A score of 8 or less on this neurological scale is indicative of the severe TBI.
What is the Glasgow Coma Scale?
In this Subphase of Single Limb Support in a “normal” Gait Cycle, we see eccentric plantarflexion to control tibial advancement.
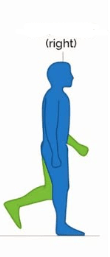
What is Midstance?
These are basic self-care tasks that individuals typically perform independently to maintain their daily life.
What are ADLs?
This is the most common cause of peripheral vertigo treated with repositioning maneuvers.
What is benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV)?
This x-ray test uses a barium contrast agent to visually examine how a person swallows.
What is a modified barium swallow study (MBSS)?
This primitive reflex presents with extension of arms and legs in response to a sudden noise or movement.
What is the Moro (Startle) reflex?
This common motor symptom of Parkinson’s disease, produces Slowness of movement.
What is bradykinesia?
Located at the front of the brain, it controls higher-order cognitive functions such as planning, decision-making, and personality.
What is the Frontal lobe?
This type of AFO’s primary effect is good swing phase control. And is contraindicated for patients who need stance phase control or when inversion or supination control is needed.
What is a PLS AFO?
This device is used to measure force, torque, or power, depending on the type and application.
What is a Dynamometer?
A positive Dix-Hallpike test suggests that BPPV is likely present in this semicircular canal on the side that was tested.
What is the posterior canal?
This type of aphasia is characterized by non-fluent effortful speech with relatively preserved comprehension.
What is Broca’s (expressive) aphasia?
The Gower’s sign, difficulty getting up from the floor is a symptom of this rare, progressive disease.
What is Duchene’s Muscular Dystrophy?
Autonomic dysreflexia typically occurs in injuries at or above this level.
What is T6?
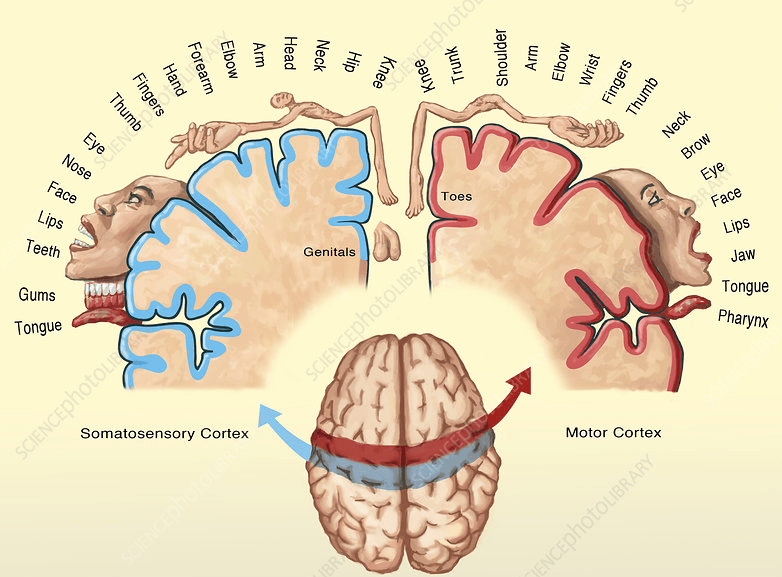
This metaphorical representation of the human body in the brain, depicts the relative proportions of the cortical areas dedicated to different body parts.
What is the Homunculus?
This characteristic gait pattern is often seen in PD and includes shuffling steps and reduced arm swing.
What is a festinating gait?
These 2 standardized, quantitative outcome assessments are used to measure finger dexterity AND unilateral gross manual dexterity.
What is The Nine-Hole Peg Test (9-HPT) and Box and Block?
This is a rapid, involuntary reflex that stabilizes vision during head movements by moving the eyes in the opposite direction of the head, keeping images clear on the retina.
What is the Vestibulo-Ocular Reflex (VOR)?
This deficit is the result of impaired coordination, weakness and tone involving motor speech articulators.
What is dysarthria?
This assessment tool is used to evaluate the gross and fine motor skills of young children, from birth to age 5 years of age.
What is the PDMS?
With this hereditary, progressive neurodegenerative disorder that affects the brain, patients may present with a chorea, cognitive decline, mood changes and motor coordination problems.
What is Huntington’s Disease?
This rare neurological disorder, caused by damage to the pons, is characterized by paralysis of voluntary muscles, except for those that control your vertical eye movements. All while consciousness and cognitive function remain intact.
What is Locked-in syndrome?
This type of gait deviation is seen when a person demonstrates poor balance and coordination, often associated with cerebellar problems.
What is ataxic gait?
This type of grasps gives the ability to hold an object between the tip of the thumb and the tip of the index finger.
What is the pincer grasp?
This central sign differentiates a central vestibular disorder from a peripheral one.
What is direction-changing nystagmus (or vertical nystagmus)?
This treatment program, an alternative to LSVT LOUD, encourages Parkinson’s patients to be loud and be clear.
What is Speak Out?
Often related to brain damage that occurs before or during birth, this common Childhood motor disability results in difficulty with muscle tone, control, coordination, and body movement.
What is Cerebral palsy (CP)?
This is the most common type of Multiple Sclerosis.
What is relapsing-remitting MS?
Visual fixation is a key behavioral sign in this phase of DoC. It is characterized by a profound lack of responsiveness but displays of fluctuating, limited awareness of the self or environment.
What is Minimally Conscious State?
In the Stroke population, a 10 MWT Cut-Off Score of this and above is indicative a community ambulator.
What is >0.8m/s?
This specialist analyzes the needs of people with disabilities, helps select appropriate assistive technology, and provides training in its use. They even help with WC our clinics.
ATP (Assistive Technology Professional)
This inner ear disorder that affects balance and hearing is characterized by sudden episodes of vertigo, tinnitus, hearing loss, and a feeling of fullness in the ear.
What is Ménière's disease?
This IDDSI level means that one graduates from Speech Therapy with a regular diet with thin liquids.
What is IDDSI level 7?
This condition in which a baby’s head is misshapen or develops a flat spot, makes the head look like a parallelogram from above.
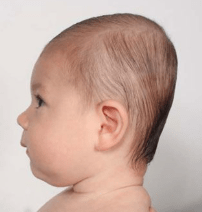
What is Plagiocephaly (Flat head syndrome)?
According to the ASIA Impairment Scale, this grade is given when Sensory function is preserved below the level of injury, but there is no motor function preserved more than three levels below the motor level on either side of the body.
What is ASIA B (Sensory Incomplete)?