What is a "factor" in factor analysis?
An unobserved or latent variable representing a construct.
What is the main reason to use SEM methods?
Issues with NHST alone
What is the equation for classical test theory?
Xi = Ti + ei
In this picture, what do H1, H2, and H3 represent?
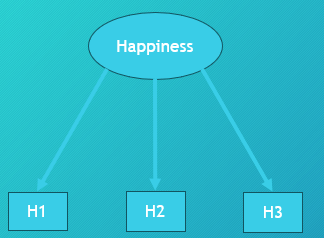
Individual observed test items loading onto the "happiness" factor.
What type of model is displayed here?
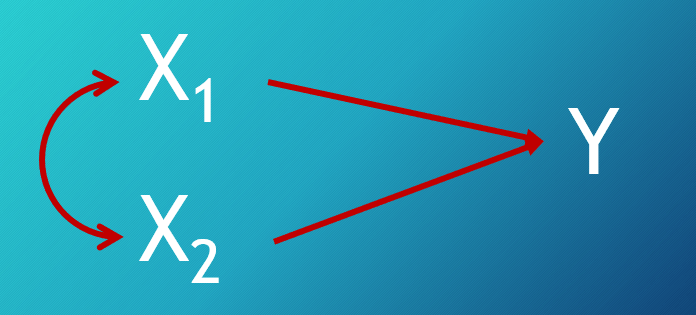
Correlated Causes Model
What are the two broad predictors of observed responses, according to item response theory?
Individual Differences
and
Characteristics of Test Items
What is being described by "...how strongly an observed variable is predicted by an unobserved (latent) factor..." ?
Factor Loading
What type of model is displayed here?
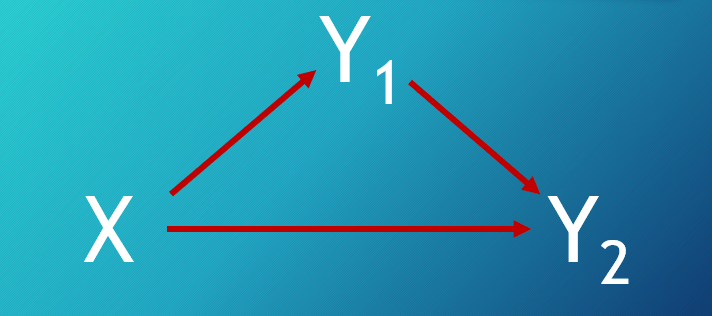
Indirect Effects Model
If classical test theory is deterministic, then item response theory is __________.
What does it mean if two factors are said to be orthogonal?
They are uncorrelated
What are the three requirements for establishing causality?
1. Establish association
2. Establish temporal precedence
3. Rule out alternative explanations
Assume test item "A" has a item difficulty of 1.
Person 1 has an ability of -3 and Person 2 has an ability of 2 on the construct for which test item A is measuring.
For which person (1 or 2) would item response theory be able to generate a more accurate prediction, regarding their accuracy on test item A?
Person 1
What are the five steps in the factor analysis process to publication?

In an indirect effects model, what does c' represent?
The direct effect
(X predicting outcome controlling for the indirect effect)
What is the item response theory assumption of local independence?
There is no statistical relation (e.g., correlation) between people's responses to pairs of items on a test once the primary trait being measured is held constant.