Continuous Reinforcement
Every instance of the response is reinforced
Cumulative record
A graphical display of responding as it unfolds over time.
An antecedent stimulus that facilitates or guides the desired response when it is not happening under appropriate stimulus control.
What are some empirically-based interventions for improving sports performances?
Miltenberger: behavioral coaching, video modeling and video feedback, auditory feedback (clickers), public posting, reinforcement, video self-evaluation
What schedule does this graph represent?

Fixed interval (see the equal distance between reinforcer deliveries and the scallops?)
Variable ratio schedule (definition and typical pattern of responding)
The number of responses required for a reinforcer changes every time. They produce a high rate of responding with little or no post-reinforcement pause.
Fading (prompt fading)
The gradual removal of a prompt as the response is increasingly emitted under discriminative-stimulus control.
What is the role of Pavlovian conditioning (i.e., classical or respondent conditioning) in behavioral sports psychology? That is, what behaviors does Pavlovian conditioning develop and how can Pavlovian conditioning correct those behaviors?
- Pavlovian conditioning can cause fear responses for certain situations. For example, if a defender running at you (a quarterback) has been paired with pain, then the sight of that defender now signals pain; thus, the sight of the defender now elicits fear responses. You may then behave operantly to avoid pain when a defender runs at you. These behaviors could be cowering or quitting football all together. Behavioral therapists may be able to use respondent/Pavlovian extinction to un-pair those two stimuli. This could be done by teaching the skills needed to avoid pain like dodging the defender or teaching relaxation techniques so he can focus on making the pass.
What schedule does this graph depict?
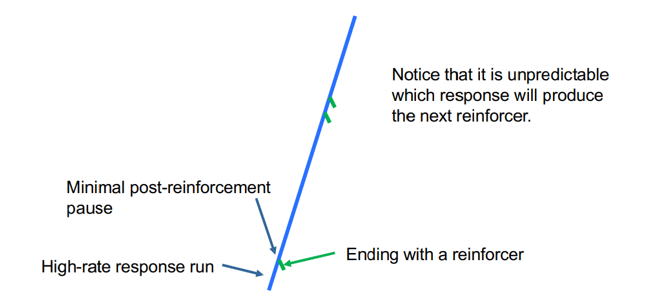
Variable Ratio
(high rate of responding, no pausing, variable reinforcer delivery)
Ratio Schedules
A schedule of reinforcement that specifies the number of responses that must be made in order for the reinforcer to be delivered.
Fixed interval schedule (definition and typical pattern of responding)
This schedule specifies a constant time interval must elapse before a single response is reinforced. This produces a pattern of responding in which a post-reinforcement pause gives way to an accelerating response rate that terminates with a reinforcer (aka a “scallop”). .
Generalization Gradient
A graph depicting increases in responding as the novel antecedent stimulus more closely resembles the SD.
What was a major limitation of many of the studies that Dr. Miltenberger presented in the lecture?
Very little long-term follow-up data
What schedule is this graph depicting?
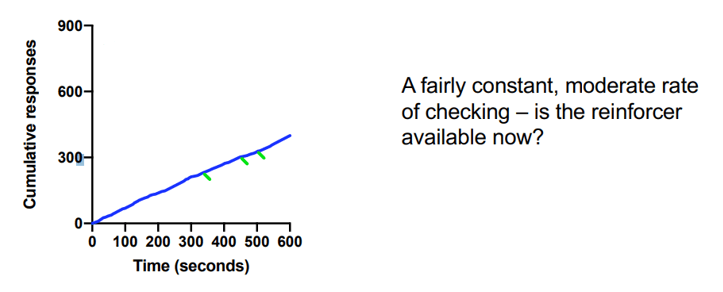
Variable Interval (see the variable reinforcer deliveries and moderate rate of responding?)
Interval Schedules
A schedule of reinforcement that specifies the amount of time that must elapse before a single response will be reinforced
Variable interval schedule (definition and typical pattern of responding)
A schedule in which the time that must elapse before a single response is reinforced is not the same every time. This produces a steady, moderate response rate with little to no post-reinforcement pause.
