic buffer, and the visual-spatial sketchpad.
What is the central executive?
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SO-3Ruw61Sg
This type of amnesia that Clive Wearing has leaves long term memories intact, explaining why he remembers people from his childhood.
What is anterograde amnesia?
Freud thought that traumatized individuals would repress memories of negative events. The existence of these types of memories suggests otherwise.
What are flash-bulb memories?