What is a unique feature of the T spine vertebrae?
Costal Facets
List the order of the erector spinae muscle group from most medial to most lateral.
Spinalis, Longissimus, Iliocostalis
In what direction is there the most available motion in the thoracic spine as a whole and segmentally?
Flexion (20 - 45 degrees total)
upper segments: 4 - 5 degreesmiddle segments: 6 - 8 degrees
lower segments: 9 - 15 degrees
Name 3 risk factors for Osteoporosis
> 50 years old
Female genderCaucasian/Asian races + Northern European Ancestry
Family Hx
Long Periods of Immobility/InactivityDepression
Use of Alcohol/Tobacco/Caffeine
Amenorrhea
Thin Body Build
This condition in infants is characterized by a lateral head tilt toward and chin rotation away from the involved side
CMT (Congenital Muscular Torticolli)
In the thoracic spine, do spinal nerve roots exit above or below their same-named vertebrae?
Below
 The Semispinalis muscle consists of three groups: thoracis, cervicis, and capitis. They originate off the thoracic and cervical TP and attach to the SP 4 - 6 segments above the origin. What are the action(s) of this muscle group?
The Semispinalis muscle consists of three groups: thoracis, cervicis, and capitis. They originate off the thoracic and cervical TP and attach to the SP 4 - 6 segments above the origin. What are the action(s) of this muscle group?
ROT to contralateral side
EXCEPT Capitis which primarily extends
As your patient comes into thoracic extension, are the ribs approximating (depressing) or separating (elevating)?
Separating/Elevating
A DEXA scan will measure the bone density at the hip and spine (where bone loss most rapidly occurs); what is the cut-off for normal bone density?
> -1.0
(the Z score should be greater than -2.0)
This condition in infants is a distortion of shape of the skull resulting from mechanical forces that occur pre/post natally
CD (Cranial Deformation)
This is the type of joint found between the rib and costal cartilage (costochondral), it allows for very minimal movement. All the ribs, EXCEPT the first rib, have this joint
Synchondroses
What are the principal muscles of respiration?
External Intercostals (elevates ribs + increases width of thoracic cavity)
Internal Intercostals (elevates ribs)
Diaphragm
A patient presents to your clinic with complaints of back pain in the thoracic region. As you are measuring their AROM, you notice that they have 15 degrees of sidebending to the right and 24 degrees to the left. Which value is most concerning?
R Sidebending (Normal ranges: 20 - 45 degrees)
This condition is measured by the Cobb Angle and can be described by 4 types of curves in the thoracic spine:
1. Thoracic
2. Thoracolumbar
3. Lumbar
4. Double Major Thoracic-Lumbar
Scoliosis
What muscle is associated with CMT?
SCM
The regional rigidity of the thoracic spine serves 4 functions, what are they?
Stability
Protection of Vital Organs (located in thorax)
Mechanical 'bellows' for Breathing
Stable Base for Muscles (to control craniocervical region)
These two muscles make up the most superficial layer of back muscles
Latissimus Dorsi
Trapezius
You have determined that your patient would benefit from a mob at Rib 10, where would the direction of your force be?
Anterior Superior (largely dependent on patient)
What is the structural cause of the extreme kyphosis seen in Scheuermann's Disease?
Wedge-Shaped Vertebra (3 - 4 vertebrae)
What are the first choice interventions for CMT?
Stretching and Strengthening
What part of the rib articulates with the vertebrae at the costovertebral joint?
Is it the head, neck, or tubercle?
Head
(tubercle forms costotransverse joint w facet at TP)
Out of all the Erector Spinae Muscles, which is the most developed in the thoracic region?
Spinalis
When would/With what condition might you see abnormal coupling of motions in the thoracic spine?
Scoliosis
Spinal Fusions
Rib Dysfunction
Instabilities
Brace (for children w Cob Angles of 20 - 40 degrees to prevent GROWTH of curve)
Exercise
What are the three classifications of CMT?
Postural: mildest form presenting as positional preference without limited PROM or nodule
Muscular: involving unilateral tightness of SCM during cervical ROT + SB without nodule
SCM Nodule: most severe form presenting w palpable bands/nodules in SCM with limitations in ROT and/or SB
According to the newer rule, how would you find the TP that correspond with the SP of vertebra T8?
Just lateral to the SP of T9 (palpate caudally)
While the iliocostalis lumborum has a very complicated origin (iliac crest, sacrum, SP of T11 - T12, and lumbar vertebrae), the thoracis and cervicis origin points are much simpler. What are they?
