What is T-spine pain more commonly caused by compared to low back or neck pain?
thoracic back pain is more likely to be caused by serious underlying pathology than neck pain or low back pain
however, don't forget as well that T-spine pain is common and usually due to muscular strain or joint irritation from retention of static postures
where do cardiac conditions refer to
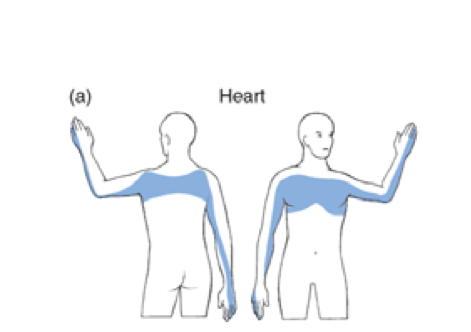 upper thoracic and shoulder
upper thoracic and shoulder
what test is used to screen for scoliosis and what is the sens/spec of it
Adam's forward bend test
positive test: presence of rib hump; can use scoliometer or inclinometer app to measure
SENS:0.92; SPEC 0.60; -LR: 0.13
basically what we should remember about this is that the values vary widely ; inter-rater reliability is fair-to-good; thus we should use baseline values as comparison for each individual patient and not transfer from pt to pt
flexion: 20-45
extension: 25-45
sidebending: 20-40
rotation: 35-60
how to test latissimus dorsi length and why we test this
pt hooklying on table with lumbar spine pressed into table, clasp hands and flex shoulders as far as possible without losing lumbar spine flexion
this is done because tight/short lats may contribute to increased T-spine kyphosis (this is more common in weightlifters)
what are the two types of structural scoliosis
idiopathic: may begin in adolescence or adulthood
degenerative: due to asymmetric degeneration of discs and/or facet joints
Risk factors for fracture of vertebra
minor trauma (if pt is >50 years old with a history of osteoporosis and taking corticosteroids) major trauma (secondary to axial/compressive loading)
often produces a wedge fracture
symptoms can include back pain, lost height, and a hunched forward posture
can rule in lumbar compression fracture with trauma if: age>70 OR history of corticosteroid use
where does stomach/esophagus and liver/gallbladder pain refer to
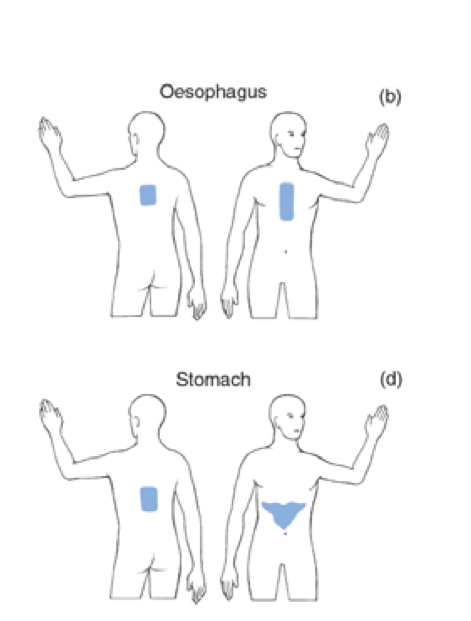
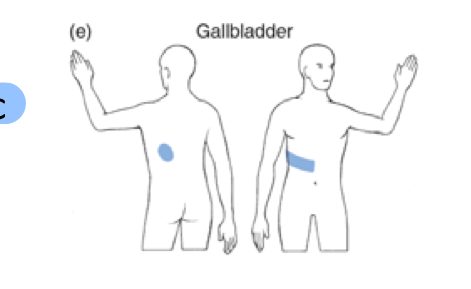 mid-thoracic and inferior scapula
mid-thoracic and inferior scapula
what are the two types of scoliosis
structural (due to structural abnormality within vertebrae; this is fixed)
nonstructural (not due to structural abnormality; not fixed, aka may be corrected)
Why do we do 1st rib caudal springing JPA
anecdotal reports indicate that 1st rib hypomobility may coincide with thoracic outlet syndrome due to brachial plexus and/or subclavian vessel compression between 1st rib and overlying clavicle (validity of this is unproven)
what is Scheuermann's kyphosis
anterior portion of the vertebrae grows slower than posterior during puberty, resulting in wedge shaped body
what is the best treatment for structural scoliosis
early intervention improves likelihood of success and includes:
minimizing curvature progression via bracing and exercise
(exercises can include PSSE like Schroth method, Rigo method, or Scientific Exercises Approach to Scoliosis)
reduce any pain associated with the scoliosis
if you are the first to ID: refer to ortho if curve is pronounced enough; if subtle, advise parents to discuss with PCP
Risk factors for infection
night sweats
underlying disease process
immunosuppression
penetrating wound
where does kidney pain refer to
 posterior low thoracic
posterior low thoracic
how are lateral curvatures named and what is the most common direction of scoliosis to occur in
lateral curvatures are named according to 1) the direction of the curve's convexity when looking at the pts back AND 2) the spinal region they are located in (the ribs also follow the rotation - ie right lateral curvature = right rip hump!)
