Ivan Pavlov.
Identify the 3 regions of the brain.

The midbrain, the forebrain and the hindbrain

Identify one case that was solved through forensic psychology.
Any of your podcast episode cases from last year!
Define personality. (Key words required!)
The unique pattern of enduring thoughts, feelings, and actions that characterise a person.
Name the theorist behind operant conditioning.
B. F. Skinner

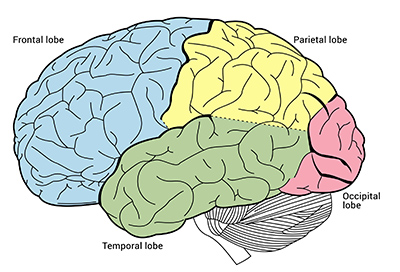
Identify the 4 lobes of the brain.

Frontal lobe, Parietal lobe, Temporal lobe, and the Occipital lobe.
Identify the two types of characteristics a criminal profile depicts about an offender.

Psychological characteristics (e.g. intelligence level and personality characteristics).
Physiological characteristics (e.g. gender, ethnicity, body build, left- or right-handedness).
Identify 2 theories of personality.
Psychodynamic, Social psychoanalytical, Humanism, Behaviourism, Trait
Name the experiment that demonstrated that dogs could be conditioned to salivate at the sound of a bell if that sound was repeatedly presented at the same time that they were given food.
"Pavlov's Dogs"
Identify 3 neurological disorders.
Lou Gehrig’s disease, Parkinsons Disease, Alzheimer’s disease, Epilepsy, Huntington’s Disease, Spina Bifida
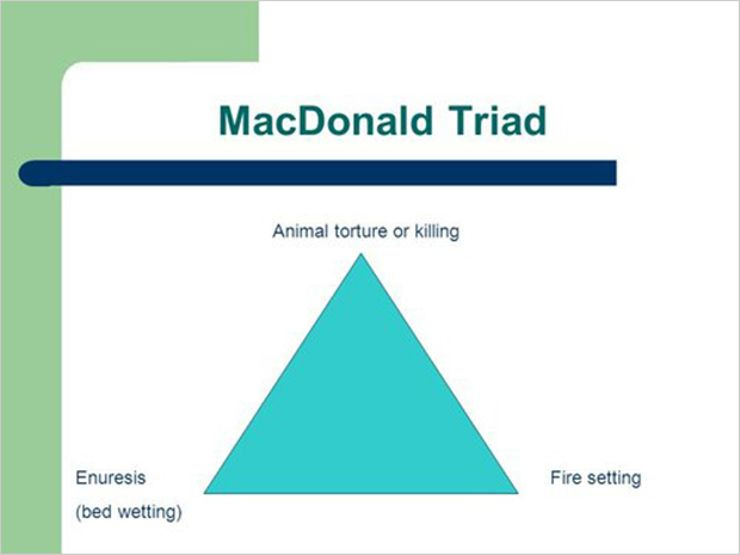
"The Macdonald Triad" comes from a 1963 paper called "The Threat to Kill", written by forensic psychiatrist J.M. Macdonald. In the paper, Macdonald observed that three behaviors were frequently seen in his most aggressive and sadistic patients.
What are the 3 behaviours in The Macdonald Triad, used to predict serial killers as children?
Explain the nature vs nurture debate in personality development.
Bonus points if you can identify the approach to psychology that matches each side of the debate!
The nature/nurture debate examines whether inherited traits and genetics or environmental factors and life experiences play a greater role in shaping a person's personality.
Biological psychology tends to stress the importance of genetics and biological influences.
Behaviourism, on the other hand, focuses on the impact that the environment has on behaviour.
Name the theorist behind the theory that there are six basic universal emotions.
Paul Ekman
The cortex is the outer layer of the forebrain and is wrinkled like a walnut. It has two halves or hemispheres separated by a deep groove.
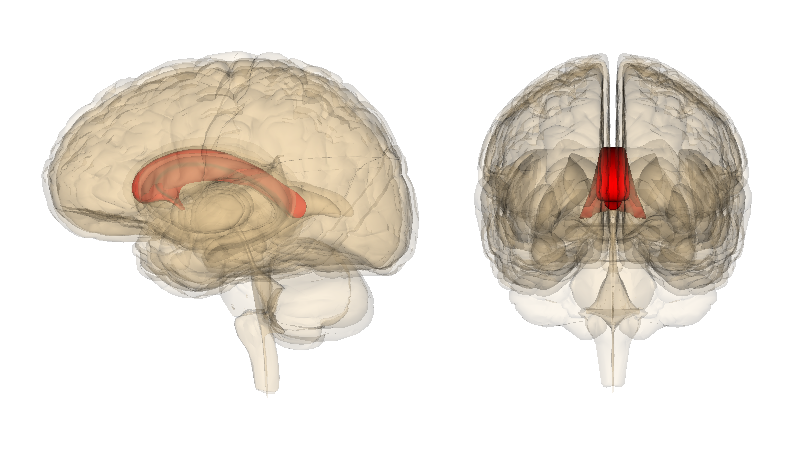
The brain's two hemispheres are joined together by a thick band of fibres - what is the name of this band of fibres?

The corpus callosum - this ensures messages can be sent across hemispheres!
List 4 factors that may limit the reliability of eyewitness testimony in a case.
Age, race, drugs and alcohol, influenced by other witnesses and/or the media, a crime that is extremely traumatic for an eyewitness may affect their recall of the event, limited time seeing the perpetrator's face, simple disguises such as hats or sunglasses can interfere with accurate eyewitness identification, time of day, even attraction levels!
Identify 3 personality tests commonly used in psychology. Explain how one of these tests measures personality.
The Rorschach Inkblot Test, Myers Briggs Personality Test, O.C.E.A.N. Personality Test, popular culture personality tests.
The tendency of participants to act differently from normal in a research study because they know they are being observed.
The Hawthorne Effect
The human brain is comprised of 86 billion neurons! Neurons are information messengers. They use electrical impulses and chemical signals (neurotransmitters) to transmit information between different areas of the brain, and between the brain and the rest of the nervous system.
Identify the 6 features that make up a neuron.
Dendrites, a nucleus, axon, axon ending, a cell body, myelin sheath.

List the 5 types of stalkers.
Rejected, intimacy seeking/erotomanic, predatory, resentful, incompetent.
Explain how one personality theory explains personality formation, identify its key theorist - any strengths and limitations.
Humanistic - Abraham Maslow and Carl Rogers
Psychoanalytical - Sigmund Freud
Behaviourist - B.F. Skinner
Social psychoanalytic - Carl Jung, Erik Erikson