Thoracis: lower ribs (attachment: upper ribs)
Cervicis: upper ribs (cervical TP)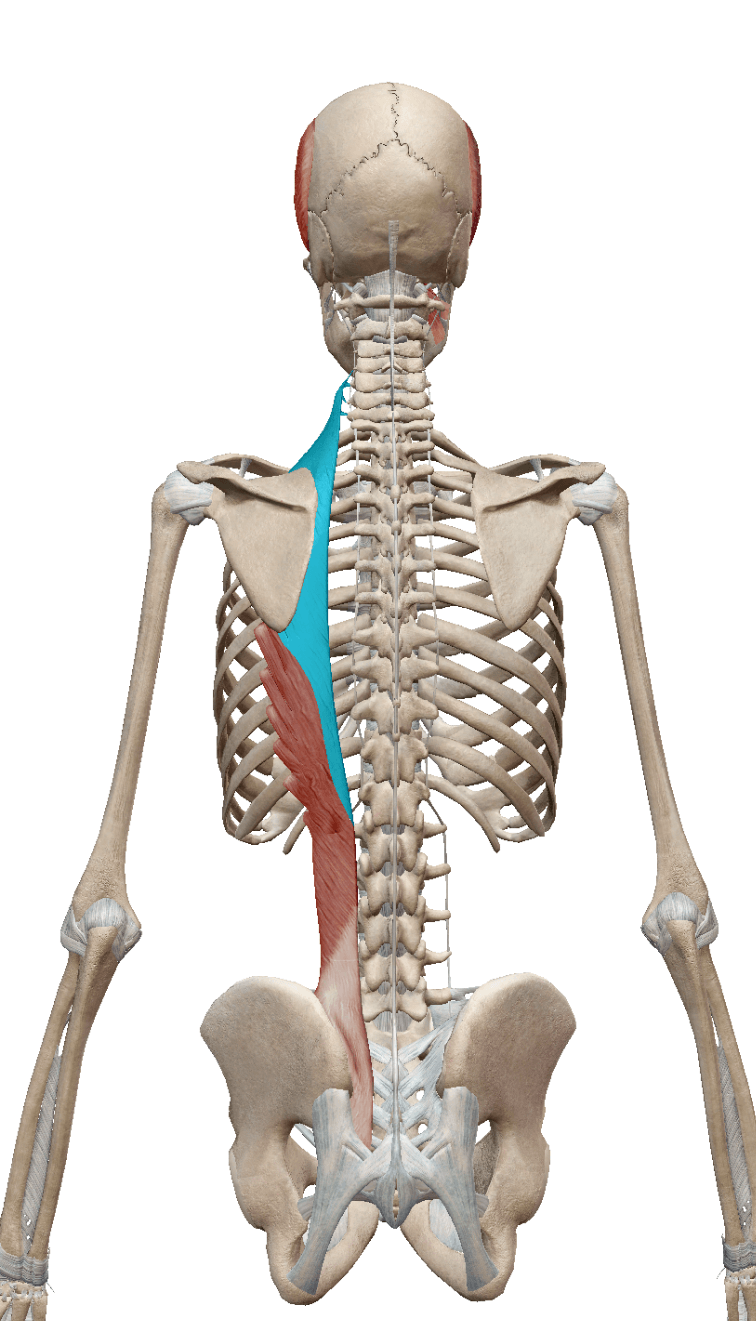
What is the function of a thoracic manipulation biomechanically speaking?
Produces BIL Distraction of the Facet Joints
What are the four categories of scoliosis causes?
Congenital (malformed vertebrae, unequal leg lengths, fused ribs)
Neuromuscular (CP, muscular dystrophy, spina bifida, polio)
Degenerative (arthritis, osteoporosis)
Idiopathic (most common)
At what age is a patient most likely to see full (100%) resolution of CMT?
3 months old
Is the thoracic curve a primary or secondary curve?
Primary
What is the innervation of the series of muscles that attach to the medial border of the scapula from varying levels of the thoracic and cervical spine and serve to downwardly rotate, adduct/retract, and elevate the scapula?
Dorsal Scapular Nerve
Describe coupling motions in the upper, middle, and lower thoracic spine.
(Hint: there are differences)
Upper: SB + ROT happen to the same side
Middle: SB + ROT occur to opposite side in extension but to same side in flexion
Lower: SB + ROT occur to same side in flexion (inconsistent w extension and neutral)
What may be some good treatment options for a patient with osteoporosis? (Name at least 1)
Guided Progression of WBing and Resistive Exercises
Posture
Strength
Balance
Endurance
What are the 9 specific health history factors associated with CMT? (Partial Credit Available)
Age @ Initial Visit
Age @ Onset of Sx
Pregnancy Hx
Delivery Hx
Use of Assistance During Delivery
Head Posture/Preference and Changes in Head/Fce
Family Hx of Torticollis/Other Congenital or Developmental Conditions
Other Known/Suspected Medical Conditions
Developmental Milestones
Fun Fact Time!
How many structures attach to T1 and the 1st Rib?
The transversospinalis muscles all serve to create contralateral rotation; what are these 3 muscles?
Semispinalis (thoracis, cervicis, capitis)
Multifidus
Rotators
Where in the rib cage would it be normal to see pump handle motions?
T1 - T6
(bucket handle motion occurs @ T7 - T12)
Following a trauma, what type of imaging is most appropriate for the thoracic area?
Chest X-Ray (more general and allows view of organs vs rib xray)
What are key exam tools for CMT? (Name 2)
Participation in Play
Cervical PROM
Cervical AROM
Prone Tolerance
Gross Motor Function
Pain (FLACC Scale)
Cervical Strength