these curves occur almost always going to the right; if it does go to the left, this is more likely to be associated with something more serious
what is a rib dysfunction
problem at costotransverse or costovertebral joint that could arise due to excessive coughing, trauma, or heavy lifting (?)
signs and symptoms for scheuermann's kyphosis
gradual onset of increasing kyphosis/slouching
may have mid- or upper back pain
some pts have difficulty breathing due to decreased lung capacity
what are the elements of Physiotherapy Scoliosis Specific Exercises (PSSE)
muscular symmetry: relax overworked muscles and strengthen underworked muscles
rotational angular breathing: rotate spine with breathing to help reshape rib cage and surrounding soft tissue
postural awareness: use mirrors to develop awareness
an infection of a nerve and the skin around it by a virus
herpes zoster (aka shingles)
this is caused by a reactivation of a dormant varicella zoster virus
where does pancreas pain refer to
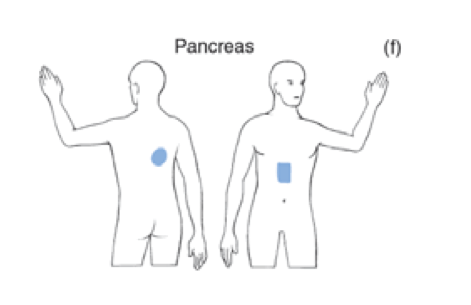 low thoracic
low thoracic
when their rib hump measures >5-7 degrees during Adam's Forward Bend Test
what is the bucket handle motion of the ribs
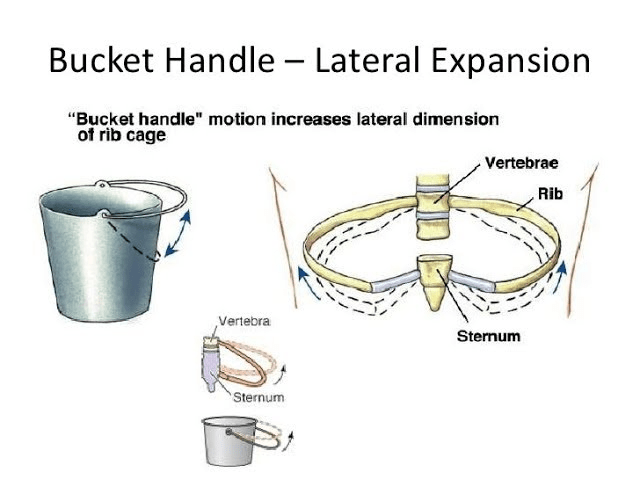 frontal plane movement
frontal plane movement
describes the lateral elevation of ribs during inspiration and lateral depression of ribs during expiration
treatment for scheuermann's kyphosis
prevent progression of kyphosis via stretching/mobilizing into extension
increase trunk extensor muscle strength and endurance
may need extension bracing
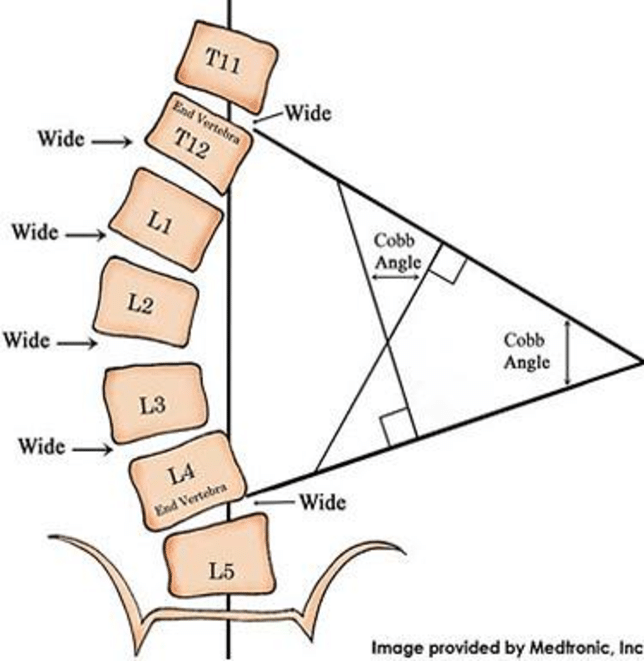
What is the Cobb angle
universal standard of measurement used to quantify scoliosis for the purpose of measuring curve progression over them
measured on radiographs
Risk factors for cancer/tumor
past history of malignancy
age>50
failure to improve with treatment
unexplained weight loss
pain at multiple sites
pain at rest
night pain
(can rule out malignancy if bolded ones are not present (SENS=1)
T-spine facet and costovertebral joints referred pain (idk what we have to know about this but here is a picture)
