A researcher assigns participants to a particular level of this type of variable.
What is a manipulated variable?
________________ ask “why,” and ___________ ask “for whom” or “when.”
What is "mediators" and "moderators"?
These three criteria must be fulfilled in order to make a causal claim.
What are covariance, temporal precedence, and internal validity?

DAILY DOUBLE!!!! According to a research study reported by CNN News, chocolate consumption is highest under age 20 and over age 70, with 21-69 year old eating less chocolate. This is an example of a ______________ association (if we were to plot it).
What is a curvilinear association?
This characterizes the STRENGTH of a correlation, a measure of statistical validity.
True or False? Experiments must have at least one independent variable and one dependent variable, but they often have MORE than one dependent variable.
What is true?
Behavioral research is _______________, which means that its findings are not expected to explain all the cases all the time (i.e., there are exceptions).
What is a probabilistic?
Not all experiments have or need this type of group, defined as the neutral (or no treatment) level of an independent variable.
What is a control group?
This pattern is called a __________________ study, and draws this conclusion about narcissism and parental praise?
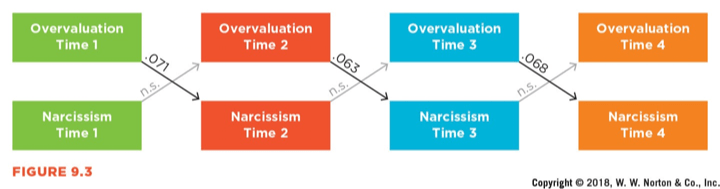
What is a cross-lag study/correlation? This study shows that overpraise by parents (in an earlier time) predicts narcissism in kids (not the reverse)!
This type of claim describes a particular rate or degree of a single variable.
What is frequency?
This type of variable is recorded; in terms of the behavior of attitudes based on self-report, behavioral observations, or physiological measures.
What is a measured variable?
The first row of the table represents _____________ and everything below the first row is called ___________.
What is the main effect and covariates?
Covariance can be established by including this type of group in the study design.
What is a comparison group?
This image depicts this type of association.
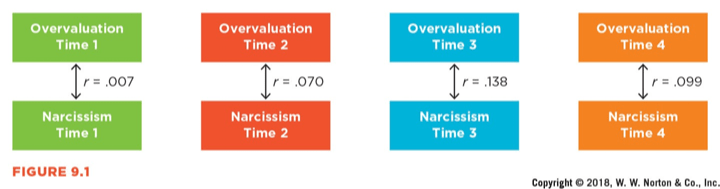
What is a cross-sectional correlation?
This refers to the high likelihood of getting a correlation by chance, assuming there is no correlation in the real world.
What is a nonsignificant result, or a (p)-value higher than .05.
This type of variable is almost always on the x-axis.
What is an independent variable?
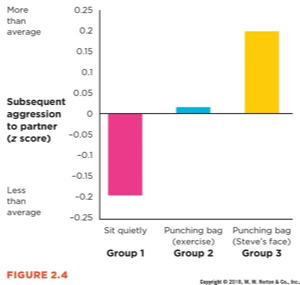
The main benefit of dividing participants into three groups was this.
What is to control for confounding and/or to distinguish between whether exercise alone breeds aggression?
In a situation when it cannot be determined which effect (A or B) came first, we would call this _____________.
What is a directionality problem or failure to establish temporal precedence.
This type of mini-longitudinal design is called _____________ and helps to determine _____________ in variables over time.
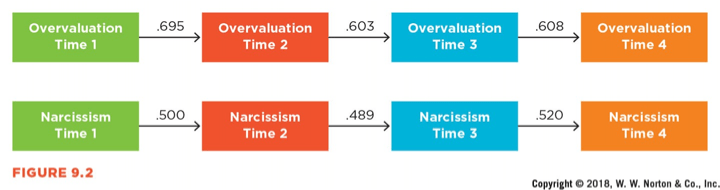
What is autocorrelation and stability (and/or non-stability)?
This occurs when, for any reason, one variable in a model has very little variance - also referred to as ceiling and floor effects.
What is restriction of range?
The purpose of including this type of variable is to make sure researchers are only varying one effect at a time.
What is a control variable?
This type of bias is being persuaded by what easily comes to mind, like an association between shark attacks and swimming on beaches (especially after watching Jaws).
What is the availability heuristic?

In a pasta study, researchers were interested in the relationship between bowl size and pasta consumption (e.g., do bigger bowls make you eat more). This type of variable would be present if some participants received Chef Boyardee pasta and others received penne vodka from a fancy restaurant.
What is a confounder?
In this example, the quality of social ties is a middle step between two variables, also referred to as _______________.
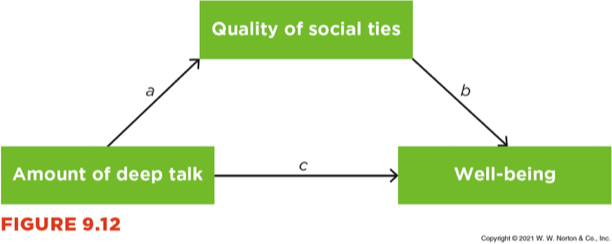
What is a mediator?
This type of association likely has a __________ beta estimate and a ___________ p-value.
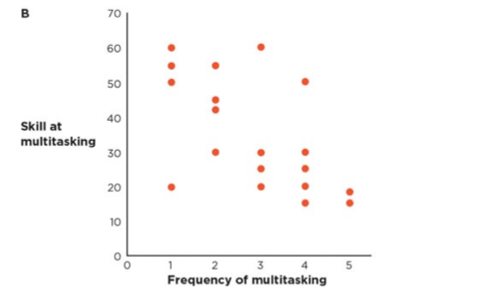
What is strong, negative and significant?