What is the Tripartite Model?
Prejudice = a negative attitude toward people in a group based solely on their membership in that group (affective)
Stereotypes = generalizations about a group of people in which identical characteristics are assigned to virtually all members of the group (cognitive)
Discrimination = unjustified negative or harmful behavior towards members of a group simply because of their membership in the group (behavioral)
Which artificial mother did the monkeys in Harlow’s studies prefer?
Cloth, regardless of where the money was being fed from
What are Piaget's 4 stages of development?
+ at what age ranges do these stages typically occur?
1. Sensorimotor (0-2)
2. Preoperational (2-7)
3. Concrete Operations (7-11)
4. Formal Operations (11 and up)
What were Eysenck's proposed Essential Traits?
- Extraversion
- Neuroticism
- Psychoticism (aggressiveness, creativity, impulsiveness)
What does the National Comorbidity Survey Replication say about the lifetime prevalence of any disoder?
it’s just under 50% of people in the US
What is the Minimal Group Paradigm?
Tafjel (1970):
Process used to examine the minimum conditions that create discrimination between groups
• Examples: Color of shirts, preference for paintings
• Generally, it takes very little for people to act in a manner consistent with in-group favoritism
What are some methodological flaws with Harlow’s studies on attachment?
-Artifact of everything taking place in a lab with monkeys taken away from their families
-Study not on humans prevents generalizability
How do individuals move between stages (3 terms)?
Assimilation: transformation of incoming information to fit current way of thinking
Accommodation: adaptation of current thinking to fit new experiences
Equilibration: integration of knowledge into one unified whole
What are the directions of Eysenck's Personality diagram?
___________ <-> ? extraversion
neuroticism <-> ______________
introversion <-> extraversion
neuroticism <-> ?emotional stability
What kinds of psychopharmacology are used for certain disorders?
-Antidepressants (SSRIs, Tricyclics) - depression
-mood stabilizers (lithium, lamictal) - bipolar
-antipsychotics - schizophrenia
What barriers might there be to getting a valid self-report of prejudice, stereotyping, and/or discrimination?
Social desirability bias: tendency of survey respondents to answer questions in a manner that will be viewed favorably by others. It can take the form of over-reporting "good behavior" or under-reporting "bad", or undesirable behavior.
== Aversive Racism
What is imprinting?
-not in humans
-ducklings attach to the first moving figure they see, even if it’s not another duck
What are the 6 stages during the sensorimotor stage, and their relevance to object permanance?
Can you name one, a couple?
Stage 1 (birth to 1 mo.): concerned primarily with reflexes related to feeding and touch
Stage 2 (1-4 mo.): no sign of object concept (no object permanance!), behavior preparing for it
Stage 3 (4-10 mo.): begin to purposefully and repeatedly manipulate objects they encounter in the environment. Will search for partially visible object.
Stage 4 (10-12 mo.): still incomplete because child lacks ability to understand visible displacement (A not B effect)
Stage 5 (12-18 mo.): Sequential displacements, searches for last visibly hidden place. Remains unable to understand invisible displacements.
Stage 6 (18-24 mo.): Mentally represent objects that undergo invisible displacements… the beginning of true thought
What was Allport's Lexical Hypothesis?
"Important aspects of life will be labelled with words, and if something is truly important and universal there will be many words for it in all languages"
What are the DSM-5 Criteria for Diagnosing Major Depressive Disorder?


What were the findings of Amodio et al. (2004)?
Response time for Black faces when it was a tool was much higher than for White faces, and the error rate was much higher when it was a tool for Black faces.
Vice versa for gun --> response time much faster for Black faces than White faces, and the error rate was much higher when it was a gun for White faces.
(IATs)
What is Bowlby's Attachment System?
• Internal working model = beliefs, expectations, and emotional reactions one brings to a new attachment relationship
• Differences in quality of parent-child attachment relationships result in different types of internal working models
• Attachment security = confidence that the attachment figure is available, responsive, and will always be there to help, save, or comfort you
• Attachment insecurity = lacking confidence that the attachment figure is available, and able to save you
What are 2 key features of the Pre-Operational stage?
Egocentrism: inability to understand another person’s point of view
Conservation failure
What does it mean when we say Five-Factor Model (FFM) traits are orthogonal?
Suggests that each of the Big 5 traits are distinct/unrelated.
What is the most widely used school of therapy in the US?
Cognitive (e.g., CBT)
Murphy, Steele, & Gross (2007)
The Cue Hypothesis
Explain study (hypothesis, method, results)
Hypothesis: Situational cues can make social identity salient
Method:
• Stanford undergraduate participants (25 male, 22 female)
• All watch 7-minute neutral (nature video)
• Watch EITHER:
• Gender-balanced conference video (150 people in 1:1 ratio of M:W)
• Gender-imbalanced conference video (150 people in 3:1 ratio of M:W)
Women felt a stronger sense of belonging, less activation of physiological measures (less arousal), and less cognitive vigilance in the gender-balanced videos.
Men had similar/same effects for the gender-unbalanced videos, as we can infer that they view these situations as more "normal."
What does attachment in Infancy Predict?
•... social behavior throughout
development
• ... attachment in adulthood
• ... risk for psychopathology
• ... relationship quality in
adulthood
What are two examples of defining characteristics of the concrete operations stage?
1. Can do conservation