when is the best time to screen to scoliosis
just before the pubescent growth spurt
for girls: 9-11 years
for boys: 11-13 years
what is the pump handle motion of the ribs
sagittal plane movement
describes anterior elevation of ribs during inspiration and depression of ribs during expiration
this motion would be limited in someone with increased kyphosis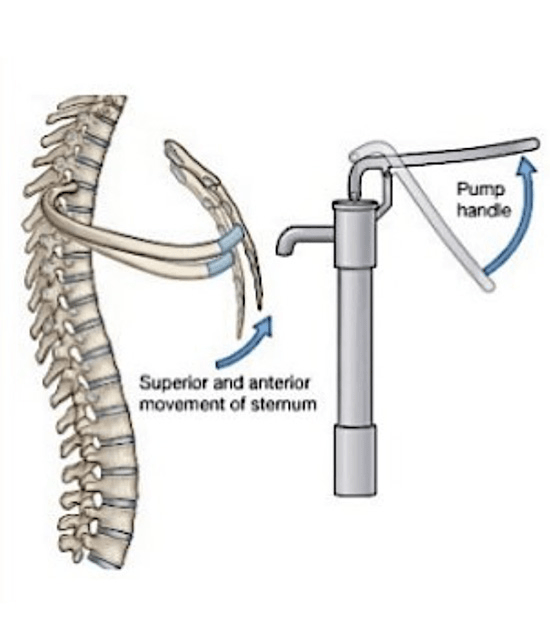
general treatment principles for those with increased kyphosis
postural education
stretch pec minor muscles (door jam or corner stretch)
self mobilizing T-spine into extension (foam roll or chair back)
manual therapy to increase trunk extension (extension mob/manip, rotational mobilization)
increase trunk extensor muscle strength and endurance for prolonged postural control
how to measure Cobb angle
line is drawn at the top of the vertebral body with the greatest lateral tilt above the curve apex and another line is drawn at the bottom of the vertebral body with the greatest lateral tilt beneath the curve apex
lines are then drawn perpendicular to the lateral tilt lines
Cobb angle is calculated where these two lines intersect
a Cobb angle >10 degrees is generally considered to be scoliosis
ankylosing spondylitis CPG
be suspicious of this if:
age<40
morning stiffness
pain not relieved by lying supine (better when active)
pain duration >3 months
can rule out AS if: age at onset >40 (SENS=1)
where can rib pain radiate/refer to?
pain generally manifests at either costovertebral junction or the intercostal muscles and may radiate laterally around torso from posterior to anterior
junction or the intercostal muscles and may radiate laterally around torso from posterior to anterior
why do lateral shifts resulting in nonstructural scoliosis occur
thought to be a protective mechanism to prevent further compression of painful spinal disc or nerve root
treatment for rib dysfunctions
postural education
pec minor stretching
self-mobilizing T-spine into extension
manual therapy to increase trunk extension (T-spine extension and rotation mobs)
increase trunk extensor muscle strength and endurance