What is a stimulus?
A singular thing that you experience through your sessions.
True.
What is an independent variable?
A publicly observable change controlled by the experimenter that is anticipated to influence behavior in a specific way.
What is frequency?
The response count divided by the time or opportunity to respond.
What is magnitude?
The force or intensity of a behavior.
How many phases does a comparison (AB) design have?
Two
AKA for "bounce"
variability
What are the 2 assumptions that guide the science of behavior analysis?
1. Behavior is determined.
2. The scientific method is a valid way to identify the determinants of behavior.
What is behavior?
an individual living organism's activity (public or private) which may be influenced by internal or external stimulation.
A falsifiable hypothesis is the same thing as a mentalistic explanation.
False. A falsifiable hypothesis can be tested and a mentalistic explanation cannot.
What is a functional variable?
A variable that, when manipulated, reliably and systematically changes behavior.
What is latency?
The interval of time between the opportunity to respond and the response itself.
What is reactivity?
When behavior changes because the individual is aware they are being watched.
What type of single-subject design involves repeated exposure to BL and treatment conditions and a return to baseline that allows us to make conclusions about causation.
The reversal (ABA) design.
This graph depicts a change in....
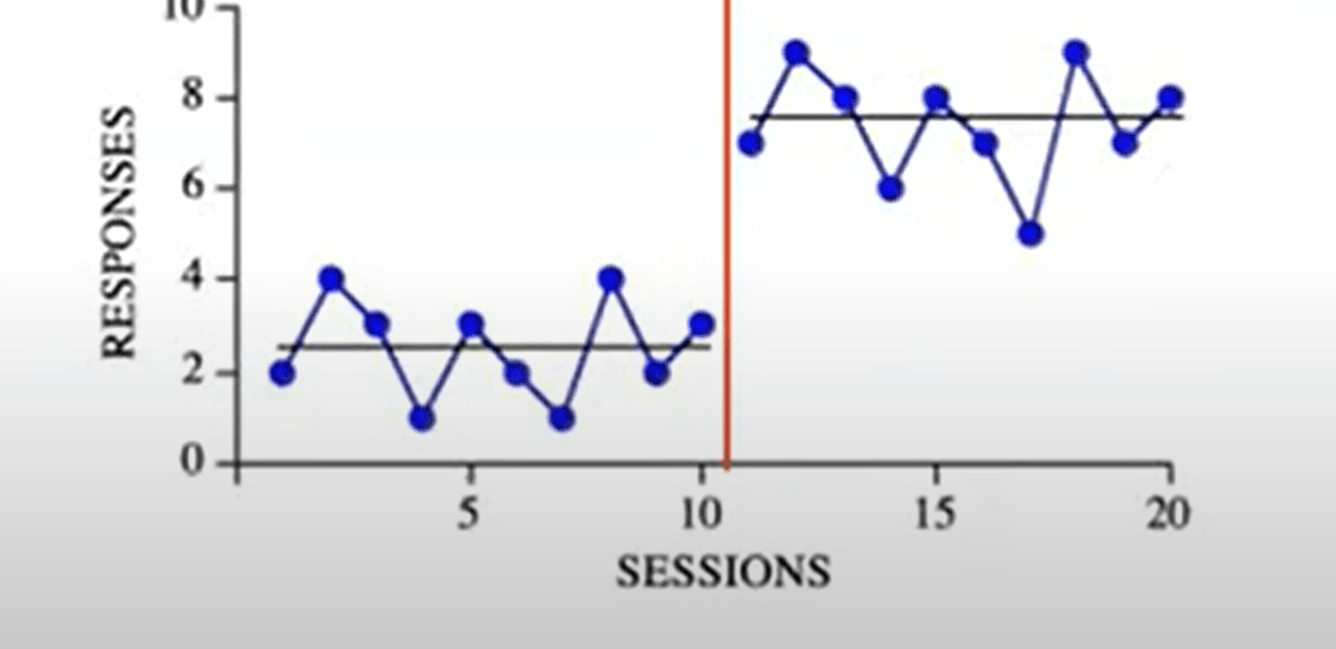
Level
What are the two goals of behavior analysis?
1. To discover functional variables that may be used to positively influence behavior.
2. To predict behavior.
Individual behavior is determined by nurture alone.
False. It is determined by nature and nurture.
What is the dependent variable in behavior analysis?
Behavior
What is duration?
The interval of time between the start and the end of the behavior?
When should you use outcome recording?
When observation could cause reactivity and when the behavior leaves distinct, lasting products.