2. Decentration of perception: can understand/classify objects in terms of more than one dimension

List & define all of the Big 5 traits.
Openness (Intellect; Facets include: fantasy, ideas, actions )
Conscientiousness (Facets include: competence, deliberation)
Extraversion (Facets include: social, outgoing, active, outspoken, dominant, adventurous)
Agreeableness (conformity/compliance/likeability/ warmth; Facets include: compliance, altruism, modesty)
Neuroticism (emotional instability; Facets include: hostility, anxiety, impulsiveness)
May want to use OCEAN or CANOE acronyms
Define lifetime prevalence
How many people will have the disorder at some point in their lifetime?
What was the procedure of Steele & Aronson's (1995) study about stereotype threat? What was their hypothesis? What did they find?
Hypothesis: black participants will underperform relative to white participants in diagnostic condition, but not in non-diagnostic condition
Given a difficult test of verbal ability.
IV: Test described as diagnostic of intellectual ability (potentially evokes stereotype threat). Also told to think of it as a challenge or not.
OR
a lab problem solving task not diagnostic of ability
DV: performance on 30-minutes of GRE verbal items
Results:

Second study:
IV: circle race before performance on a 25-minute test or not
DV: Performance on the test
Results:

What is the Strange Situation Test?
Measure of attachment developed by Mary Ainsworth
• Early childhood (12-18 months)
• Separation and reunions
• Effective use of caregiver: goes to parent when distressed (safe haven) and returns to play when distress has resolved (secure base)
• Related to parent-child interactions at home
Strange Situation: odd behaviors, stereotypies, incompatible approach-avoid behaviors during reunion. Conflicting behavioral tendencies activated simultaneously and lead to incomplete or contradictory actions
What are examples of abilities during the formal operations stage?
Overall: Can apply logic and systematic thought to abstract problems
Reasoning abilities:
- Deductive reasoning: ability to come to specific conclusions based on information and predictions (general - specific)
- Inductive reasoning: ability to make generalizations from observations (specific - general)

Which of the big 5 traits could be considered somewhat universal?
Only conscientiousness, extraversion, and agreeableness.
Define point prevalence
How many people have a disorder right now, or over a given year?
What is the contact hypothesis?
The idea that if groups come together with equal status and common goals, prejudice between groups can be recuced.
What home behaviors are associated with each kind of attachment style in babies?
- Anxious and Avoidant: parent may reject or ignore distressed child, parent is inconsistently the secure base (Type A Insecure); 20% of infants; lacks confidence that the caregiver is available and responsive
-secure - parent is the secure base (Type B); 70% of 1-year-olds; confident in the caregiver’s ability and responsiveness
-ambivalent/resistant (Type C): parent is also inconsistently available; 10% of infants; lacks confidence that the caregiver is available and responsive
-disorganized/disoriented - parents are frightening towards the child
What is Kohlber's theory of Moral Development?
1. Pre-Conventional: before age 9
• How do I avoid punishment? (obedience)
• What’s in it for me? (self-interest)
2. Conventional: older children adolescents, most adults
• How can I be “good”? (social norms)
• How can I maintain the rules? (law and order)
3. Post-Conventional: rare with adolescents, but some adults attain
• How do I maintain the social contract? (justice)
• What is ethical? (principled conscience)
Which 7 Factors emerge in China and Spain using endogenous scales?
China: E, C, unselfishness, harmfulness, gentle temper, intellect, dependency/fragility
Spain: positive valence, negative valence, C, O, A, pleasantness of emotional experience, engagement/ passion
What is onset?
When do people first experience disorder?
What was the procedure of Sherif et al. (1961): Robber's Cave? What did they find?
• “Normal,” “well-adjusted” 12-year-old boy scouts randomly assigned to 1 of 2 groups
• Stage 1: each group separately engaged in team-building and bonding exercises for 1 week. Teams named themselves “Eagles” and “Rattlers”
• Stage 2: competition between groups (e.g., tug of war, baseball)
• Stage 3: contact and superordinate goals (fixing the camp water supply, pushing a stuck-in-a-rut truck that was carrying food for both groups)
Note: contact alone did not reduce prejudice!
What is the issue with Piaget's stages of development, in terms of culture?
Context matters! Piaget was testing a very limited sample of white, upper middle class children, usually children of professors.
Horrific uses of these stages

Explain Person Vs. Situation debate in personality psychology.
- Mischel (1968) argues that behaviour is too inconsistent across situations for individual differences to be characterized by traits.
- Interactionism: The view that persons and situations are constantly interacting with one another to produce behavior.
- The effects of a personality variable may depend on the situation, or vice versa
- Certain types of people go to or find themselves in different types of situations
- People change the situations they are in
What is comorbidity?
When you have more than 1 disorder at the same time
What is Vgotsky's Sociocultural Theory of Cognitive
Development?
• Teacher = facilitator for learning and meaningful exchange
• Strategies must match the social context and help students
realize and contribute their own unique strengths
• What is learned outside the classroom (i.e., prior knowledge) is
essential to what happens in the classroom
What is the difference between temperament and traits?
- Temperament emerges early in childhood and is understood as largely heritable/biological/innate
- Traits typically emerge later in life, stabilize over the lifespan, and are largely the product of experience
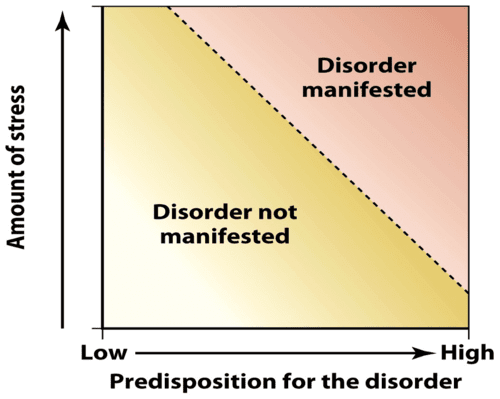
What is diathesis? What is stress? How do they interact in the diathesis-stress model?
Diathesis: predisposition or vulnerability to disord. Examples: genetics, some personality traits, brain injury Stress: Life stressors (e.g, College!)