US/CS vs SD
US/CS elicit reflex responses while SD evoke operant behaviors because the SD signals that a reinforcer is available.
What are some examples of “problem behaviors” that exist in sports?
Examples: Aggression, temper-tantrums, excessive socializing during drills
Definition: Disruptive, non-athletic activities that interfere with athletic performance or create aversiveness for other
What type of schedule does this graph depict?
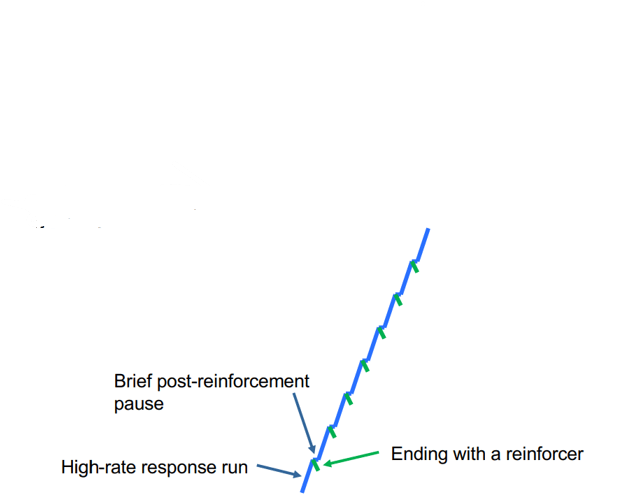
Fixed Ratio (see the evenly spaced reinforcer deliveries and no reinforcement pausing?)
Fixed ratio schedule (definition and typical pattern of responding)
The number of responses required for a reinforcer is the same every time. They produce a post-reinforcement pause followed by a high-constant rate of responding which ends with a reinforcer (aka a “break and run”).
Schedule Thinning
A procedure used to gradually reduce the rate of reinforcement, while being careful to maintain the desired behavior.
Discriminated operant
A behavior that is systematically influenced by antecedent stimuli.
What are the 4 steps that behavioral sports psychologists teach athletes to reduce anger?
(a) helping the athlete to identify anger-causing situations, (b) teaching the athlete to perform substitute behaviors to compete with the anger, (c) prompting the athlete to practice the substitute behaviors using imagery and/or simulations and/or role-playing, and (d) encouraging the athlete to use the coping skills in competitive situations and to receive feedback.
What is this graph depicting?
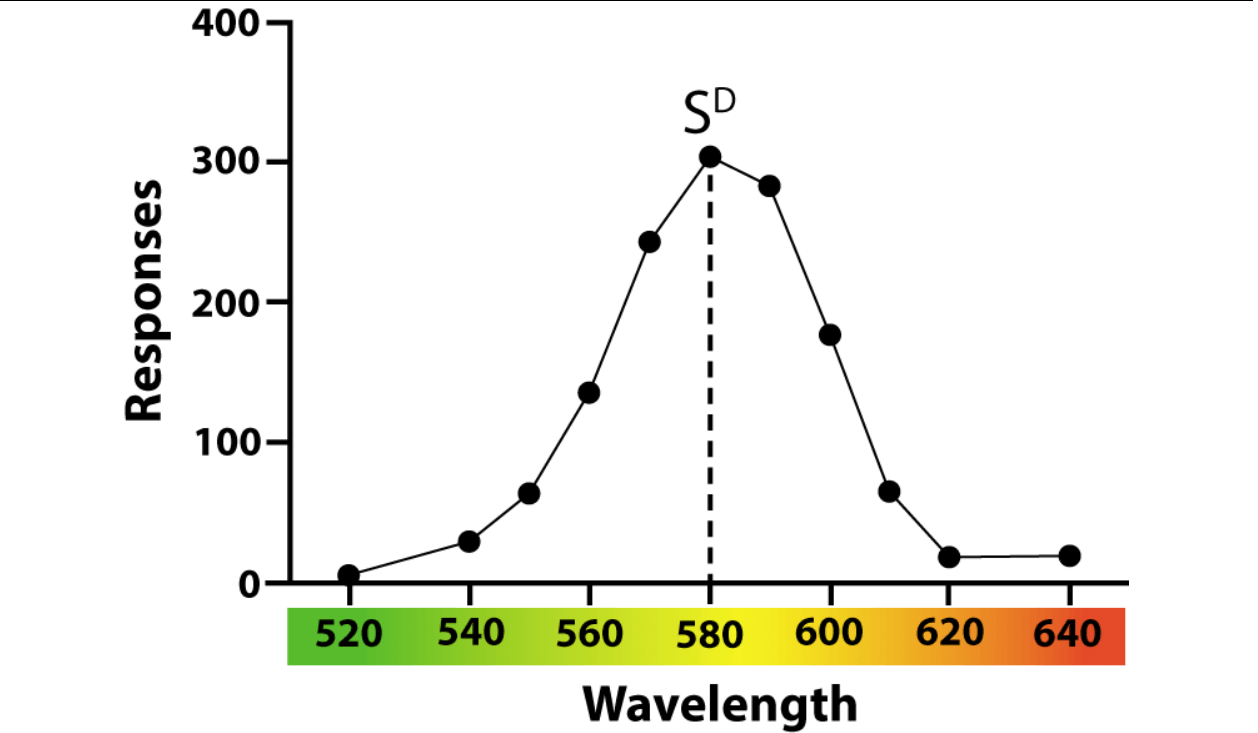
Generalization gradient
Antecedent stimulus
A stimulus that is present before the behavior occurs.
Discriminative stimulus (SD)
An antecedent stimulus that can evoke a specific operant response because the individual has learned that when the SD is present, that the response will be reinforced.