Which design involves rapidly turning ON and OFF the independent variables to evaluate if this systematically and repeatedly changes behavior?
The alternating-treatments design
This graph depicts a change in...
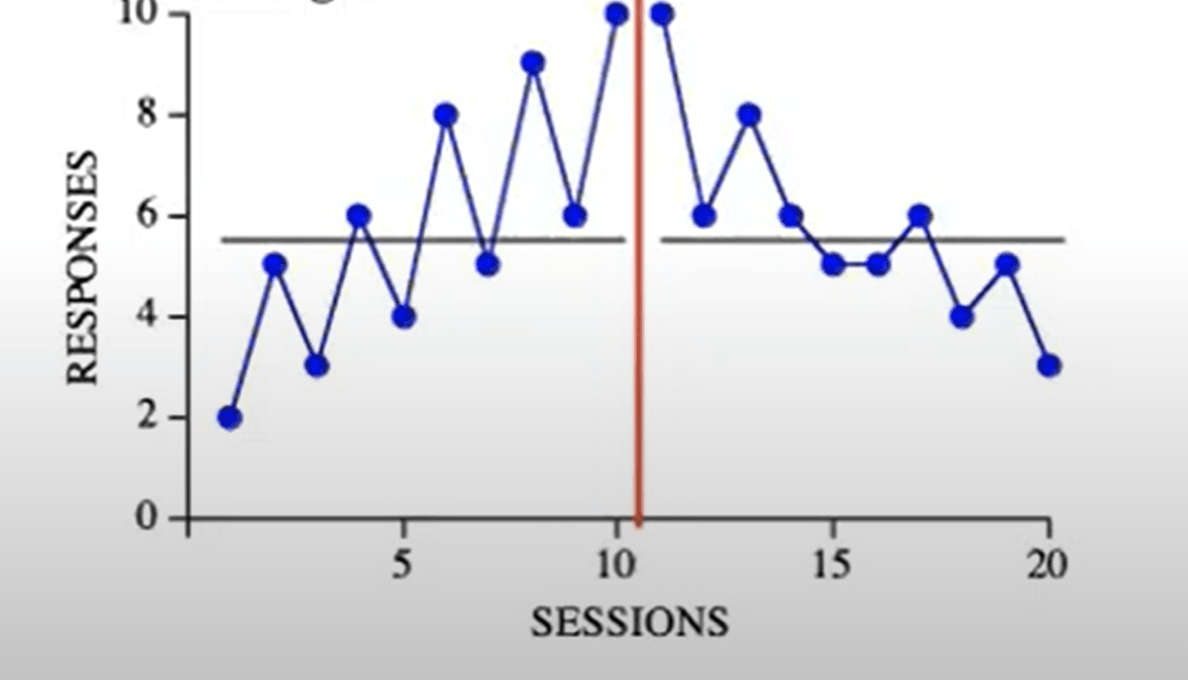
Trend
What are 4 dimensions of behavior that we can objectively measure?
frequency, latency, duration, magnitude
What is determinism?
Behavior has a knowable cause or causes.
Applied behavior analysts research and practice behavioral service delivery in clinical settings.
True.
What is a confounded variable?
A variable that influences behavior within an experiment, but is not controlled by the researcher.
What is event recording?
Recording each instance behavior at the moment it occurs.
Which direct observation method estimates how frequently behavior occurs by recording whether or not behavior occurs during any portion of a series of intervals?
Partial-interval recording
Which single-subject design evaluates the functional relation between an IV and DV by conducting a series of time-staggered A-B comparisons either across behaviors, across situations, or across individuals?
Multiple-baseline design
This graph depicts a change in....
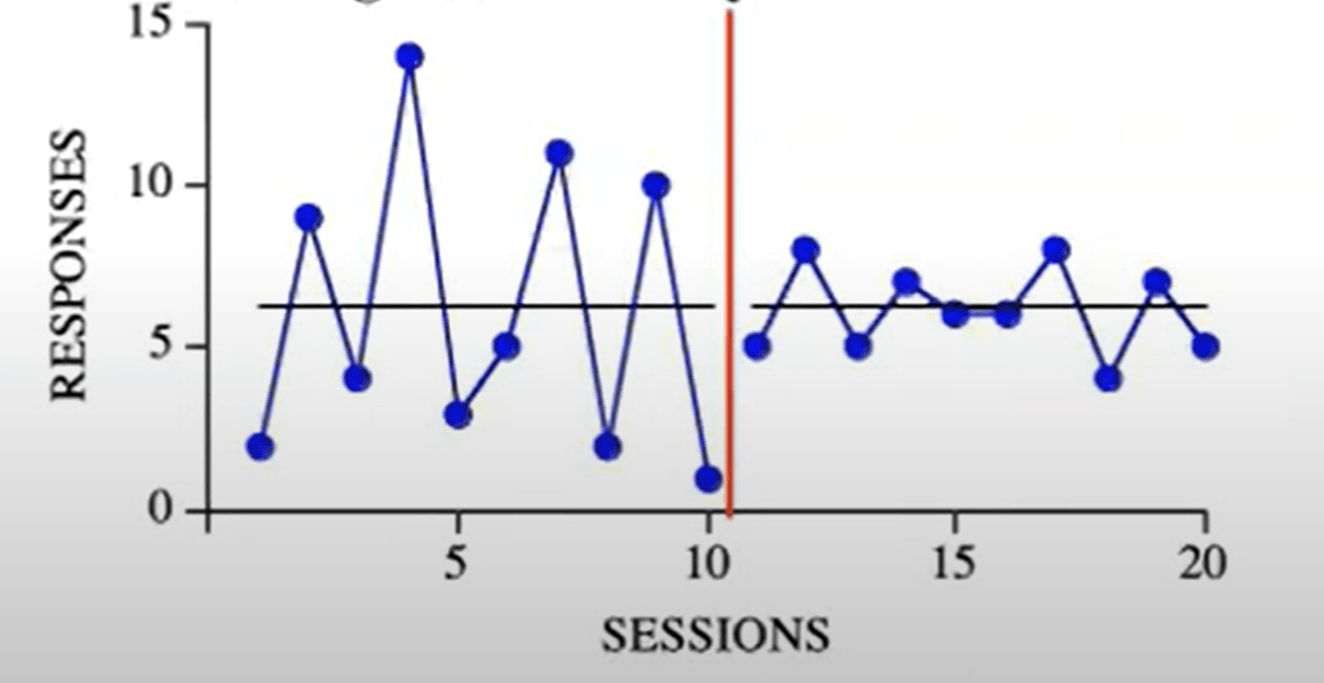
Variability (bounce)
What are 3 types of replication?
across individuals, across labs, within-individual
What is a behavioral/operational defintion?
A precise specification of the topography of the target behavior, allowing observers to reliably identify instances and non-instances.
A comparison (or AB) experimental design can imply causation.
What is internal validity?
When an experiment provides clear evidence that a functional relation exists between the IV and DV.
What type of direct-observation method is used to estimate how frequently behavior occurs by recording whether or not behavior occurs throughout each interval in a series of intervals?
Whole-interval recording.
What direct-observation method would you use to measure latency and duration of a behavior?
Duration.
What are the 4 defining features of single-subject experimental designs?
•Focus on individual subjects
•They experience both ON and OFF conditions
•Repeatedly measure behavior in each phase
•Assess internal validity through replication and controlling confounding variables
What is visual analysis?
Looking at a graph of time-series data to evaluate if a convincing change occurred when the independent variable was introduced/removed.
What is inter-observer agreement or IOA?
The extent to which two independent observers’ data are the same after having directly observed the same behavior at the same time.
What does it mean if a behavioral definition has social validity?
The consumer of the intervention or an expert in the field indicates that the behavioral definition accurately reflects the behavior of interest
Self-report and direct observation are both methods for measuring behavior.
True.
Which variable is being turned ON and OFF during an experiment?
The independent variable.
How do you calculate interobserver agreement?
(Agreements)/(Agreements+disagreements)*100
What is the difference between latency and duration?
Duration is recording the onset and offset of the behavior. The latency of the behavior is starting to record as soon as the opportunity to respond is presented (like an instruction) and the onset of the behavior.
What are 4 weaknesses of using a group design?
The use of control groups, overreliance on stats, the control and experimental groups are inherently different, and they focus on groups rather than individuals.
What are the three guidelines for conducting a visual analysis?
Step 1: draw a trend arrow through the baseline data to predict what will happen if the IV is never turned on
Step 2: eval if the bx in BL is too variable (bouncy) to have confidence in the prediction of the trend arrow
Step 3: draw trend or level lines (if no trend) through the intervention data. Evaluate if there is a convincing change in trend or level (depending on the change of interest)
What are 3 fields within behavior analysis and what do they do?
1. Organizational behavior management (OBM). They conduct research in the workplace.
2. Applied behavior analysis (ABA). They conduct research in clinics and provide behavioral service delivery.
3. Experimental Analysis of Behavior (EAB). They conduct research in a laboratory.