S-delta (S∆)
An antecedent stimulus that decreases a specific operant response because the individual has learned that when this stimulus is present, that response will not be reinforced (extinction).
What strategies do behavioral sports psychologists teach to reduce excessive nervousness or fear?
They teach athletes to (a) recognize and change negative thinking that might cause the fear or nervousness, (b) restructure the environment to “tune out” and prompt relaxing thoughts, (c) practice a relaxing breathing technique called deep center breathing, (d) practice progressive muscle relaxation by alternatively tensing and relaxing various muscle groups and paying close attention to how the muscles feel when they are relaxed versus tense, (e) maintain a sense of humor, and (i) visualize relaxing scenes
Which data path depicts the response pattern of which schedule of reinforcement?
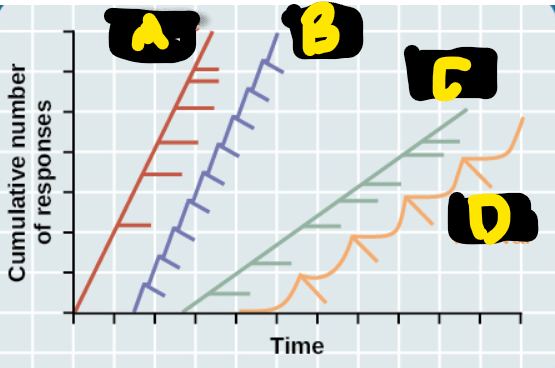
A: VR
B: FR
C: VI
D: FI
Discriminative stimulus for punishment (SDp)
An antecedent stimulus that decreases a specific operant response because the individual has learned that when this stimulus is present, the response will be punished.
Discrimination Training
A procedure in which an operant response is reinforced in the presence of an SD and extinguished in the presence of an S∆.
Generalization
Occurs when a novel stimulus resembling the SD evokes the response, despite that response never having been reinforced in the presence of that novel stimulus.
What four behavioral functions might self-talk serve?
- Conditioned stimulus to elicit various emotions (e.g., relaxation)
- Cue for attending or focusing on relevant stimuli
- Discriminative stimuli that prompt strategic body positions for motor skills
- Conditioned reinforcer
Read the APOPO Rats section!